Ueno Station
UENJU02JK30JY05JJ01 G16 H17 Ueno Station 上野駅 | |
|---|---|
 Main building of the station | |
| Location |
7 Ueno (JR Station) 3 Higashi-Ueno (Tokyo Metro) Taitō, Tokyo Japan |
| Operated by | |
| Line(s) | |
| Connections |
|
| History | |
| Opened | 28 July 1883 |
| Location | |
 Ueno Station Location within Special wards of Tokyo  Ueno Station Ueno Station (Tokyo)  Ueno Station Ueno Station (Japan) | |
Ueno Station (上野駅 Ueno-eki) is a major railway station in Tokyo's Taitō ward. It is the station used to reach the Ueno district and Ueno Park -- which contains Tokyo National Museum, The National Museum of Western Art, Ueno Zoo, Tokyo University of the Arts and other famous cultural facilities. A major commuter hub, it is also the traditional terminus for long-distance trains from northern Japan, although with the extension of the Shinkansen lines to Tokyo Station this role has diminished in recent years. A similar extension of conventional lines extended the Takasaki Line, Utsunomiya Line and Joban Line to Tokyo Station via the Ueno-Tokyo Line in March 2015, using existing little-used tracks and a new viaduct.[1]
Ueno Station is close to Keisei-Ueno Station, the Tokyo terminus of the Keisei Main Line to Narita Airport Station.
Lines
This station is served by the following lines:
As this station was the traditional point of arrival and departure for journeys to northern Japan, it became the inspiration for many poems and song lyrics, including a famous poem by Ishikawa Takuboku. There is a memorial plate about this poem in the station.
Station layout


Like most major stations in Japan, Ueno station contains and is surrounded by extensive shopping arcades. Ueno's includes a branch of the Hard Rock Cafe.
JR East platforms
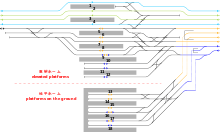
The station has two main levels of tracks and a deep underground station for the Tohoku Shinkansen tracks. Through tracks 1 to 4 on two island platforms on the main level are used by Yamanote Line and Keihin-Tohoku Line trains. Tracks 5 to 9 on two island platforms and one side of a terminal platform lead to the Ueno-Tokyo Line to Tokyo Station and beyond on the Tokaido Main Line. Tracks 10 to 12 terminate inside the building, and below these on a lower deck are further terminal tracks 13 to 17 (Track No.18 has been removed). Two subterranean island platforms serve Shinkansen tracks 19 to 22.
Chest-high platform edge doors were installed on the two Yamanote Line platforms (2 and 3) in November 2015, and brought into use from December.[2]
| 1 | JK Keihin-Tōhoku Line | for Tabata, Akabane, Minami-Urawa, and Ōmiya |
| 2 | JY Yamanote Line | for Tabata, Ikebukuro, and Shinjuku |
| 3 | JY Yamanote Line | for Tokyo and Shinagawa |
| 4 | JK Keihin-Tōhoku Line | for Tokyo, Kawasaki, Yokohama, and Ōfuna |
| 5-8 | JU Utsunomiya Line | for Ōmiya, Koga, Oyama, Utsunomiya, and Kuroiso |
| JU Takasaki Line | for Ōmiya, Ageo, Kumagaya, and Takasaki | |
| 6 | JJ Jōban Line | for Matsudo, Toride, Tsuchiura, and Mito ■ Narita Line for Narita (via Abiko) |
| 7-9 | JU Ueno–Tokyo Line | for Tokyo, Shinagawa, Yokohama and Odawara |
| 8 | ■ Jōban Line | □ Ltd. Express Hitachi / Tokiwa for Tsuchiura, Mito, Hitachi, and Iwaki |
| 9-12 | JJ Jōban Line | for Matsudo, Toride, Tsuchiura, and Mito ■ Narita Line for Narita (via Abiko) |
| 13-15 | JU Utsunomiya Line | for Ōmiya, Koga, Oyama, Utsunomiya, and Kuroiso |
| JU Takasaki Line | for Ōmiya, Ageo, Kumagaya, and Takasaki | |
| 14-16 | ■ Takasaki Line | □ Ltd. Express Akagi / Swallow Akagi for Takasaki and Maebashi □ Ltd. Express Kusatsu for Naganohara-Kusatsuguchi |
| 16-17 | ■ Jōban Line | □ Ltd. Express Hitachi / Tokiwa for Tsuchiura, Mito, Hitachi, and Iwaki |
| 19-20 | ■ Tohoku Shinkansen | for Sendai, Morioka, Shin-Aomori and Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto |
| ■ Yamagata Shinkansen | for Fukushima, Yamagata, and Shinjo | |
| ■ Akita Shinkansen | for Morioka and Akita | |
| ■ Joetsu Shinkansen | for Takasaki and Niigata | |
| ■ Hokuriku Shinkansen | for Nagano, Toyama, and Kanazawa | |
| 21-22 | ■ Shinkansen | for Tokyo |
 Yamanote Line platform 2 in March 2016 following the addition of low-height platform edge doors
Yamanote Line platform 2 in March 2016 following the addition of low-height platform edge doors- Platforms 14 and 15
Tokyo Metro platforms


Both the Ginza and Hibiya line station have two tracks. However, unlike in other Tokyo Metro stations, each line's tracks are counted separately.
| 1 | H Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line | for Ginza, Roppongi and Naka-Meguro |
| 2 | H Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line | for Kita-Senju TS Tobu Skytree Line for Kuki and Minami-Kurihashi |
| 1 | G Tokyo Metro Ginza Line | for Ginza and Shibuya |
| 2 | G Tokyo Metro Ginza Line | for Asakusa |
 The Ginza Line platforms in January 2018
The Ginza Line platforms in January 2018 The Hibiya Line platforms in January 2018
The Hibiya Line platforms in January 2018 JR Ueno Station District Gate in January 2018
JR Ueno Station District Gate in January 2018
Adjacent stations
| « | Service | » | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tohoku/Yamagata/Akita/Joetsu/Hokuriku Shinkansen | ||||
| Tokyo | All services[Note 1] | Ōmiya | ||
| Yamanote Line JY05 | ||||
| Okachimachi JY04 | - | Uguisudani JY06 | ||
| Keihin-Tōhoku Line JK30 | ||||
| Akihabara AKBJK28 |
Rapid (weekdays) |
Tabata JK34 | ||
| Okachimachi JK29 | Rapid (weekends and national holidays) |
Tabata JK34 | ||
| Okachimachi JK29 | Local | Uguisudani JK31 | ||
| Ueno-Tokyo Line | ||||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
All services | see below | ||
| Ueno–Tokyo Line — Utsunomiya Line/Takasaki Line JU02 | ||||
| Terminus | Akagi | Akabane ABNJU04 | ||
| Terminus | Kusatsu | Akabane ABNJU04 | ||
| Terminus | Minakami | Akabane ABNJU04 | ||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
Rapid Rabbit · Urban |
Akabane ABNJU04 | ||
| Terminus | Commuter Rapid | Oku JU03 | ||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
Local | Oku JU03 | ||
| Ueno–Tokyo Line — Jōban Line (Rapid) JU02 JJ01 | ||||
| Ueno–Tokyo Line — Jōban Line JU02 JJ01 | ||||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
Hitachi | Tsuchiura | ||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
Tokiwa | Kashiwa JJ07 | ||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
Special Rapid | Nippori NPRJJ02 | ||
| Tokyo TYOJU01 |
Rapid[Note 2] | Nippori NPRJJ02 | ||
| Tokyo Metro Ginza Line G16 | ||||
| Ueno-hirokoji G15 | - | Inaricho G17 | ||
| Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line H17 | ||||
| Naka-okachimachi H16 | - | Iriya H18 | ||
History


The station opened on July 28, 1883. After the destruction of this first building in the fires caused by the 1923 Great Kantō earthquake, Japanese Government Railways constructed the current station buildings. In 1927, Tokyo Underground Railway (now Tokyo Metro) opened Japan's first subway line from here to Asakusa Station. Following World War II, the neighbourhood in front of Ueno Station was a major center of black market activity. Today, that market is gathering people as a name of Ameya-Yokochō.
Passenger statistics
In fiscal 2013, the JR East station was used by 181,880 passengers daily (boarding passengers only), making it the thirteenth-busiest station operated by JR East.[3] In fiscal 2013, the Tokyo Metro station was used by an average of 211,539 passengers per day (exiting and entering passengers), making it the eighth-busiest station operated by Tokyo Metro.[4]
The daily passenger figures for each operator in previous years are as shown below.
| Fiscal year | JR East | Tokyo Metro |
|---|---|---|
| 1999 | 195,654[5] | |
| 2000 | 189,388[6] | |
| 2005 | 179,978[7] | |
| 2010 | 172,306[8] | |
| 2011 | 174,832[9] | 201,602[10] |
| 2012 | 183,611[11] | 212,509[12] |
| 2013 | 181,880[3] | 211,539[4] |
- Note that JR East figures are for boarding passengers only.
Bus services
Highway buses
- Sky / Panda; For Hirosaki, Aomori Station[13]
- Yuhi; For Tsuruoka Station, Amarume Station, and Sakata Station[14]
- Tono Kamaishi; For Shin-Hanamaki Station, Tōno Station, Kamaishi Station, and Yamada[14]
- Tokyo Sunrise; For Yamagata Station, Sagae Station, Sakurambo-Higashine Station, and Shinjō Station[15]
- Rainbow; Yonezawa Station, Kaminoyama-Onsen Station, and Yamagata Station[15]
- For Chino, Matsumoto Bus Terminal, and Nagano Station[16]
- Dream Kanazawa; For Toyama Station, Kanazawa Station, and Kanazawa Institute of Technology[17]
- Kimasshi; For Kanazawa Station[15]
- Yamato; For Tenri Station, Nara Station, Kintetsu-Kōriyama Station, Hōryū-ji, Ōji Station, and Goidō Station[18]
- For Ōtsu Station, Yamashina Station, Sanjō Station, and Kyōto Station[19]
- Flying Liner; For Kyōto Station, Ōsaka Station, Ōsaka Namba Station, Ōsaka Abenobashi Station, and Fujiidera Station[15]
- Mamakari Liner; For Okayama Station, Kurashiki Station[15]
See also
References
- ↑ JR東日本:東京−上野の新線 愛称を「上野東京ライン」 [JR East names new line between Tokyo and Ueno "Ueno-Tokyo Line"]. Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). Japan: The Mainichi Newspapers. Archived from the original on 2013-12-09. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- ↑ 山手線上野駅に可動式ホーム柵設置 [Platform edge doors installed at Yamanote Line Ueno Station]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 16 November 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- 1 2 各駅の乗車人員 (2013年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2013)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- 1 2 各駅の乗降人員ランキング [Station usage ranking] (in Japanese). Tokyo Metro. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (1999年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 1999)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2000年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2000)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2005年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2005)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2010年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2010)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2011年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2011)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 駅別乗降人員順位表(2011年度1日平均) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2011)] (in Japanese). Japan: Tokyo Metro. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗車人員 (2012年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2012)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ 各駅の乗降人員ランキング (2012年) [Station usage ranking (2012)] (in Japanese). Tokyo Metro. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ "高速バス - 弘南バス株式会社". www.konanbus.com (in Japanese). Retrieved 2016-01-24.
- 1 2 "高速バス | 国際興業バス". 5931bus.com (in Japanese). Retrieved 2016-01-24.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "時刻表・運賃表 | 東北急行バス". www.tohoku-express.co.jp (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2016-02-05. Retrieved 2016-01-24.
- ↑ "高速バス長野・松本-東京ディズニーリゾート・成田空港線". www.alpico.co.jp. Retrieved 2016-01-24.
- ↑ "デジタル時刻表 | ジェイアールバス関東". time.jrbuskanto.co.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2016-01-24.
- ↑ "奈良~横浜・上野・東京スカイツリータウン前・「東京ディズニーリゾート®」 | 夜行高速バス | 京成バス". www.keiseibus.co.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2016-01-24.
- ↑ "千葉中央バス/高速バス/京都線". www.chibachuobus.co.jp (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2016-01-24.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ueno Station. |
- Ueno Station (Tokyo Metro) (in Japanese)
- Ueno Station (JR East) (in Japanese)
- JR East Ueno Station map
- Ueno Station Panorama
Coordinates: 35°42′48″N 139°46′36″E / 35.713434°N 139.776725°E