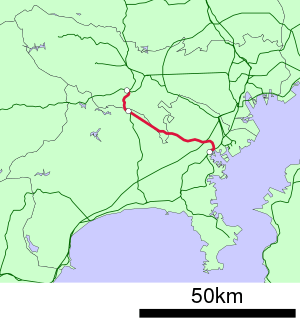
Yokohama Line
| Yokohama Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| JH | |||
|
A Yokohama Line E233-6000 series EMU | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | 横浜線 | ||
| Type | Heavy rail | ||
| Locale | Kanagawa Prefecture | ||
| Termini |
Hachiōji Higashi-Kanagawa | ||
| Stations | 20 | ||
| Daily ridership | 840,200 (daily 2015)[1] | ||
| Operation | |||
| Opened | 1908 | ||
| Operator(s) | JR East | ||
| Rolling stock | E233-6000 series | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 42.6 km (26.5 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC overhead catenary | ||
| Operating speed | 95 km/h (59 mph) | ||
| |||
| Route map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Yokohama Line (横浜線 Yokohama-sen) is a Japanese railway line of the East Japan Railway Company (JR East) connecting Higashi-Kanagawa Station in Yokohama, Kanagawa and Hachiōji Station in Hachiōji, Tokyo. The line forms part of what JR East refers to as the "Tokyo Mega Loop" (東京メガループ) around Tokyo, consisting of the Keiyo Line, Musashino Line, Nambu Line, and Yokohama Line.[2] The line's name comes from the section between Nagatsuta and Higashi-Kanagawa that runs through the city of Yokohama. Nicknamed the Hama-sen (浜線) by locals,[3] the line serves commuters in the southwestern suburbs of Tokyo and northeastern suburbs of Yokohama.
Operation
Despite the line's name, only approximately half of trains run as far as Yokohama Station. Rapid (快速 Kaisoku) trains operate every 20 minutes during the daytime.
Stations
- Local trains stop at all stations.
- Information on the limited express Hama Kaiji service can be found on its page.
- Rapid trains stop at stations marked "●" and pass those marked "|".
Rolling stock
- 205-500 series 4-car EMUs
- E233-6000 series 8-car EMUs x28 (since February 2014)
Yokohama Line services are operated using a fleet of 28 8-car E233-6000 series electric multiple unit (EMU) trains, introduced from 16 February 2014.[4] Through trains to and from the Sagami Line are served by 4-car 205-500 series EMUs.[5]
- Sagami Line 205-500 series EMU, April 2011
- Yokohama Line E233-6000 series EMU, January 2014
Former
- 72 series
- 103 series (from 2 October 1972 until 26 February 1989)
- 205 series 8-car EMUs (1988 to August 2014)
8-car 205 series EMU trains were introduced in 1988.[6] In these sets, the second car from the Higashi-Kanagawa end had six pairs of doors on each side to allow rapid boarding and disembarking during peak periods. The last 205 series set on the Yokohama Line ran on 23 August 2014.[7]
 72 series EMU, July 1984
72 series EMU, July 1984 103 series EMU at Fuchinobe Station, circa 1988
103 series EMU at Fuchinobe Station, circa 1988- A Yokohama Line 205 series EMU, April 2011
History

The line was opened by the private Yokohama Railway (横浜鉄道 Yokohama Tetsudō) on 23 September 1908 and leased to the government in 1910.[8] The line was nationalized on 1 October 1917.[8]
The Higashi-Kanagawa to Haramachida (now Machida) section was electrified on 1 October 1932, with the Haramachida to Hachiōji section electrified on 14 April 1941.[8]
The Higashi-Kanagawa to Kozukue section was double-tracked by 1968, extended to Aihara by 1980, and completed to Hachiōji on 6 March 1988.[8]
References
- ↑ "平成27年 大都市交通センサス 首都圈報告書" (PDF). P.92. 国土交通省.
- ↑ Saka, Masayuki (August 2014). 東京メガループ 車両・路線の沿革と現況 [Tokyo Megaloop: History and current situation of trains and line]. Tetsudō Daiya Jōhō Magazine (in Japanese). Vol. 43 no. 364. Japan: Kōtsū Shimbun. pp. 28–39.
- ↑ Aizawa, Masao (1996). Hamasen chimei arekore yokohama-hen. 230 Club Shinbunsha. ISBN 978-4-931353-24-4.
- ↑ "E233系6000番台が営業運転を開始" [E233-6000 series enter revenue service]. Japan Railfan Magazine (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 17 February 2014. Retrieved 17 February 2014.
- ↑ "横浜線開業100周年~その1: バトンタッチしてきた車両たち". Japan Railfan Magazine. Vol. 49 no. 574. February 2009. pp. 94–97.
- ↑ "JR東日本 横浜線にE233系6000番代を投入" [JR East to introduce E233-6000 series on Yokohama Line]. Tetsudō Daiya Jōhō Magazine (in Japanese). Vol. 42 no. 356. Japan: Kōtsū Shimbun. December 2013. p. 60.
- ↑ 横浜線用の205系が営業運転を終了 [End of 205 series revenue operations on Yokohama Line]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 24 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 "横浜線開業100周年~その2: 開業から現在までの他線との接続の歴史". Japan Railfan Magazine. Vol. 49 no. 574. February 2009. pp. 98–99.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yokohama Line. |
.svg.png)