Santiago de Compostela Airport
| Santiago de Compostela Airport Aeroporto de Santiago de Compostela Aeropuerto de Santiago de Compostela | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public/Military | ||||||||||
| Owner | ENAIRE | ||||||||||
| Operator | Aena | ||||||||||
| Serves | Santiago, Galicia, Spain | ||||||||||
| Location | Santiago de Compostela | ||||||||||
| Focus city for | |||||||||||
| Built | 1932 | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 1,213 ft / 370 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 42°53′47″N 08°24′55″W / 42.89639°N 8.41528°WCoordinates: 42°53′47″N 08°24′55″W / 42.89639°N 8.41528°W | ||||||||||
| Website |
www | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
 SCQ Location in Galicia  SCQ SCQ (Spain) | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics (2017) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||

Santiago de Compostela Airport (Galician: Aeroporto de Santiago de Compostela, Spanish: Aeropuerto de Santiago de Compostela) (IATA: SCQ, ICAO: LEST) is an international airport serving the autonomous community and historical region of Galicia in Spain. It is the 2nd busiest airport in northern Spain after Bilbao Airport.
The airport is located in the parish of Lavacolla, 12 km from Santiago de Compostela and handled 2,644,925 passengers in 2017. It is the main focus city of Vueling in the northwest Iberian Peninsula, and Ryanair's only focus city in Northern Spain. The Christian pilgrimage route of the Camino de Santiago runs near the airport.
History
The airport was set up by a group of aviation enthusiasts in October 1932 and two months directors were chosen to select where the airport was going to be built. In 1935 construction work started at the airport where two years later on 27 September 1937 the first scheduled flight from Santiago de Compostela took place. After the Spanish Civil war, political prisoners (who were held in the concentration camp of Lavacolla) were forced to work in the construction of the airport.[1]
In 1969 a new terminal was built at the airport. It has had several expansions taking place since it opened. It closed in 2011 following a brand new terminal being built at the airport. In 1981, a cargo terminal was built, giving the airport capacity to handle cargo flights.[2] During the 1990s, the airport had non-stop service to South America operated by Viasa.[3]
On 13 October 2011 a new passenger terminal opened at the airport, replacing the old terminal, opened in 1969 and remodeled in 1993.
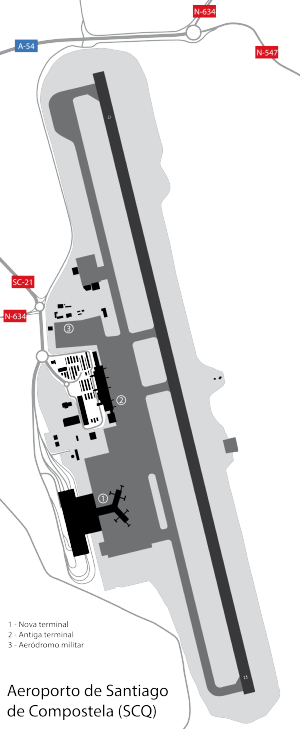
Terminal
The airport currently has one operating terminal. The Old terminal at Santiago de Compostela airport opened in 1969 and had lots of expansions during its lifetime. The terminal closed on the night of 13 October 2011 where operations transferred to the new terminal.
The New terminal at Santiago de Compostela Airport officially opened on 13 October 2011 and passenger operations transferred there the following day. It is adjacent to the old terminal and has a size of 74,000 sq m. It has 22 check-in desks, 3 security checkpoints, 13 gates of which 5 have airbridges and 4 baggage carousels. The baggage hall is split into two zones, one for Schengen flights and one for Non-Schengen. It can handle as much as 4 million passengers per year.[4] The terminal is due to be expanded in the future. This includes adding another 5 airbridges to 5 of the current gates as well as 3 more baggage carousels and an expanded shopping area.[5]
Airlines and destinations
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aer Lingus | Dublin |
| Air Europa | Gran Canaria, Lanzarote, Tenerife–South Seasonal: Fuerteventura, Ibiza, Menorca, Palma de Mallorca |
| easyJet | Seasonal: London–Gatwick, Milan–Malpensa |
| easyJet Switzerland | Basel/Mulhouse, Geneva |
| Iberia | Madrid |
| Iberia Express | Madrid |
| Iberia Regional | Bilbao, Tenerife–North Seasonal: Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Madeira, Palma de Mallorca |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Ryanair | Alicante, Barcelona, Bergamo, Gran Canaria, Hahn, Lanzarote, London–Stansted, Madrid, Málaga, Palma de Mallorca, Seville, Tenerife–South, Valencia |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Seasonal: Zürich |
| Vueling | Alicante, Amsterdam, Barcelona, Fuerteventura, Lanzarote, Málaga, Palma de Mallorca, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Rome–Fiumicino, Tenerife–North Seasonal: Brussels, Zürich |
Statistics
During the early 2000s, numbers increased significantly at the airport, from 1.24 million in 2002 to peak at 2.46 million in 2011. Because of the financial crisis in Spain, those numbers decreased to 2.1 million in 2014. Cargo has decreased significantly over the last ten years. The Spanish economic recovery in the mid-2010s and the rise of Santiago de Compostela as an international destination are again increasing passenger numbers, breaking the 2.50 million mark for the first time in 2016.[6]
Traffic figures by year
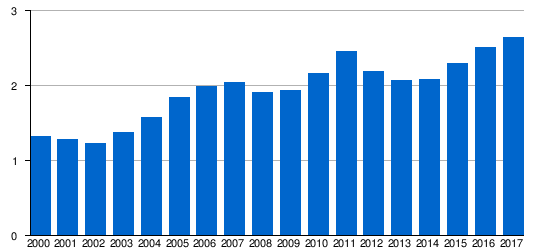 |
| Updated: 12 January 2018.[6] |
| Passengers handled | Passengers % Change | Aircraft movements | Aircraft % Change | Freight (tonnes) | Freight % Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 1,332,893 | - | 19,660 | - | 6,773 | - |
| 2001 | 1,281,334 | 19,084 | 6,228 | |||
| 2002 | 1,240,730 | 17.362 | 5,716 | |||
| 2003 | 1,381,826 | 18,454 | 5,318 | |||
| 2004 | 1,580,675 | 21,593 | 4,938 | |||
| 2005 | 1,843,118 | 25,693 | 3,805 | |||
| 2006 | 1,994,519 | 24,719 | 2,587 | |||
| 2007 | 2,050,172 | 24,643 | 2,749 | |||
| 2008 | 1,917,466 | 21,945 | 2,418 | |||
| 2009 | 1,944,068 | 20,166 | 1,988 | |||
| 2010 | 2,172,869 | 21,252 | 1,964 | |||
| 2011 | 2,464,330 | 22,322 | 1,787 | |||
| 2012 | 2,194,611 | 19,511 | 1,815 | |||
| 2013 | 2,073,055 | 18,688 | 1,929 | |||
| 2014 | 2,083,873 | 19,431 | 2,095 | |||
| 2015 | 2,296,248 | 20,540 | 2,311 | |||
| 2016 | 2,510,740 | 21,227 | 2,936 | |||
| 2017 | 2,644,925 | 21,520 | - | - |
Traffic figures by month
| 2017 Passengers | 2018 Passengers | Passengers % Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 158,617 | 177,018 | |
| February | 148,412 | 167,158 | |
| March | 202,894 | 214,110 | |
| April | 243,308 | 232,963 | |
| May | 237,741 | 245,963 | |
| June | 245,925 | 262,159 | |
| July | 271,943 | 265,768 | |
| August | 271,303 | 267,549 | |
| September | 244,639 | 257,990 | |
| October | 234,532 | - | - |
| November | 182,907 | - | - |
| December | 200,975 | - | - |
Route statistics
| Rank | City | Passengers | % Change 2016 / 17 |
Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 617.524 | Iberia, Iberia Express, Ryanair | ||
| 2 | 421.845 | Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 3 | 154.607 | Air Europa, Iberia Regional, Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 4 | 119.011 | Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 5 | 107.847 | Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 6 | 100.714 | Ryanair | ||
| 7 | 95.207 | Air Europa, Iberia Regional, Ryanair | ||
| 8 | 88.724 | Air Europa, Ryanair | ||
| 9 | 84.631 | Ryanair | ||
| 10 | 76.660 | Air Europa, Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| Rank | City | Passengers | % Change 2016 / 17 |
Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95.032 | easyJet Switzerland | ||
| 2 | 77.477 | Ryanair | ||
| 3 | 67.475 | easyJet, Vueling | ||
| 4 | 50.330 | Ryanair | ||
| 5 | 47.529 | easyJet Switzerland | ||
| 6 | 47.158 | Vueling | ||
| 7 | 36.525 | Swiss, Vueling | ||
| 8 | 36.394 | Ryanair | ||
| 9 | 32.631 | Aer Lingus | ||
| 10 | 29.782 | - | Lufthansa | |
| Rank | Country | Passengers | % Change 2016 / 17 |
Scheduled Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.014.228 | Air Europa, Iberia, Iberia Express, Iberia Regional, Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 2 | 179.087 | easyJet Switzerland, Swiss, Vueling | ||
| 3 | 147.234 | easyJet, Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 4 | 99.573 | easyJet, Ryanair, Vueling | ||
| 5 | 73.998 | Lufthansa, Ryanair | ||
| 6 | 47.404 | Vueling | ||
| 7 | 32.631 | Aer Lingus | ||
| 8 | 22.571 | Vueling | ||
| 9 | 16.109 | Vueling | ||
| 10 | 4.111 | Iberia Regional |
| Rank | Carriers | Passengers | % Change 2016 / 17 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.111.690 | ||
| 2 | 597.178 | ||
| 3 | 406.586 | ||
| 4 | 142.538 | ||
| 5 | 118.366 | ||
| 6 | 75.599 | ||
| 7 | 50.410 | ||
| 8 | 37.263 | - | |
| 9 | 32.629 | ||
| 10 | 20.313 |
Ground transportation
Road
The airport is linked with Santiago de Compostela (13 km) by the Autovía A-54. This motorway is currently being extended to Lugo (94.5 km) where it will connect with the Autovía A-6, providing toll-free motorway access to the rest of Spain; and to the French border through the Autovía A-8 that intersects with the Autovía A-6 near Lugo. Nearby Autopista AP-9 connects the airport directly to A Coruña (66 km), Ferrol (88 km), Pontevedra (75 km), Vigo (100 km) and the Portuguese border. Ourense (116 km) is reachable through the Autopista AP-53 that connects with the Autopista AP-9.
There are several major car rental companies at the airport. The airport has more than 5,000 short and long-term covered parking spaces in the new terminal building. In addition, there are several low-cost, long-term private parking facilities around the airport.
Bus services
A city bus service operated by Empresa Freire every 30 minutes connects the airport with the center of Santiago de Compostela, and the bus and train terminals in the city. From the station in Santiago de Compostela, private coach operators run direct services in a multiple daily basis to most cities and towns in Galicia, including A Coruña, Ferrol, Lugo, Ourense, Pontevedra and Vigo, as well as long-distance services to the rest of Spain, and international services. In addition, three regional services link the airport directly to A Coruña, to Lugo, including several stops in the French Way of the Camino de Santiago, and to the A Mariña coastal area (home to As Catedrais beach) in the province of Lugo.
Rail
There are no rail facilities at the airport. However the train station in Santiago de Compostela, located 12 km. away, is connected to the airport by the city bus service every 30 minutes. There are combined available train+bus tickets to and from the airport. The train station in Santiago de Compostela has medium and long-distance high-speed Alvia and AVE services to most cities in Galicia, including A Coruña, Ferrol, Ourense, Pontevedra, Vilagarcía and Vigo; and further to Madrid Chamartín and the rest of Spain.
Foot and Bike
The Camino de Santiago runs next to the runway of the airport. This is the busiest and final journey in the Camino de Santiago that goes through the famous Monte do Gozo. There are dedicated pathways for both pedestrians and bikers towards the city. The walking distance from the runway to the Cathedral is estimated at 10.90 km.
Accidents and Incidents
- On 3 March 1978, a McDonnell Douglas DC-8-63 operated by Iberia from Madrid–Barajas Airport with 211 passengers and 11 crew members, registration EC-BMX. The aircraft touched down far down the runway after a high approach, aquaplaned off the runway, dropped into a hollow 20m deep and caught fire. The crash was settled with 70 injured people, 10 of them seriously injured, and no fatalities.[8]
- On 7 June 2001, a Beechcraft B300C Super King Air 350, registration F-GOAE, departed from Le Mans-Arnage Airport (LME), France, to Santiago De Compostela Airport (SCQ), Spain, on a cargo flight according to instrument flight rules. Near the destination airport, the meteorological conditions were reported to be good, and the crew requested a visual approach to runway 17, even though the active runway was 35. Once cleared to land, the aircraft encountered a fog patch and from this moment it began a high ate descent (2000 to 3000 ft/min). A minute after entering an unexpected and unforeseen fog patch, the aircraft struck some trees in level flight and with an airspeed of 148 kt. The wings and engines detached from the fuselage, and they dragged along a scrubland area until they came to a stop. The crew suffered minor injuries and the aircraft was completely destroyed.[9]
- On 2 August 2012, an Airnor Cessna 500 Citation I, registration EC-IBA, flying from Asturias crashed whilst on approach to the airport with the loss of both crew members.[10]
References
- ↑ http://www.laopinioncoruna.es/galicia/2010/03/13/miles-presos-construyeron-obras-civiles-militares-galicia-1960/366159.html
- ↑ History of Santiago de Compostela Airport
- ↑ http://airline-memorabilia.blogspot.com/2011/08/viasa-1995-espana.html
- ↑ New Terminal
- ↑ New Terminal Expansion
- 1 2 "Annual Statistics" (in Spanish). Aena Aeropuertos S.A. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 Estadísticas aena-aeropuertos.
- ↑ http://www.aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19780303-0
- ↑ http://www.aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=20010607-0
- ↑ Santiago de Compostela accident
External links
![]()