Reutlingen
| Reutlingen | ||
|---|---|---|
.jpg) A street view of Reutlingen | ||
| ||
 Reutlingen Location of Reutlingen within Reutlingen district 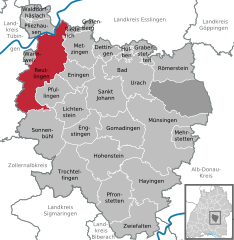  | ||
| Coordinates: 48°29′N 9°13′E / 48.483°N 9.217°ECoordinates: 48°29′N 9°13′E / 48.483°N 9.217°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | Baden-Württemberg | |
| Admin. region | Tübingen | |
| District | Reutlingen | |
| Government | ||
| • Lord Mayor | Barbara Bosch (Ind.) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 87.06 km2 (33.61 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 382 m (1,253 ft) | |
| Population (2017-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 115,762 | |
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,400/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 72760–72770 | |
| Dialling codes | 07121, 07072, 07127 | |
| Vehicle registration | RT | |
| Website | www.reutlingen.de | |
Reutlingen (German pronunciation: [ˈʁɔʏtlɪŋən] (![]()
Geography


Reutlingen is located about 35 km (22 mi) south of the State capital of Baden-Württemberg, Stuttgart. It lies in the Southwest corner of Germany, right next to the Swabian Jura, and that is why it is often called The gate to the Swabian Jura (German: Das Tor zur Schwäbischen Alb). The Echaz river, a tributary of the Neckar, flows through the town centre.
Along with the old university town of Tübingen (about 15 km (9.3 mi) to the west), Reutlingen is the centre of the Neckar-Alb region. It is also part of the larger Stuttgart Metropolitan Region.
History
| Imperial City of Reutlingen Reichsstadt Reutlingen | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1240–1803 | |||||||||
| Status | Free Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Reutlingen | ||||||||
| Government | Republic | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Founded | 4th–5th century | ||||||||
• Gained Reichsfreiheit | 1240 | ||||||||
• Co-founded Swabian League | 1331 | ||||||||
• Signed Augsburg Confession | 1530 | ||||||||
• Destroyed by fire | 1726 | ||||||||
| 1803 | |||||||||
| |||||||||


The first settlements in the area are believed to date from the 4th or 5th century. Some time around 1030, Count Egino started to build a castle on top of the Achalm, one of the largest mountains in Reutlingen district (about 706 m). One of the towers of this castle was rebuilt in the 19th century and is open to visitors. The name Reutlingen was first mentioned in writing in the so-called Bempflingen Treaty (German: Bempflinger Vertrag) which is dated approximately 1089–90.
Around 1180, Reutlingen received market rights and, between 1220 and 1240 it was promoted to city status and city-walls and fortifications were built. Shortly thereafter, from 1247–1343, the town's landmark, the St. Mary's Church (German: Marienkirche) was built.
In 1377 Reutlingen was the scene of a victory by the Swabian League, formed in the previous year by 14 Swabian cities, led by Ulm, over the Count of Württemberg. In 1519, a later Swabian League came to Reutlingen's help when Ulrich, Duke of Württemberg attempted to seize the city; the League landed a crushing blow, conquering Württemberg and selling it to Charles V. In 1495 and 1516 the jews were exiled from the town.[4]
As a result of such struggles, Reutlingen became an Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire, free from allegiance to the Duke of Württemberg. In 1530, Reutlingen's city council signed the Augsburg Confession, and in 1580 and the Formula of Concord, key documents of Lutheranism. In 1803, in the wake of the French Revolutionary Wars, Reutlingen lost its independence in the German Mediatisation, being restored to Württemberg.
The worst disaster in the history of Reutlingen happened in 1726, when a major fire swept through the city, destroying 80% of all residential houses and almost all public buildings, and making 1,200 families homeless. The impact of this fire, which lasted three days, is still visible today.
During World War II, the wings of the V-1 flying bomb were manufactured in Reutlingen, making the city the target of several allied bombing raids.
On 24 July 2016 a Syrian asylum seeker killed a pregnant woman in a machete attack.[5]
| Significant minority groups | |
| Nationality | Population (2018) |
|---|---|
| 3,173 | |
| 2,594 | |
| 2,013 | |
| 1,875 | |
| 1,732 | |
| 1,391 | |
| 1,305 | |
| 960 | |
| 955 | |
| 726 | |
| 674 | |
Lord Mayors
- 1929–1933: Karl Haller
- 1933–1945: Richard Dederer, NSDAP,
- 1945–1973: Oskar Kalbfell, SPD,
- 1973–1994: Manfred Oechsle, CDU,
- 1995–2003: Stefan Schultes, CDU,
- since 2003: Barbara Bosch, independent,
Mutscheltag
On Mutscheltag (the first Thursday after Epiphany), townspeople gather in halls and homes to play games of dice, the winner of which earns parts or whole Mutschel loaves of bread. The Mutschelspiele (Mutschel games) consist of small games scored by tally marks, and are won both independently and by grand total at the end of the hour or night. This tradition is unique to the city of Reutlingen.
Notable people
- Ernst Boepple (1887–1950), German Nazi official and SS officer executed for war crimes
- Ferdinand Heim, (1895–1971), the "Scapegoat of Stalingrad"
- Erwin Fischer (1904–1996), jurist
- Helmuth Naumer, (1907–1990), German artist
- Friedrich Schlotterbeck (1909–1979), socialist, resistance fighter and author
- Walter Vielhauer (1909–1986), trade unionist, politician, resistance fighter
- Gertrud Lutz (1910–1944), resistance fighter
- Willy Hack (1912–1952), German SS officer and concentration camp official executed for war crimes
- Martin Hengel (1926–2009), Protestant parson and historian
- Willi Betz (born 1927), founder of biggest forwarding agency in Europe
- Friedrich Wilhelm Schnitzler, (1928–2011), landowner, business manager (Südmilch) and politician (CDU)
- Roland Kayn (1933–2011), organist and composer
- Ernst Messerschmid (born 1945), German Space Shuttle astronaut and physicist, D1-Space-Shuttle-Mission
- Claus Kleber, (born 1955), German television journalist
- Friedrich List, (1789–1846), German and American economist
- Dominik Kuhn, (born 1969), Swabian comedian
Transport
City buses are run by Reutlinger Stadtverkehr (RSV), while trains from Reutlingen Hauptbahnhof and Reutlingen West, -Sondelfingen and Reutlingen-Betzingen are ran by Deutsche Bahn.
Main sights

- Church of the Virgin Mary, built in Gothic style in the 13th–14th centuries. Nearby is a statue of emperor Frederick II.
- Marktbrunnen ("Market Fountain", 16th century), surmounted by the statue of emperor Maximilian II.
- Spitalhof, built as a hospital in the 14th century. Damaged by a fire, it was largely rebuilt in the 18th century.
- Church of St. Nicholas, built in the 14th century as a chapel.
- Gerber- und Färberbrunnen ("Tanners' and Dyers' Fountain"), 1920.
- City Hall, built in 2013.
- Spreuerhofstraße, the world's narrowest street.
University
Reutlingen University is a university of applied sciences, focusing on hands-on learning, which is apparent in their mandatory internship for all business majors. The university is an internationally friendly school with 111 cooperative campuses worldwide. Classes are generally taught in German; however, in some Bachelor programs and in the Master's programs classes are taught in English.
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Reutlingen is twinned with:
|
|
References
- ↑ "Bevölkerung nach Nationalität und Geschlecht am 31. Dezember 2017". Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg (in German). 2018.
- ↑ "Einwohnerzahl | Stadt Reutlingen". www.reutlingen.de (in German). Retrieved 2018-08-09.
- ↑ Engste Straße der Welt (in German)
- ↑ Erich Keyser (Herausgeber): „Württembergisches Städtebuch“; Band IV Teilband Baden-Württemberg Band 2 aus „Deutsches Städtebuch. p. 99
- ↑ Darko Janjevic. "Police arrest Syrian man after woman killed in knife attack in Germany". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 25 July 2016.
An attacker has allegedly killed one woman and injured five in the city of Reutlingen in southwest Germany, according to local police.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Reutlingen. |
- Official website

- The University of Applied Sciences in Reutlingen

- RSV website (in German)