Principality of Serbia (medieval)
| Principality of Serbia Кнежевина Србија Kneževina Srbija | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| early 8th century[1][2]–c. 969-971 | |||||||||||||
 Emblem of
prince Strojimir | |||||||||||||
.png) Serbia, during the rule of Časlav (927–960) | |||||||||||||
| Capital | several cities | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Serbian (Old Serbian) | ||||||||||||
| Religion |
Slavic paganism (before 860s) Christianity (c. 870) | ||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
| Prince | |||||||||||||
• c. 780 | Višeslav (first known by name) | ||||||||||||
• 831–850 | Vlastimir (notable) | ||||||||||||
• 850–891 | Mutimir (first Christian) | ||||||||||||
• 927–960 | Časlav (last) | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Medieval | ||||||||||||
• Established | early 8th century[1][2] | ||||||||||||
• Byzantine annexation | c. 969-971 | ||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | RS | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Today part of |
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Principality of Serbia (Serbian: Кнежевина Србија / Kneževina Srbija) or Serbian Principality (Serbian: Cрпска кнежевина / Srpska kneževina), was an early medieval state of the Serbs, located in western regions of Southeastern Europe. It existed from the beginning of the 7th century up to c. 969-971 and was ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty. Its first ruler known by name was Višeslav who started ruling around 780. In 822, the Serbs were said to rule the "greater part of Dalmatia",[3] while at the same time the Bulgars had taken the lands to the east, preparing to conquer Serbia. Vlastimir defeated the Bulgar army in a three-year-war (839–842), and the two powers lived in peace for some decades. Vlastimir's three sons succeeded in ruling Serbia together, although not for long; Serbia became a key part in the power struggle between the Byzantines and Bulgars (in predominantly Byzantine alliance), which also resulted in major dynastic wars for a period of three decades. Central parts of the principality were shortly occupied by the Bulgarian army for three years (924–927), until Serbian prince Časlav succeeded to liberate the land and unite several Serbian regions, becoming the most powerful ruler of the Vlastimirović dynasty. An important process during this period was the Christianization of the Serbs, establishment of Christianity as state-religion c. 869, and the founding of the first Serbian eparchy (diocese), the Eparchy of Ras. The principality was annexed by the Byzantines in c. 969-971 and ruled as the Catepanate of Ras. The main information of the history of principality and Vlastimirović dynasty are recorded in the contemporary historical work De Administrando Imperio (written c. 950–960).[4]
Background
Slavs (Sklavenoi) settled the Balkans in the 6th century.[5] The history of the early medieval Serbian principality and the Vlastimirović dynasty is recorded in the work De Administrando Imperio (On the Governance of the Empire, abbr. "DAI"), compiled by the Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (r. 913–959). The work mentions the first Serbian ruler, without a name (known conventionally as "Unknown Archon"), that led the White Serbs to the Southeastern Europe and received the protection of Emperor Heraclius (r. 610–641), and was said to have died long before the Bulgar invasion (680).[6][7] The Serbian ruler was titled "Prince (archon) of the Serbia" (αρχων Σερβλίας).[8] The DAI mentions that this ruler was inherited by the son, i.e. the first-born.[7] According to some Serbian authors, his descendants succeeded him,[6] but their names are unknown until the coming of Višeslav. However, it is very likely that attempts by one ruling župan after another to subjugate his neighbours led to many conflicts and the custom of the early Slavs, whereby the ruler was succeeded by his eldest relative, not necessarily by his own son, gave rise to further conflicts.[9]
Višeslav, Radoslav and Prosigoj (circa 780–830)
The time and circumstances of the first three Serbian rulers are almost unknown. The first of the dynasty known by name was Višeslav who began his rule around 780, being a contemporary of Charlemagne (fl. 768–814).[10][11] The first capital of the Serbs was Ras, in Raška.[11] The Serbs at that time were organized into župe (sing. župa), a confederation of village communities (roughly the equivalent of a county), headed by a local župan (a magistrate or governor); the governorship was hereditary, and the župan reported to the Serbian prince, whom they were obliged to aid in war.[12] According to DAI, "baptized Serbia" (known erroneously in historiography as Raška[13]), included the inhabited cities (καστρα/kastra) of Destinikon (Δεστινίκον), Tzernabouskeï (Τζερναβουσκέη), Megyretous (Μεγυρέτους), Dresneïk (Δρεσνεήκ), Lesnik (Λεσνήκ), Salines (Σαληνές), while the "small land" (χοριον/chorion) of Bosna (Βοσωνα), part of Serbia, had the cities of Katera (Κατερα) and Desnik (Δέσνηκ).[14] The other Serb-inhabited lands (or principalities) that were mentioned included the "countries" of Paganija, Zahumlje and Travunija,[14] while the "land" of Duklja was held by the Byzantines (it was presumably settled with Serbs as well).[15] These polities bordered Serbia to the north.[14] The exact borders of the early Serbian state are unclear.[13]
Although Višeslav is only mentioned by name, the DAI mentions that the Serbs served the Byzantine Emperor, and that they were at this time at peace with the Bulgars, whose neighbours they were and with whom they shared a common frontier.[16] The Bulgars, under Telerig, planned to colonize Bulgaria with Slavs from the neighbouring Berziti,[17] as the earlier Bulgar expansion had caused massive Slav migrations and depopulation of Bulgaria — in 762, more than 200,000 people fled to Byzantine territory and were relocated to Asia Minor.[18] The Bulgars were defeated in 774, after Constantine V learnt of their planned raid.[17] In 783, a large Slavic uprising took place in the Byzantine Empire, stretching from Macedonia to the Peloponnese, which was subsequently quelled by Byzantine patrikios Staurakios.[17] In Pannonia, to the north of Serbia, Charlemagne started his offensive against the Avars.[17]
Višeslav was succeeded by his son Radoslav, then grandson Prosigoj,[10] and one of these two most likely ruled during the revolt of Ljudevit Posavski against the Franks (819–822);[19] according to Einhard's Royal Frankish Annals, written in 822, Ljudevit went from his seat at Sisak to the Serbs (believed to have been somewhere in western Bosnia),[19] with Einhard mentioning "the Serbs, who control the greater part of Dalmatia" (ad Sorabos, quae natio magnam Dalmatiae partem obtinere dicitur).[20] Višeslav's great-grandson Vlastimir began his rule in c. 830, and he is the oldest Serbian ruler of which there is substantial data on.[7]
Countering Bulgarian expansion (805–29)
In the east, the Bulgarian Empire grew strong. In 805, khan Krum conquered the Braničevci, Timočani and Obotrites, to the east of Serbia, and banished their tribal chiefs and replaced them with administrators appointed by the central government.[21] In 815, the Bulgarians and Byzantines signed a 30-year peace treaty.[22] In 818 during the rule of Omurtag (814–836), the Braničevci and Timočani together with other tribes of the frontiers, revolted and seceded from Bulgaria because of an administrative reform that had deprived them much of their local authority.[23] The Timočani left the societas (association, alliance[24]) of the Bulgarian Empire, and sought, together with the Danubian Obotrites and Guduscani, protection from Holy Roman Emperor Louis the Pious (r. 813–840), and met him at his court at Herstal.[24] The Timočani migrated into Frankish territory, somewhere in Lower Pannonia, and were last mentioned in 819, when they were persuaded by Ljudevit to join him in fighting the Franks.[24] The Danubian Obotrites stayed in Banat, and resisted the Bulgars until 824, when nothing more is heard of them.[25] The khan sent envoys to the Franks and requested that the precise boundary be demarcated between them, and negotiations lasted until 826, when the Franks neglected him.[25] The Bulgars answered with attacking the Slavs that lived in Pannonia, and subjugated them, then they sent ships up the Drava river, and, in 828, had devastated Upper Pannonia, north of the Drava.[25] There was more fighting in 829, as well, and by this time, the Bulgars had conquered all of their former Slavic allies.[25][26]
The Bulgarian Khanate (later Empire) had a general policy of expansion in which they would first impose the payment of tribute on a neighboring people and the obligation of supplying military assistance in the form of an alliance (societas), leaving them internal self-government and local rulers, and when the need for this kind of relationship expired, they would terminate the self-government of the said people and impose their direct and absolute power, integrating them fully into the Bulgarian political and cultural system.[27]
Vlastimir, Mutimir and Prvoslav (830–892)

.png)
Vlastimir succeeded his father, Prosigoj, in c. 830.[28] He united the Serbian tribes in the vicinity.[29][30] The Serbs were alarmed, and most likely consolidated due to the spreading of the Bulgarian Khanate towards their borders (a rapid conquest of neighbouring Slavs[31][32]), in self-defence,[31][33] and possibly sought to cut off the Bulgar expansion to the south (Macedonia).[30] Emperor Theophilos (r. 829–842) was recognized as the nominal suzerain (overlord) of the Serbs,[31] and most likely encouraged them to thwart the Bulgars.[30] The thirty-year-peace treaty between the Byzantines and Bulgars, signed in 815, was still in effect.[28] According to Constantine VII, the Serbs and Bulgars had lived peacefully as neighbours until the Bulgar invasion in 839 (in the last years of Theophilos).[31] It is not known what exactly prompted the war,[30] as Porphyrogenitus gives no clear answer; whether it was a result of Serbian-Bulgarian relations, i.e. the Bulgar conquest to the southeast, or a result of the Byzantine-Bulgarian rivalry, in which Serbia was at the side of the Byzantines as an Imperial ally.[28] According to Porphyrogenitus, the Bulgars wanted to continue their conquest of the Slav lands - to force the Serbs into subjugation. Presian I (r. 836–852) launched an invasion into Serbian territory in 839, which led to a war that lasted for three years, in which the Serbs were victorious; Presian was heavily defeated and lost a large number of his men, he made no territorial gains and was driven out by the army of Vlastimir.[30][34] The Serbs had an advantage in the forests and gorges.[30][33] The defeat of the Bulgars, who had become one of the greater powers in the 9th century, shows that Serbia was an organized state, fully capable of defending its borders; a very high military and administrative organizational frame to present such effective resistance. It is not known whether Serbia at the time of Vlastimir had a fortification system and developed military structures with clearly defined roles of the župan.[35] After the victory over the Bulgars, Vlastimir's status rose,[33] and according to Fine he went on to expand to the west, taking Bosnia, and Herzegovina (known as Hum).[36] In the meantime; Braničevo, Morava, Timok, Vardar and Podrimlje were occupied by the Bulgars.[37] Vlastimir married off his daughter to Krajina, the son of a local župan of Trebinje, Beloje, in ca. 847/848.[38] With this marriage, Vlastimir elevated the title of Krajina to archon.[38] The Belojević family was thus entitled the rule of Travunia.
After Vlastimir's death, the rule was divided between his three sons: Mutimir, Strojimir and Gojnik.[29] The brothers defeated the Bulgars once again in 834–835, also capturing the son of the Bulgarian Khan. The Serbs and the Bulgarians concluded peace, and the Christianization of the Slavs began; by the 870s the Serbs were baptized and had established the Eparchy of Ras (mentioned in the Fourth Council of Constantinople, 878–880), on the order of Emperor Basil I. Mutimir maintained the communion with the Eastern Church (Constantinople) when Pope John VIII invited him to recognize the jurisdiction of the bishopric of Sirmium. The Serbs and Bulgarians adopted the Old Slavonic liturgy instead of the Greek. Sometime after defeating the Bulgarians, Mutimir ousted his brothers, who fled to Bulgaria. He kept Gojnik's son Petar Gojniković in his court, but he managed to escape to Croatia. Mutimir 'ruled until 890, being succeeded by his son Prvoslav. However, Prvoslav was overthrown by Petar who had returned from his exile in Croatia in c. 892.
Peter, Pavle and Zaharije (892–927)
The name Peter suggests that Christianity had started to permeate into Serbia, undoubtedly through Serbia's contacts with the Bulgarians and Byzantines. Peter secured himself on the throne (after fending off a challenge from Klonimir, son of Stojmir) and was recognised by Tsar Symeon I of Bulgaria. An alliance was signed between the two states. Already having Travunia’s loyalty, Peter began to expand his state north and west. He annexed the Bosna River valley, and then moved west securing allegiance from the Narentines, a fiercely independent, pirateering Slavic tribe. However, Peter’s expansion into Dalmatia brought him into conflict with Prince Michael of Zahumlje. Michael had also grown powerful, ruling not only Zachlumia, but exerting his influence over Travunia and Dioklea. Porphyrogenitus explains that Michael’s roots were different from Vlastimirović dynasty, and was unwilling to yield authority to Peter.[39]
Although allied to Symeon, Peter became increasingly disgruntled by the fact that he was essentially subordinate to him. Peter’s expansion toward the coast facilitated contacts with the Byzantines, by way of the strategos of Dyrrhachium. Searching for allies against Bulgaria, the Byzantines showered Peter with gold and promises of greater independence if he would join their alliance - a convincing strategy. Peter might have been planning an attack on Bulgaria with the Magyars, showing that his realm had stretched north to the Sava river. However, Michael of Zahumlje forewarned Symeon of this plan, since Michael was an enemy of Peter, and a loyal vassal of Symeon. What followed was multiple Bulgarian interventions and a succession of Serb rulers. Symeon attacked Serbia (in 917) and deposed Peter, placing Pavle Branović (a grandson of Mutimir) as Prince of Serbia, subordinate to Symeon (although some scholars suggest that Symeon took control over Serbia directly at this time. Unhappy with this, the Byzantines then sent Zaharije Prvoslavljevic in 920 to oust Pavle, but he failed and was sent to Bulgaria as prisoner. The Byzantines then succeeded in turning Prince Pavle to their side. In turn, the Bulgarians started indoctrinating Zaharije. Zaharije invaded Serbia with a Bulgarian force, and ousted his cousin Pavel in 922. However, he too turned to Byzantium. A punitive force sent by the Bulgarians was defeated.Thus we see a continuous cycle of dynastic strife amongst Vlastimir’s successors, stirred on by the Byzantine and Bulgarians, who were effectively using the Serbs as pawns. Whilst Bulgarian help was more effective, Byzantine help seemed preferable. Simeon made peace with the Byzantines to settle affairs with Serbia once and for all. Frustrated by the traitorous smaller neighbour militarily, the Bulgarians decided to finish the things once and for all. In 924, he sent a large army accompanied by Časlav, son of Klonimir. The army forced Zaharije to flee to Croatia. The Serbian župans were then summoned to recognise Caslav as the new Prince. When they came, however, they were all imprisoned and taken to Bulgaria, as too was Časlav. Much of Serbia was ravaged, and many people fled to Croatia, Bulgaria and Constantinople. Simeon made Serbia into a Bulgarian province, so that Bulgaria now bordered Croatia and Zahumlje. He then resolved to attack Croatia, because it was a Byzantine ally and had sheltered the Serbian Prince.[39]
At the battle of the Bosnian Highlands, Croatian King Tomislav defeated the Bulgarians, whilst Prince Michael of Zahumlje maintained neutrality. During the fall of central Serbia, Michael was the pre-eminent Serb prince, having been awarded the honorary title of patrikios by the Byzantine Emperor, and may have ruled over Zachlumia, Travunia and Dioklea.
Časlav (927–960)
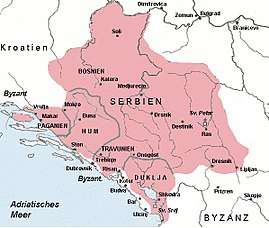
The Bulgarian rule over Serbia lasted only three years. After Symeon died, Časlav Klonimirović (927- c. 960s) led Serb refugees back to Serbia. He secured the allegiance of the Dalmatian duchies and expelled Bulgarian rule from central Serbia. After Tomislav’s death, Croatia was in near anarchy as his sons vied for sole rule, so Caslav was able to extend his rule north to the Vrbas river (gaining the alliegence of the chiefs of the various Bosnian župas).[39]
During this apogee of Serbian power, Christianity and culture penetrated Serbia as the Serb prince lived in peaceful and cordial relations with the Byzantines. However, strong as it had grown to be, Serbia’s power (as other early Slavic states) was only as strong as its ruler. There was no centralised rule, a confederacy of Slavic principalities existed instead. The existence of the unified Grand Principality was dependent on the allegiance of the lesser princes to Caslav. When he died defending Bosnia against Magyar incursions (sometime between 950 and 960), the coalition disintegrated.[39]
After this, there is a gap in the history of hinterland Serbia, in western sources Rascia, as it is annexed by the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Empire. The dynasty continues to rule the maritime regions, and in the 990s, Jovan Vladimir (Vlastimirović) rises as the most powerful Serbian prince, with a realm of present-day Montenegro, eastern Herzegovina, and Koplik in Albania, this state becomes known as Duklja, after the ancient Roman town of Doclea. However, by 997, it had been conquered and made subject to Bulgaria again by tsar Samuel.[39]
When the Byzantines finally defeated the Bulgarians, they regained control over most of the Balkans for the first time in four centuries. Serbian lands were governed by a strategos presiding over the Theme of Sirmium. However, local Serbian princes continued to reign as suzerains to the Byzantines, maintaining total autonomy over their lands, such as in Rascia, while only nominally being Byzantine vassals. Forts were maintained in Belgrade, Sirmium, Niš and Braničevo. These were, for the most part, in the hands of local nobility, which often revolted against Byzantine rule.
Fall and aftermath
After Časlav died ca 960, "Rascia" (hinterland of Serbia) was annexed by the Byzantines (Catepanate of Serbia, 971–976) and Bulgars. Serbia lost its centralized rule and the provinces once again came under the Empire. Jovan Vladimir emerged later as a ruler of a little land called Duklja, centered in Bar on the Adriatic coast, as a Byzantine vassal. His realm was called Serbia, Dalmatia, Sklavonia etc., and eventually had much of the maritime provinces, including Travunia and Zachlumia. His realm probably stretched into the hinterland to include some parts of Zagorje (inland Serbia and Bosnia) as well. Vladimir’s pre-eminent position over other Slavic nobles in the area explains why Emperor Basil approached him for an anti-Bulgarian alliance. With his hands tied by war in Anatolia, Emperor Basil required allies for his war against Tsar Samuel, who ruled a Bulgarian empire stretched over Macedonia. In retaliation, Samuel invaded Duklja in 997, and pushed through Dalmatia up to the city of Zadar, incorporating Bosnia and Serbia into his realm. After defeating Vladimir, Samuel reinstated him as a vassal Prince. We do not know what Vladimir’s connection was to the previous princes of Serbia, or to the rulers of Croatia- much of what is written in the Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja about the genealogy of the Doclean rulers is mythological. Vladimir was murdered by Vladislav, Samuel’s brother and successor, circa 1016 AD. The last prominent member of his family, his uncle Dragimir, was killed by some local citizens in Kotor in 1018. That same year, the Byzantines had defeated the Bulgarians, and in one masterful stroke re-took virtually the entire Southeastern Europe.[39]
Government
| Vlastimirović dynasty |
|---|
The Serbian ruler was titled "Prince (archon) of the Serbs" (αρχων Σερβλίας).[40] In Serbo-Croatian historiography, the Slavic title of knez (кнез) is used instead of the Greek arhont (архонт).[41] The DAI mentions that the Serbian throne is inherited by the son, i.e. the first-born; his descendants succeeded him, though their names are unknown until the coming of Višeslav.[6][42] The Serbs at that time were organized into župe (sing. župa), a confederation of village communities (roughly the equivalent of a county), headed by a local župan (a magistrate or governor); the governorship was hereditary, and the župan reported to the Serbian prince, whom they were obliged to aid in war.[12]
According to V. Ćorović, the Serbs at first lived withdrawn in gorges, in their old tribal organization. Byzantine supreme rule was nominally recognized. Domestic rulers, veliki župani, ruled Serbia by right of inheritance. The land was divided between the ruler's brothers; the oldest, as the ruler, had for certain domestic rule in the collective.[43]
Historian B. Radojković (1958) proposed that Serbia was a "divided principality". According to him, Višeslav could have been a chief military leader (veliki vojvoda) who with his company seized the entire power in his hands and turned himself into a hereditary ruler, as veliki župan; in this way, the first Serbian state was thus established after 150 years of permanent living in the new homeland and existence of military democracy.[44] However, B. Radojković's work was discredited by Sima Ćirković in 1960.[45]
Geography
Cities
According to DAI, baptized Serbia (known erranously in historiography as "Raška"[13]), included the following cities (καστρα/kastra), with spellings used in Moravcsik's transcript (1967):
| "Inhabited city" | Notes |
|---|---|
| Serbia (proper) | |
| Destinikon (Δεστινίκον) | Slavicized as Destinik and Dostinik. It was most likely southeast of Ras.[46] —P. Skok and V. Korać: Drsnik, in Metohija. —R. Novaković: Gradeš in Gedže, Orahovac[47] |
| Tzernabouskeï (Τζερναβουσκέη) | Slavicized as Crnobuški and Černavusk. — |
| Megyretous (Μεγυρέτους) | Slavicized as Međurečje (meaning "[land] between rivers"). —V. Ćorović: Samobor, Goražde or Soko at Piva-Tara confluence |
| Dresneïk (Δρεσνεήκ) | Slavicized as Drežnik and Drsnik. —V. Ćorović: Drežnik |
| Lesnik (Λεσνήκ) | Slavicized as Lešnik and Lesnica —V. Ćorović: Lešnica |
| Salines (Σαληνές) | Slavicized as Soli. —V. Ćorović: Tuzla |
| Bosnia | |
| Katera (Κατερα) | Slavicized as Kotor.[48] —V. Ćorović: Kotorac in Vrhbosna.[49] —Bulić: Possibly Bobac/Bobos in Kotor Varoš.[50] |
| Desnik (Δέσνηκ) | —V. Ćorović: Unidentified.[49] —Bulić: Unidentified.[50] |
The "small land" (χοριον/chorion) of Bosnia (Βοσωνα/Bosona), part of Serbia,[51] according to Ćorović was likely divided from Raška at the Drina, and had the cities of Katera (Κατερα) and Desnik (Δέσνηκ).[52] The other Serb-inhabited lands (or principalities) that were mentioned in DAI included the maritime Paganija, Zahumlje and Travunija,[4] while maritime Duklja was held by the Byzantines, it was presumably settled with Serbs as well.[15] All of the maritime lands bordered Serbia to the north.[4]
According to S. Novaković, the first Serbian towns were situated in the eastern and southeastern part towards the Ibar and Bulgaria.[48] The dynasty members' flights to Croatia indicates that royal seats were located in the west.[48] The meeting between Petar Gojniković and the strategos of Dyrrhachion in Narentine lands points to the latter as well.[48] It may be assumed that the eastern frontier was protected from the Bulgars, while the rulers ruled from the western part of the country.[48] The locations of the Serbian towns were proposed in the 19th century, most of the sites were unsurveyed, however.[48]
Religion

The establishment of Christianity as state-religion dates to the time of Prince Mutimir and Byzantine Emperor Basil I (r. 867–886),[53][54] who, after managing to put the Serbs under his nominal rule, sends priests together with admiral Niketas Ooryphas, before the operations against the Saracens in 869 when Dalmatian fleets were sent to defend the town of Ragusa).[52]
The Christianization was due partly to Byzantine and subsequent Bulgarian influence.[53] It is important to note that at least during the rule of Kotsel of Pannonia (861–874), communications between Serbia and Great Moravia must have been possible.[53] This fact, the pope was presumably aware of, when planning Methodios' diocese as well as the Dalmatian coast, which was in Byzantine hands as far north as Split.[53] There is a possibility that some Cyrillomethodian pupils reached Serbia in the 870s, perhaps even sent by Methodius himself.[53] Serbia is accounted Christian as of about 870.[53]
The first Serbian bishopric was founded at the political center at Ras, near modern Novi Pazar on the Ibar river.[53] The initial affiliation is uncertain, it may have been under the subordination of either Split or Durazzo, both then Byzantine.[53] The early church of Saint Apostles Peter and Paul at Ras, can be dated to the 9th–10th century, with the rotunda plan characteristic of first court chapels.[55] The bishopric was established shortly after 871, during the rule of Mutimir, and was part of the general plan of establishing bishoprics in the Slav lands of the Empire, confirmed by the Council of Constantinople in 879–880.[55] The Eparchy of Braničevo was founded in 878 (as continuation of Viminacium and Horreum Margi).
The seal of Strojimir (died between 880–896), the brother of Mutimir, was bought by the Serbian state in an auction in Germany. The seal has a Patriarchal cross in the center and Greek inscriptions that say: "God, help Strojimir (CTPOHMIP)".[56][57]
Petar Gojniković (r. 892–917), was evidently a Christian prince.[53] Christianity presumably was spreading in his time,[29] also since Serbia bordered Bulgaria, Christian influences and perhaps missionaries came from there.[29] This would increase in the twenty-year peace.[58] The previous generation (Mutimir, Strojimir and Gojnik) had Slav names, the following (Petar, Stefan, Pavle, Zaharija) has Christian names, a notice of strong Byzantine missions to Serbia, as well as to the Slavs of the Adriatic coast, in the 870s.[53]
The Bulgarian annexation of Serbia in 924 was important for the future direction of the Serbian church.[55] By now, at latest, Serbia must have received the Cyrillic alphabet and Slavic religious text, already familiar but perhaps not yet preferred to Greek.[55]
Notable early church buildings include the monastery of Archangel Michael in Prevlaka (Ilovica), built in the beginning of the 9th century, on the location of older churches of three-nave structure with three apses to the East, dating from the 3rd and 6th centuries, Bogorodica Hvostanska (6th century) and Church of Saints Peter and Paul.[59]
Archaeology
Part of a series on the |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Serbia | ||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||
- Church of Saint Apostles Peter and Paul in Ras
- Sočanica basilica
- Gradina, Sebečevska reka, in Raška[60]
- Gradina Martinića, Zeta[60]
- Gradina, Brsenica, near Sjenica[60]
- Gradina on Jelica, near Čačak[60]
- Gradina on Postenj, near Petar's Church[60]
See also
- List of Serbian monarchs
- Names of Serbia
- Duklja
- Serbia in the Middle Ages
- White Serbia (before 610)
- Serbian Grand Principality (1091–1217)
- Serbian Kingdom (1217–1345)
- Serbian Empire (1345–1371)
- Fall of the Serbian Empire (1371–1402)
- Serbian Despotate (1402–1459)
References
- 1 2 Ćirković 2004, p. 14.
- 1 2 Hupchick 2017, p. 128.
- ↑ Scholz 1970, p. 111.
- 1 2 3 Moravcsik 1967.
- ↑ Janković 2004, p. 39-61.
- 1 2 3 Благојевић 1989, p. 19.
- 1 2 3 Живковић 2006, p. 11.
- ↑ Moravcsik 1967, p. 156, 160.
- ↑ Encyclopaedia Britannica (Firma), Vol. 20, ISBN 0852291736, p. 233.
- 1 2 Samardžić & Duškov 1993, p. 24.
- 1 2 Strizović 2004, p. 19.
- 1 2 Fine 1991, p. 225, 304.
- 1 2 3 Novaković 2010.
- 1 2 3 Moravcsik 1967, pp. 153–155.
- 1 2 Fine 1991, p. 53.
- ↑ Moravcsik 1967, p. 155.
- 1 2 3 4 Ćorović 2001, ch. Бугари и балкански Словени
- ↑ Ćirković 2004, p. 16.
- 1 2 Ćirković 2004, pp. 14–15.
- ↑ Pertz 1845, p. 83.
- ↑ Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (1966). Études historiques. 3. Éditions de l'Académie bulgare des sciences. p. 66.
- ↑ Живковић 2006, p. 13.
- ↑ Slijepčević 1958, pp. 35, 41, 52
- 1 2 3 Komatina 2010, p. 4
- 1 2 3 4 Komatina 2010, p. 19
- ↑ Einhard, year 827
- ↑ Komatina 2010, p. 24
- 1 2 3 Живковић 2006.
- 1 2 3 4 Fine 1991, p. 141.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Runciman 1930, ch. 2, n. 88
- 1 2 3 4 Bury 1912, p. 372
- ↑ Fine 1991, pp. 109–110.
- 1 2 3 Ćorović 2001, ch. 2, III
- ↑ Fine 1991, pp. 108, 110.
- ↑ Живковић 2006, p. 19
- ↑ Fine 1991, p. 110.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica: a new survey of universal knowledge, Volume 20, p. 341: "the eastern provinces (Branichevo, Morava, Timok, Vardar, Podrimlye) were occupied by the Bulgars."
- 1 2 Живковић 2006, p. 17
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Ćirković 2004.
- ↑ Moravcsik 1967, p. 156.
- ↑ SANU 1995, p. 37.
- ↑ Живковић 2006, p. 22–23.
- ↑ Ćorović 2001, "Прва српска држава".
- ↑ Radojković 1959, p. 9.
- ↑ Ćirković 1960, p. 195–198.
- ↑ Petrović & Vlahović 1984, p. 128.
- ↑ Novaković 1981.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Bulić 2013, p. 219.
- 1 2 Ćorović 1935, p. 9.
- 1 2 Bulić 2013, p. 156.
- ↑ Moravcsik 1967, p. 153, 155.
- 1 2 Ćorović 2001.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Vlasto 1970, p. 208.
- ↑ De Administrando Imperio, ch. 29 [Of Dalmatia and of the adjacent nations in it]: "...the majority of these Slavs [Serbs, Croats] were not even baptized, and remained unbaptized for long enough. But in the time of Basil, the Christ-loving emperor, they sent diplomatic agents, begging and praying him that those of them who were unbaptized might receive baptism and that they might be, as they had originally been, subject to the empire of the Romans; and that glorious emperor, of blessed memory, gave ear to them and sent out an imperial agent and priests with him and baptized all of them that were unbaptized of the aforesaid nations..."
- 1 2 3 4 Vlasto 1970, p. 209.
- ↑ Živković 2007, p. 23–29.
- ↑ "Glas javnosti (2006): Pečat srpskog kneza Strojimira". 2006.
- ↑ Fine 1991, p. 142.
- ↑ Јанковић 2007.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Јанковић 2012.
Sources
- Primary sources
- Moravcsik, Gyula, ed. (1967) [1949]. Constantine Porphyrogenitus: De Administrando Imperio (2nd revised ed.). Washington D.C.: Dumbarton Oaks Center for Byzantine Studies.
- Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (1840). De Ceremoniis (Reiske, J. J. ed.). Impensis E. Weberi.
- Pertz, Georg Heinrich, ed. (1845). Einhardi Annales. Hanover.
- Scholz, Bernhard Walter, ed. (1970). Carolingian Chronicles: Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard's Histories. University of Michigan Press.
- Шишић, Фердо, ed. (1928). Летопис Попа Дукљанина (Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja). Београд-Загреб: Српска краљевска академија.
- Кунчер, Драгана (2009). Gesta Regum Sclavorum. 1. Београд-Никшић: Историјски институт, Манастир Острог.
- Живковић, Тибор (2009). Gesta Regum Sclavorum. 2. Београд-Никшић: Историјски институт, Манастир Острог.
- Secondary sources
- Bataković, Dušan T., ed. (2005). Histoire du peuple serbe [History of the Serbian People] (in French). Lausanne: L’Age d’Homme.
- Благојевић, Милош (1989). Србија у доба Немањића: Од кнежевине до царства 1168-1371 (Serbia under the Nemanjić Dynasty: From Principality to Empire 1168-1371). Београд: Вајат.
- Bulić, Dejan (2013). "The Fortifications of the Late Antiquity and the Early Byzantine Period on the Later Territory of the South-Slavic Principalities, and their re-occupation". The World of the Slavs: Studies of the East, West and South Slavs: Civitas, Oppidas, Villas and Archeological Evidence (7th to 11th Centuries AD). Belgrade: The Institute for History. pp. 137–234.
- Bury, John B. (1912). A History of the Eastern Empire from the Fall of Irene to the Accession of Basil I. (A.D. 802-867). London: Macmillan.
- Ćorović, Vladimir (1935). "Teritorijalni razvoj bosanske države u srednjem vijeku". Glas SKA. Belgrade (167): 9–13.
- Ćirković, Sima (1960). "Критике и прикази: Разматрања о деоном владању и деоним кнежевинама". Istoriski glasnik. Društvo istoričara NR Srbije (1–2): 195–198. Archived from the original on 16 June 2016.
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing.
- Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Ferjančić, Božidar (1997). "Basile I et la restauration du pouvoir byzantin au IXème siècle" [Vasilije I i obnova vizantijske vlasti u IX veku]. Zbornik radova Vizantološkog instituta (in French). Belgrade (36): 9–30.
- Ferjančić, Božidar (2007). Vizantijski izvori za istoriju naroda Jugoslavije II (fototipsko izdanje originala iz 1959 ed.). Belgrade. pp. 46–65. ISBN 978-86-83883-08-0.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp Jr. (1991) [1983]. The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press.
- Hupchick, Dennis P. (2017). The Bulgarian-Byzantine Wars for Early Medieval Balkan Hegemony: Silver-Lined Skulls and Blinded Armies. New York: Springer.
- Janković, Đorđe (2004). "The Slavs in the 6th Century North Illyricum". Гласник Српског археолошког друштва. 20: 39–61.
- Јанковић, Ђорђе (2007). Српско Поморје од 7. до 10. столећа (Serbian Maritime from 7th to 10th Century) (PDF). Београд: Српско археолошко друштво.
- Јанковић, Ђорђе (2012). "О проучавању и публиковању утврђених места у Србији из VII-X столећа". Гласник Српског археолошког друштва. 28: 313–334.
- Kaimakamova, Miliana; Salamon, Maciej (2007). Byzantium, new peoples, new powers: the Byzantino-Slav contact zone, from the ninth to the fifteenth century. Towarzystwo Wydawnicze "Historia Iagellonica". ISBN 978-83-88737-83-1.
- Komatina, Predrag (2010). "The Slavs of the mid-Danube basin and the Bulgarian expansion in the first half of the 9th century" (PDF). Зборник радова Византолошког института. 47: 55–82.
- Komatina, Predrag (2015). "The Church in Serbia at the Time of Cyrilo-Methodian Mission in Moravia". Cyril and Methodius: Byzantium and the World of the Slavs. Thessaloniki: Dimos. pp. 711–718.
- Mrgić, Jelena (2004). "Rethinking the territorial development of the medieval Bosnian state". Historical Review. Istorijski institut SANU. LI: 46–53. ISSN 0350-0802. Retrieved 2012-09-12.
- Novaković, Relja (1981). Gde se nalazila Srbija od VII do XII veka: istorijsko-geografsko razmatranje : problemi i znanja. Istorijski institut.
- Novaković, Relja: "O nekim pitanjima granice Srbije, Hrvatske i Bosne u X veku", Zbornik Filozofskog fakulteta u Beogradu - serija A: istorijske nauke, no. 7/1, p. 153-158.
- Obolensky, Dimitri (1974) [1971]. The Byzantine Commonwealth: Eastern Europe, 500-1453. London: Cardinal.
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of the Byzantine State. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Petrović, Petar Ž.; Vlahović, Petar (1984). Raška: antropogeografska proučavanja. Etnografski institut Srpske akademije nauka i umetnosti. p. 128.
- Radojković, Borislav M. (1959) [1958]. "Разматрања о деоном владању и деоним кнежевинама". Istoriski časopis. Naučno delo. VIII.
- Runciman, Steven (1930). A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. London: G. Bell & Sons.
- Runciman, Steven (1988) [1929]. The Emperor Romanus Lecapenus and His Reign: A Study of Tenth-Century Byzantium. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Samardžić, Radovan; Duškov, Milan, eds. (1993). Serbs in European Civilization. Belgrade: Nova, Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Institute for Balkan Studies.
- SANU (1995). Glas. 377–381. Srpska akademija nauka i umetnosti. p. 37.
- Slijepčević, Đoko M. (1958). The Macedonian question:the struggle for southern Serbia. American Institute for Balkan Affairs.
- Stephenson, Paul (2000). Byzantium's Balkan Frontier: A Political Study of the Northern Balkans, 900–1204. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Stephenson, Paul (2003a). The Legend of Basil the Bulgar-Slayer. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Stephenson, Paul (2003b). "The Balkan Frontier in the Year 1000". Byzantium in the Year 1000. BRILL. pp. 109–134.
- Strizović, Đorđe (2004). Прошлост која живи. Доситеј.
- Treadgold, Warren T. (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press.
- Vlasto, Alexis P. (1970). The Entry of the Slavs into Christendom: An Introduction to the Medieval History of the Slavs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Живковић, Тибор (2000). Словени и Ромеји: Славизација на простору Србије од VII до XI века (The Slavs and the Romans). Београд: Историјски институт САНУ, Службени гласник.
- Живковић, Тибор (2002). Јужни Словени под византијском влашћу 600-1025 (South Slavs under the Byzantine Rule 600-1025). Београд: Историјски институт САНУ, Службени гласник.
- Живковић, Тибор (2004). Црквена организација у српским земљама: Рани средњи век (Organization of the Church in Serbian Lands: Early Middle Ages). Београд: Историјски институт САНУ, Службени гласник.
- Живковић, Тибор (2006). Портрети српских владара: IX-XII век (Portraits of Serbian Rulers: IX-XII Century). Београд: Завод за уџбенике и наставна средства.
- Živković, Tibor (2007). "The Golden Seal of Stroimir" (PDF). Historical Review. Belgrade: The Institute for History. 55: 23–29.
- Živković, Tibor (2008). Forging unity: The South Slavs between East and West 550-1150. Belgrade: The Institute of History, Čigoja štampa.
- Živković, Tibor (2011). "The Origin of the Royal Frankish Annalist's Information about the Serbs in Dalmatia". Homage to Academician Sima Ćirković. Belgrade: The Institute for History. pp. 381–398.
- Živković, Tibor (2012). De conversione Croatorum et Serborum: A Lost Source. Belgrade: The Institute of History, Čigoja štampa.
- Živković, Tibor (2013a). "On the Baptism of the Serbs and Croats in the Time of Basil I (867–886)" (PDF). Studia Slavica et Balcanica Petropolitana (1): 33–53.
- Živković, Tibor (2013b). "The Urban Landcape of Early Medieval Slavic Principalities in the Territories of the Former Praefectura Illyricum and in the Province of Dalmatia (ca. 610-950)". The World of the Slavs: Studies of the East, West and South Slavs: Civitas, Oppidas, Villas and Archeological Evidence (7th to 11th Centuries AD). Belgrade: The Institute for History. pp. 15–36.
- Zlatarski, Vasil (1918). История на Първото българско Царство. I. Епоха на хуно-българското надмощие (679—852) (Internet ed.). Sofia. (in Bulgarian)
Further reading
- Steven Runciman, A History of the First Bulgarian Empire, London 1930.
- Ćorović, Vladimir (2001). "Istorija srpskog naroda".
- Janković, Đorđe (2007). "Serbian Maritime from 7th to 10th Century: Summary of the Monograph".
- Novaković, Relja (2010). "Gde se nalazila Srbija od VII do XII veka: Zaključak i rezime monografije".
