Lymphotoxin beta receptor
Lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTBR), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 (TNFRSF3), is a cell surface receptor for lymphotoxin involved in apoptosis and cytokine release.[5][6][7] It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of receptors. It is expressed on the surface of most cell types, including cells of epithelial and myeloid lineages, but not on T and B lymphocytes. The protein specifically binds the lymphotoxin membrane form (a complex of lymphotoxin-alpha and lymphtoxin-beta). The encoded protein and its ligand play a role in the development and organization of lymphoid tissue and transformed cells. Activation of the encoded protein can trigger apoptosis.[5]
Not only does the LTBR help trigger apoptosis, it can lead to the release of the cytokine interleukin 8. Overexpression of LTBR in HEK293 cells increases IL-8 promoter activity and leads to IL-8 release. LTBR is also essential for development and organization of the secondary lymphoid organs and chemokine release.[8]
Structure
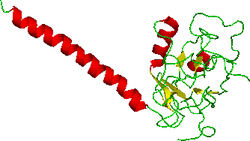
The Ramachandran plots show that 64.6% of all residues were in a favored region. This structure was found using X-ray diffraction. The resolution is 3.50 angstroms. The alpha and beta angles are 90 degrees while the gamma angle is 120 degrees.[9]
Interactions
Lymphotoxin beta receptor has been shown to interact with Diablo homolog[10] and TRAF3.[11][12][13]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000111321 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030339 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: LTBR lymphotoxin beta receptor (TNFR superfamily, member 3)".
- ↑ Baens M, Chaffanet M, Cassiman JJ, van den Berghe H, Marynen P (April 1993). "Construction and evaluation of a hncDNA library of human 12p transcribed sequences derived from a somatic cell hybrid". Genomics. 16 (1): 214–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1161. PMID 8486360.
- ↑ Crowe PD, VanArsdale TL, Walter BN, Ware CF, Hession C, Ehrenfels B, Browning JL, Din WS, Goodwin RG, Smith CA (April 1994). "A lymphotoxin-beta-specific receptor". Science. 264 (5159): 707–10. Bibcode:1994Sci...264..707C. doi:10.1126/science.8171323. PMID 8171323.
- ↑ Chang YH, Hsieh SL, Chen MC, Lin WW (August 2002). "Lymphotoxin beta receptor induces interleukin 8 gene expression via NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation". Exp. Cell Res. 278 (2): 166–74. doi:10.1006/excr.2002.5573. PMID 12169272.
- ↑ "MolProbity Ramachandran analysis" (PDF).
- ↑ Kuai, Jun; Nickbarg Elliott; Wooters Joe; Qiu Yongchang; Wang Jack; Lin Lih-Ling (Apr 2003). "Endogenous association of TRAF2, TRAF3, cIAP1, and Smac with lymphotoxin beta receptor reveals a novel mechanism of apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. United States. 278 (16): 14363–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208672200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12571250.
- ↑ VanArsdale, T L; VanArsdale S L; Force W R; Walter B N; Mosialos G; Kieff E; Reed J C; Ware C F (Mar 1997). "Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling complex: role of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 recruitment in cell death and activation of nuclear factor kappaB". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. UNITED STATES. 94 (6): 2460–5. Bibcode:1997PNAS...94.2460V. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.6.2460. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 20110. PMID 9122217.
- ↑ Wu, M Y; Wang P Y; Han S H; Hsieh S L (Apr 1999). "The cytoplasmic domain of the lymphotoxin-beta receptor mediates cell death in HeLa cells". J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 274 (17): 11868–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.17.11868. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10207006.
- ↑ Marsters, S A; Ayres T M; Skubatch M; Gray C L; Rothe M; Ashkenazi A (May 1997). "Herpesvirus entry mediator, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family, interacts with members of the TNFR-associated factor family and activates the transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1". J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 272 (22): 14029–32. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.22.14029. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9162022.
Further reading
- Elewaut D, Ware CF (2007). "The unconventional role of LT alpha beta in T cell differentiation". Trends Immunol. 28 (4): 169–75. doi:10.1016/j.it.2007.02.005. PMID 17336158.
- Browning JL, Ngam-ek A, Lawton P, et al. (1993). "Lymphotoxin beta, a novel member of the TNF family that forms a heteromeric complex with lymphotoxin on the cell surface". Cell. 72 (6): 847–56. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90574-A. PMID 7916655.
- Crowe PD, VanArsdale TL, Walter BN, et al. (1994). "A lymphotoxin-beta-specific receptor". Science. 264 (5159): 707–10. Bibcode:1994Sci...264..707C. doi:10.1126/science.8171323. PMID 8171323.
- Baens M, Chaffanet M, Cassiman JJ, et al. (1993). "Construction and evaluation of a hncDNA library of human 12p transcribed sequences derived from a somatic cell hybrid". Genomics. 16 (1): 214–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1993.1161. PMID 8486360.
- Baens M, Aerssens J, van Zand K, et al. (1996). "Isolation and regional assignment of human chromosome 12p cDNAs". Genomics. 29 (1): 44–52. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1213. PMID 8530100.
- Wang X, Bornslaeger EA, Haub O, et al. (1996). "A candidate gene for the amnionless gastrulation stage mouse mutation encodes a TRAF-related protein". Dev. Biol. 177 (1): 274–90. doi:10.1006/dbio.1996.0162. PMID 8660894.
- Nakano H, Oshima H, Chung W, et al. (1996). "TRAF5, an activator of NF-kappaB and putative signal transducer for the lymphotoxin-beta receptor". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (25): 14661–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.25.14661. PMID 8663299.
- Matsumoto M, Hsieh TY, Zhu N, et al. (1997). "Hepatitis C virus core protein interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of lymphotoxin-beta receptor". J. Virol. 71 (2): 1301–9. PMC 191185. PMID 8995654.
- VanArsdale TL, VanArsdale SL, Force WR, et al. (1997). "Lymphotoxin-beta receptor signaling complex: role of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3 recruitment in cell death and activation of nuclear factor kappaB". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (6): 2460–5. Bibcode:1997PNAS...94.2460V. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.6.2460. PMC 20110. PMID 9122217.
- Wu MY, Hsu TL, Lin WW, et al. (1997). "Serine/threonine kinase activity associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the lymphotoxin-beta receptor in HepG2 cells". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (27): 17154–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.27.17154. PMID 9202035.
- Chen CM, You LR, Hwang LH, Lee YH (1997). "Direct interaction of hepatitis C virus core protein with the cellular lymphotoxin-beta receptor modulates the signal pathway of the lymphotoxin-beta receptor". J. Virol. 71 (12): 9417–26. PMC 230246. PMID 9371602.
- Mizushima S, Fujita M, Ishida T, et al. (1998). "Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the human homolog of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 5 (TRAF5)". Gene. 207 (2): 135–40. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00616-1. PMID 9511754.
- Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Zapata JM, et al. (1998). "TRAF-4 expression in epithelial progenitor cells. Analysis in normal adult, fetal, and tumor tissues". Am. J. Pathol. 152 (6): 1549–61. PMC 1858434. PMID 9626059.
- Boussaud V, Soler P, Moreau J, et al. (1999). "Expression of three members of the TNF-R family of receptors (4-1BB, lymphotoxin-beta receptor, and Fas) in human lung". Eur. Respir. J. 12 (4): 926–31. doi:10.1183/09031936.98.12040926. PMID 9817170.
- Murphy M, Walter BN, Pike-Nobile L, et al. (1999). "Expression of the lymphotoxin beta receptor on follicular stromal cells in human lymphoid tissues". Cell Death Differ. 5 (6): 497–505. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400374. PMID 10200501.
- Wu MY, Wang PY, Han SH, Hsieh SL (1999). "The cytoplasmic domain of the lymphotoxin-beta receptor mediates cell death in HeLa cells". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (17): 11868–73. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.17.11868. PMID 10207006.
- Yu KY, Kwon B, Ni J, et al. (1999). "A newly identified member of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TR6) suppresses LIGHT-mediated apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (20): 13733–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.20.13733. PMID 10318773.
- Rooney IA, Butrovich KD, Glass AA, et al. (2000). "The lymphotoxin-beta receptor is necessary and sufficient for LIGHT-mediated apoptosis of tumor cells". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (19): 14307–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.19.14307. PMID 10799510.
- Langeggen H, Berge KE, Johnson E, Hetland G (2003). "Human umbilical vein endothelial cells express complement receptor 1 (CD35) and complement receptor 4 (CD11c/CD18) in vitro". Inflammation. 26 (3): 103–10. doi:10.1023/A:1015585530204. PMID 12083416.
- Chang YH, Hsieh SL, Chen MC, Lin WW (2002). "Lymphotoxin beta receptor induces interleukin 8 gene expression via NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation". Exp. Cell Res. 278 (2): 166–74. doi:10.1006/excr.2002.5573. PMID 12169272.
External links
- Lymphotoxin+beta+Receptor at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)