Krabbe disease
| Krabbe disease | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | GALC deficiency, Galactocerebrosidase deficiency |
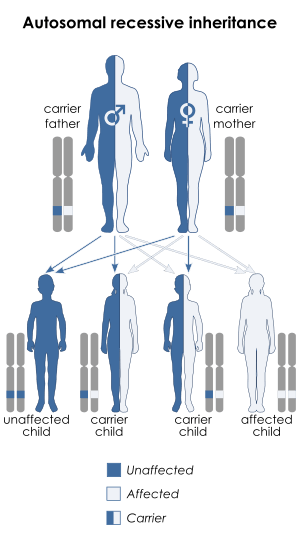 | |
| Krabbe disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner | |
| Specialty |
Endocrinology |
Krabbe disease (KD) (also known as globoid cell leukodystrophy[1] or galactosylceramide lipidosis) is a rare and often fatal lysosomal storage disease that results in progressive damage to the nervous system. KD involves dysfunctional metabolism of sphingolipids and is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The disease is named after the Danish neurologist Knud Krabbe (1885–1965).[2]
New York,[3] Missouri and Kentucky[4] include Krabbe in the newborn screening panel.[5]
Signs and symptoms
Infants with Krabbe disease are normal at birth. Symptoms begin between the ages of 3 and 6 months with irritability, fevers, limb stiffness, seizures, feeding difficulties, vomiting, and slowing of mental and motor development. In the first stages of the disease, doctors often mistake the symptoms for those of cerebral palsy. Other symptoms include muscle weakness, spasticity, deafness, optic atrophy, optic nerve enlargement,[6] blindness, paralysis, and difficulty when swallowing. Prolonged weight loss may also occur. Juvenile- and adult-onset cases of Krabbe disease also occur, which have similar symptoms but slower progression.
Causes
Krabbe disease is caused by mutations in the GALC gene located on chromosome 14 (14q31),[7] which is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Mutations in the GALC gene cause a deficiency of an enzyme called galactosylceramidase.[8] In rare cases it may be caused by a lack of active saposin A.
The buildup of unmetabolized lipids adversely affects the growth of the nerve's protective myelin sheath (the covering that insulates many nerves) resulting in demyelination and severe progressive degeneration of motor skills. As part of a group of disorders known as leukodystrophies, Krabbe disease results from the imperfect growth and development of myelin.
GALC deficiency also results in a build-up of a glycosphingolipid called psychosine, which is toxic to oligodendrocytes.[9]
Diagnosis
The disease may be diagnosed by its characteristic grouping of certain cells (multinucleated globoid cells), nerve demyelination and degeneration, and destruction of brain cells. Special stains for myelin (e.g.; luxol fast blue) may be used to aid diagnosis.
Treatment
Although there is no known cure for Krabbe disease, bone marrow transplantation has been shown to benefit cases early in the course of the disease. Generally, treatment for the disorder is symptomatic and supportive. Physical therapy may help maintain or increase muscle tone and circulation. Cord blood transplants from unrelated donors have been successful in stopping the disease as long as they are given before overt symptoms appear.[10]
Prognosis
In infantile Krabbe disease, death usually occurs in early childhood. A 2011 study found 1, 2, 3 year survival rates of 60%, 26%, and 14%, respectively. A few survived for longer. Patients with late-onset Krabbe disease tend to have a slower progression of the disease and live significantly longer.[11]
Epidemiology
Krabbe disease occurs in about one in 100,000 births.[12] A higher incidence, about six in 1,000,[12] has been reported in certain communities in Israel.[13] Scandinavian countries have comparatively high rates of the disease, reported to be one in 50,000 births.[14]
Society and culture
Former Buffalo Bills quarterback Jim Kelly has been a leader in gaining recognition and research funding for Krabbe disease, following the diagnosis of his son, Hunter, in 1997. Hunter Kelly died of the disease on August 5, 2005, at the age of 8.
Cove Ellis is a child from Georgia that was diagnosed with the disease in early 2016. Cove's family, along with her community, have worked to raise awareness of the disease and helped pass "Cove's Law", which is a bill created to allow parents the option to test unborn babies for the disease, for early recognition can save children with Krabbe disease.[15]
Other animals
Krabbe disease may also be found in cats[16] and in dogs, particularly Westies and Cairn Terriers.[17][18] The disease may also be found in dolphins.
See also
References
- ↑ Li, Y; Sands, MS (November 2014). "Experimental therapies in the murine model of globoid cell leukodystrophy". Pediatric Neurology (Review). 51 (5): 600–6. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.08.003. PMC 4252788. PMID 25240259.
- ↑ synd/1457 at Who Named It?
- ↑ Duffner, Patricia K.; Caggana, Michele; Orsini, Joseph J.; Wenger, David A.; Patterson, Marc C.; Crosley, Carl J.; Kurtzberg, Joanne; Arnold, Georgianne L.; Escolar, Maria L. (2009-04-01). "Newborn Screening for Krabbe Disease: the New York State Model". Pediatric Neurology. 40 (4): 245–252. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2008.11.010.
- ↑ (KRS 214.155)
- ↑ "unbs_state - Hunter's Hope Foundation". www.huntershope.org. Retrieved 2016-11-14.
- ↑ Hussain, S. A.; Zimmerman, H. H.; Abdul-Rahman, O. A.; Hussaini, S. M.; Parker, C. C.; Khan, M. (May 2011). "Optic Nerve Enlargement in Krabbe Disease: A Pathophysiologic and Clinical Perspective". Journal of Child Neurology. 26 (5): 642–644. doi:10.1177/0883073810387929. PMID 21285037.
- ↑ Cannizzaro, L.A. (1994). "Regional mapping of the human galactocerebrosidase gene (GALC) to 14q31 by in situ hybridization". Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 66 (4): 244–245. doi:10.1159/000133703.
- ↑ "Krabbe disease". National Institutes of Health.
- ↑ Kohlschütter, A (2013). "Lysosomal leukodystrophies: Krabbe disease and metachromatic leukodystrophy". Handbook of Clinical Neurology. 113: 1611–18. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-59565-2.00029-0. PMID 23622382.
- ↑ Escolar ML, Poe MD, Provenzale JM, Richards KC, Allison J, Wood S, Wenger DA, Pietryga D, Wall D, Champagne M, Morse R, Krivit W, Kurtzberg J (2005). "Transplantation of Umbilical-Cord Blood in Babies with Infantile Krabbe's Disease". New England Journal of Medicine. 352 (20): 2069–2081. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa042604. ISSN 0028-4793. OCLC 206940639. PMID 15901860. BL Shelfmark 6084.000000.
- ↑ Duffner, Patricia K.; Barczykowski, Amy; Jalal, Kabir; Yan, Li; Kay, Denise M.; Carter, Randy L. "Early Infantile Krabbe Disease: Results of the World-Wide Krabbe Registry". Pediatric Neurology. 45 (3): 141–148. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2011.05.007.
- 1 2 "Krabbe disease". Genetics Home Reference. United States National Library of Medicine. 2008-05-02. Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- ↑ Zlotogora J. "Krabbe disease: Increased incidence in a highly inbred community". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 21: 765–770. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320210420.
- ↑ Books.Google.com
- ↑ Miller, Andy (March 18, 2017). "Georgia lawmakers considering bill on testing newborns for rare genetic disorder". Athens Banner-Herald. Athens Banner-Herald. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- ↑ Salvadori C, Modenato M, Corlazzoli DS, Arispici M, Cantile C (May 2005). "Clinicopathological features of globoid cell leucodystrophy in cats". J. Comp. Pathol. 132 (4): 350–6. doi:10.1016/j.jcpa.2004.12.001. PMID 15893994.
- ↑ NYtimes.com
- ↑ Capucchio MT, Prunotto M, Lotti D, Valazza A, Galloni M, Dore B, Pregel P, Amedeo S, Catalano D, Cornaglia E, Schiffer D (2008). "Krabbe's disease in two West Highland White terriers". Clin. Neuropathol. 27 (5): 295–301. doi:10.5414/npp27295. PMID 18808060.
This article incorporates public domain text from the United States National Library of Medicine and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |