Kepler-90i
| Exoplanet | List of exoplanets | |
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Parent star | ||
| Star | Kepler-90 | |
| Constellation | Draco | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 18h 57m 44.0384s[1] |
| Declination | (δ) | +49° 18′ 18.4958″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude | (mV) | 13.89[2] |
| Distance | 2840±40[1] ly (870±10[1] pc) | |
| Spectral type | G0V | |
| Mass | (m) | 1.2 (± 0.1)[3] M☉ |
| Radius | (r) | 1.2 (± 0.1)[3] R☉ |
| Temperature | (T) | 6080[3] K |
| Metallicity | [Fe/H] | −0.12 (± 0.18)[3] |
| Age | ~2 Gyr | |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Radius | (r) | 1.32±0.21[3] R⊕ |
| Temperature | (T) | 709 K (436 °C; 817 °F)[3] |
| Orbital elements | ||
| Semi-major axis | (a) | 0.107+0.025 −0.040[4] AU |
| Orbital period | (P) | 14.44912±0.00020[3] d |
| Inclination | (i) | 89.20 +0.59 −1.30[3]° |
| Discovery information | ||
| Discovery date | 2017 Shallue et al.[3][4] | |
| Discoverer(s) | Kepler spacecraft[4] | |
| Discovery method | Transit[3] and deep learning, a class of machine learning algorithms.[4] | |
| Discovery status | Published[4] | |
| Other designations | ||
KOI-351 i; KIC 11442793 i; iWISE J185744.03+491818.5 i; i2MASS J18574403+4918185 i; iKepler-90 i[3] | ||
| Database references | ||
| Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia | data | |
| SIMBAD | data | |
| Exoplanet Archive | data | |
| Open Exoplanet Catalogue | data | |
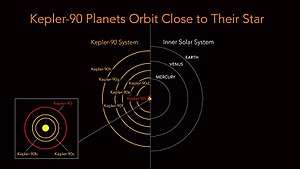
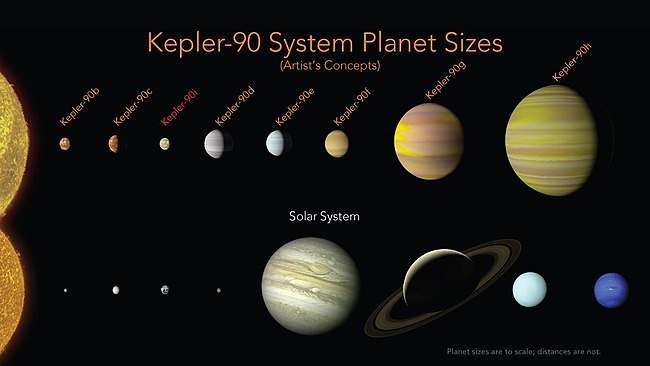
Kepler-90i (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation KOI-351 i)[3] is a super-Earth exoplanet with a radius 1.32[3] that of Earth, orbiting the early G-type main sequence star Kepler-90 every 14.45 days, discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft.[4][5] It is located about 2,545 light-years (780 parsecs, or nearly 2.4078×1016 km) from Earth in the constellation Draco. The exoplanet is the eighth in the star's multiplanetary system. As of December 2017, Kepler-90 is the star hosting the most exoplanets found. Kepler-90i was found with the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured, and by a newly utilized computer tool, deep learning, a class of machine learning algorithms.[4][6][7]
Characteristics
Mass, radius and temperature
Kepler-90i is a super-Earth exoplanet with a radius of 1.32 R⊕[3], indicating that it is small enough to be rocky. With an Earth-like composition, Kepler-90i would have a mass of about 2.5 M⊕. It has an equilibrium temperature of 709 K (436 °C; 817 °F), similar to the average temperature of Venus.
Host star
The planet orbits a (G-type) star named Kepler-90. The star has a mass of 1.2 M☉ and a radius 1.2 R☉. It has a surface temperatures of 6080 K and has an estimated age of around 2 billion years, with considerable uncertainty. In comparison, the Sun is about 4.6 billion years old[8] and has a surface temperature of 5778 K.[9]
The star's apparent magnitude, or how bright it appears from Earth's perspective, is 14. It is too dim to be seen with the naked eye.
Orbital characteristics
Kepler-90i orbits its host star about every 14.45 days with a semi-major axis of 0.1234 AU.
Due to its very close distance to its host star, it is likely to be tidally locked, meaning that one side permanently faces the star in eternal daylight and the other side permanently faces away from the star in eternal darkness.
Discovery
In 2009, NASA's Kepler spacecraft was observing stars on its photometer, the instrument it uses to detect transit events, in which a planet crosses in front of and dims its host star for a brief and roughly regular period of time. In its last test, Kepler observed 50000 stars in the Kepler Input Catalog, including Kepler-90; the preliminary light curves were sent to the Kepler science team for analysis, who chose obvious planetary companions from the bunch for follow-up at observatories. Discovery of the exoplanet was aided by a newly utilized computer tool, deep learning, a class of machine learning algorithms.[4][6]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ Staff (31 December 2013). "TEPcat: Kepler-90h". Keele Astrophysics Group. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Kepler-90 i". NASA Exoplanet Archive. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Shallue, Christopher J.; Vanderburg, Andrew (16 December 2017). "Identifying Exoplanets With Deep Learning: A Five Planet Resonant Chain Around Kepler-80 And An Eighth Planet Around Kepler-90" (PDF). Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ↑ St. Fleur, Nicholas (14 December 2017). "An 8th Planet Is Found Orbiting a Distant Star, With A.I.'s Help". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- 1 2 Chou, Felecia; Hawkes, Alison; Northon, Karen (14 December 2017). "Release 17-098 – Artificial Intelligence, NASA Data Used to Discover Eighth Planet Circling Distant Star". NASA. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ↑ Chou, Felicia; Hawkes, Alison; Landau, Elizabeth (14 December 2017). "Artificial Intelligence, NASA Data Used to Discover Eighth Planet Circling Distant Star". NASA. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ↑ Cain, Fraser (16 September 2008). "How Old is the Sun?". Universe Today. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ↑ Cain, Fraser (15 September 2008). "Temperature of the Sun". Universe Today. Retrieved 14 December 2017.

