Kakuda, Miyagi
| Kakuda 角田市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
|
Kakuda city hall | |||
| |||
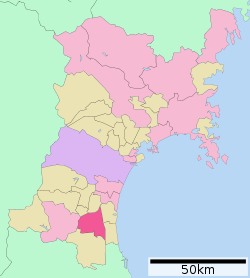 Location of Kakuda in Miyagi Prefecture | |||
 Kakuda | |||
| Coordinates: 37°58′37.3″N 140°46′55.4″E / 37.977028°N 140.782056°ECoordinates: 37°58′37.3″N 140°46′55.4″E / 37.977028°N 140.782056°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Tōhoku | ||
| Prefecture | Miyagi | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Yasushi Ito | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 147.53 km2 (56.96 sq mi) | ||
| Population (September 2017) | |||
| • Total | 29,764 | ||
| • Density | 202/km2 (520/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) | ||
| - Tree | Live Oak | ||
| - Flower | Japanese Gentian | ||
| Phone number | 0224-63-2111 | ||
| Address | Kakuda Azadaibō 41, Kakuda-shi, Miyagi-ken 981-1592 | ||
| Website | http://www.city.kakuda.lg.jp/ | ||

Kakuda (角田市 Kakuda-shi) is a city located in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. As of 30 September 2017, the city had an estimated population of 29,764, and a population density of 202 persons per km² in 11,357 households.[1] The total area of the city is 147.58 square kilometres (56.98 sq mi).
Geography
Kakuda is in southeastern Miyagi Prefecture in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan. The Abukuma River flows through the city.
Neighboring municipalities
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[2] the population of Kakuda has remained constant over the past 40 years.
| Census Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1970 | 31,170 |
| 1980 | 33,731 |
| 1990 | 35,431 |
| 2000 | 33,199 |
| 2010 | 31,336 |
Climate
Kakuda has a humid climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Kakuda is 12.6 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1259 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 24.9 °C, and lowest in January, at around 1.6 °C.[3]
History
The area of present-day Kakuda was part of ancient Mutsu Province, and was the location of Kakuda Castle during the Sengoku period. It was part of the holdings of Sendai Domain during the Edo period under the Tokugawa shogunate.
The town of Kakuda was established with the creation of the post-Meiji restoration modern municipalities system on April 1, 1889. It annexed the neighboring villages of Kitago, Sakura, Nishine, Higashine, Fujio, and Edano on October 1, 1954. Kakuda was raised to city status on October 1, 1958.
Government
Kakuda has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 18 members.[4].
Economy
Kakuda has a mixed economy based on light manufacturing of automotive parts and electrics, and on agriculture, primarily the cultivation of soybeans and plums. The area was traditionally noted for its sericulture.
Education
Kakuda has eight public elementary schools and three public middle schools operated by the city government and one public high school operated by the Miyagi Prefectural Board of Education. The prefecture also operates one special education school.
Transportation
Railway
Highway
Sister city relations


Local attractions
- Kōzō-ji – Buddhist temple
- JAXA Kakuda Space Center
- Site of Kakuda Castle
Noted people from Kakuda
- Shinichi Ito – motorcycle racer
References
- ↑ Kakuda city official statistics (in Japanese)
- ↑ Kakuda population statistics
- ↑ Kakuda climate data
- ↑ Kakuda City Council home page(in Japanese)
- ↑ "US-Japan Sister Cities by State". Asia Matters for America. Honolulu, HI: East-West Center. Retrieved 20 November 2015.
External links
- Official Website (in Japanese)


