Finke River
| Finke (Larapinta[1]) | |
| River | |
 The Finke River after rain, Northern Territory | |
| Name origin: William Finke | |
| Country | Australia |
|---|---|
| States | Northern Territory, South Australia |
| Part of | Lake Eyre Basin |
| Length | 750 km (466 mi) |
| National parks | West MacDonnell; Finke Gorge |
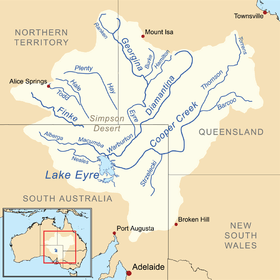 Map of the Lake Eyre Basin showing the Finke River | |
| [2] | |
The Finke River is one of the largest rivers in central Australia.
The Finke River
Its source is in the Northern Territory's MacDonnell Ranges, and the name Finke River is first applied at the confluence of the Davenport and Ormiston Creeks, just north of Glen Helen.[3] From here the river meanders for approximately 600 km (370 mi) to the western edge of the Simpson Desert in northern South Australia.[4] Usually the river is a string of waterholes, but it can become a raging torrent during rare flood events. In extreme events, water from the Finke River flows into the Macumba River, and thence into Lake Eyre, a total distance from headwater streams of around 750 km (470 mi). Major tributaries include Ellery Creek, and the Palmer and Hugh Rivers. The Finke River flows through the West MacDonnell and Finke Gorge National Parks.
Name

The Finke River was named by John McDouall Stuart in 1860 after an Adelaide man, William Finke, who was one of the promoters of his expedition.[5] The indigenous name for the river in parts of the Northern Territory is Larapinta,[1] which lends its name to an Alice Springs suburb; Larapinta Drive, which runs west from Alice Springs; and the Larapinta Trail.
Antiquity of the Finke River
The Finke River has long been cited as "the oldest river in the world", particularly by tour operators, and in popular books and brochures. In places such as the James Range, the Finke flows through deeply incised meanders[6] (see Google Maps image). Because meanders only form on flat plains, the river must have formed before the ranges were pushed up; this happened in a mountain building event referred to as the Alice Springs Orogeny which peaked between 400 and 300 million years ago (Devonian to Carboniferous Periods).[7][8] Therefore, some parts of the river's course must have already existed around this time. But southern parts of its course must be much younger because the areas where the Finke now flows near the southern edge of the Northern Territory, and further south, were under the sea during the Mesozoic Era,[7] part of the Great Artesian Basin.
The antiquity of the Finke River is not unique, but applies equally to other large mountain-sourced river systems in central Australia, e.g. the Todd and Hale Rivers and many others, because most of the central Australian mountain belts formed at around the same time.[9] There are other eroded mountain ranges of equal or greater age to the MacDonnell Ranges, both in Australia and on other continents, so present rivers in those areas may have evolved from ancestral streams of equal and greater antiquity than the Finke.
See also
References
- 1 2 "Larapinta". Northern Territory Place Names Register. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
- ↑ "Map of Finke River, NT". Bonzle Digital Atlas of Australia. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- ↑ Google Maps image
- ↑ Google Maps image
- ↑ Finke River: Northern Territory Place Names Register (accessed 1 October 2007)
- ↑ Pickup G, Allan G, Baker VR (1988). Warner RF, ed. "History, palaeochannels and palaeofloods of the Finke River, central Australia". Fluvial Geomorphology of Australia. London: Academic Press: 177–200.
- 1 2 Wells AT, Forman DJ, Ranford LC, Cook PJ (1970). "Geology of the Amadeus Basin, Central Australia". Bureau of Mineral Resources, Australia, Bulletin. 100.
- ↑ Haines PW, Hand M, Sandiford M (2001). "Palaeozoic synorogenic sedimentation in central and northern Australia: a review of distribution and timing with implications for the evolution of intracontinental orogens". Australian Journal of Earth Sciences. 48 (6): 911–928. doi:10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00909.x.
Abstract
- ↑ Mabbutt JA (1967). Jennings JN, Mabbutt JA, eds. "Denudation chronology in central Australia: Structure, climate and landform inheritance in the Alice Springs area". Landform Studies from Australia and New Guinea. Canberra: Australian National University Press: 144–181.
Coordinates: 24°08′39.55″S 132°52′20.76″E / 24.1443194°S 132.8724333°E