Fenoterol
-_and_(SS)-_fenoterol.svg.png) | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation (MDI) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 6.5 hours approximately [1][2][3][4] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.205.960 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 303.35 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Fenoterol is a β2 adrenoreceptor agonist designed to open up the airways to the lungs. It is classed as sympathomimetic β2 agonist and asthma medication.
Fenoterol is produced and sold by Boehringer Ingelheim as Berotec N and in combination with ipratropium as Berodual N.

Side effects
Fenoterol is a short-acting β2 agonist, which also stimulates β1 receptors at doses above the recommended therapeutic doses. It was widely used in New Zealand in the early 1990s but withdrawn from that market[5] because of its association with an excess number of deaths.
It is thought that the association of increased risk of death was because it was typically used in excessively large doses for severe acute asthma attacks[6] in the absence of medical assistance. Instances were known of patients who had used up to 80 puffs before seeking medical attention. Both excessive prescribed doses and patient's excessive self-medication with β agonists in acute asthma not responding to usual doses, are now generally recognized as undesirable with all β agonist asthma inhalers.
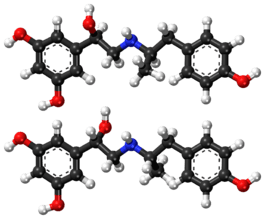
Stereoisomers
5-(1-Hydroxy-2-{[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]amino}ethyl)benzene-1,3-diol is a molecule with two different stereogenic centers. Thus, four stereoisomers may exist, the (R,R)-, (R,S)-, (S,R)- and (S,S)-stereoisomers (see the figure below). Fenoterol is a racemate of the (R,R)- and the (S,S)-enantiomers. This racemate is 9 to 20 times more effective, as compared to the racemate of the (R,S)- and (S,R)-enantiomers.[7]

References
- ↑ "Fenoterol Hydrobromide Drug Information, Professional". Drugs.com. 1996-01-01. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- ↑ "Fenoterol - Drug Monograph". DrugInfoSys.com. 2016-10-27. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- ↑ "Berotec Inhalation Solution (Fenoterol HBr)". RxMed.com. Retrieved 2018-06-11.
- ↑ Svedmyr, Nils (1985-05-06). "Fenoterol: A Beta2-adrenergic Agonist for Use in Asthma; Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Clinical Efficacy and Adverse Effects". Pharmacotherapy. Wiley. 5 (3): 109–126. doi:10.1002/j.1875-9114.1985.tb03409.x. ISSN 0277-0008.
- ↑ Beasley R, Pearce N, Crane J, Burgess C (1995). "Withdrawal of fenoterol and the end of the New Zealand asthma mortality epidemic". International Archives of Allergy and Immunology. 107 (1–3): 325–7. doi:10.1159/000237016. PMID 7613161.
- ↑ Spitzer WO, Suissa S, Ernst P, et al. (February 1992). "The use of beta-agonists and the risk of death and near death from asthma". The New England Journal of Medicine. 326 (8): 501–6. doi:10.1056/NEJM199202203260801. PMID 1346340.
- ↑ Beale J. P.; Stephenson N.C. (1972). "X-ray analysis of Th 1165 and salbutamol". Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 24: 277–280.