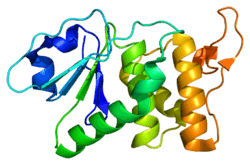DUSP18
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 18 is an enzyme that is encoded by the DUSP18 gene in humans.[5][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000167065 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000047205 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Hood KL, Tobin JF, Yoon C (Oct 2002). "Identification and characterization of two novel low-molecular-weight dual specificity phosphatases". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 298 (4): 545–51. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)02488-9. PMID 12408986.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: DUSP18 dual specificity phosphatase 18".
Further reading
- Wu Q, Huang S, Sun Y, et al. (2006). "Dual specificity phosphotase 18, interacting with SAPK, dephosphorylates SAPK and inhibits SAPK/JNK signal pathway in vivo". Front. Biosci. 11: 2714–24. doi:10.2741/2001. PMID 16720344.
- Jeong DG, Cho YH, Yoon TS, et al. (2006). "Structure of human DSP18, a member of the dual-specificity protein tyrosine phosphatase family". Acta Crystallogr. D. 62 (Pt 6): 582–8. doi:10.1107/S0907444906010109. PMID 16699184.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Collins JE, Wright CL, Edwards CA, et al. (2005). "A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome". Genome Biol. 5 (10): R84. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84. PMC 545604. PMID 15461802.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Wu Q, Gu S, Dai J, et al. (2003). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dual-specificity phosphatase18 gene from human fetal brain". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1625 (3): 296–304. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(02)00629-2. PMID 12591617.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.