DUSP23
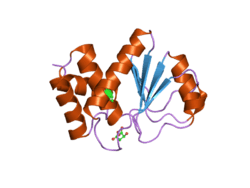
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 23, also known as low molecular mass dual specificity phosphatase 3 (LDP-3), is an enzyme (EC 3.1.3.16 and EC 3.1.3.48) that in humans is encoded by the DUSP23 gene.[5][6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000158716 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026544 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: dual specificity phosphatase 23".
- ↑ Wu Q, Li Y, Gu S, Li N, Zheng D, Li D, Zheng Z, Ji C, Xie Y, Mao Y (August 2004). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dual-specificity phosphatase 23 gene from human fetal brain". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36 (8): 1542–53. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2003.12.014. PMID 15147733.
Further reading
- Talmud PJ, Drenos F, Shah S, et al. (2009). "Gene-centric association signals for lipids and apolipoproteins identified via the HumanCVD BeadChip". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 85 (5): 628–42. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.10.014. PMC 2775832. PMID 19913121.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
- Liu CY, Wu MC, Chen F, et al. (2010). "A Large-scale genetic association study of esophageal adenocarcinoma risk". Carcinogenesis. 31 (7): 1259–63. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq092. PMC 2893800. PMID 20453000.
- Alonso A, Burkhalter S, Sasin J, et al. (2004). "The minimal essential core of a cysteine-based protein-tyrosine phosphatase revealed by a novel 16-kDa VH1-like phosphatase, VHZ". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (34): 35768–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403412200. PMID 15201283.
- Takagaki K, Satoh T, Tanuma N, et al. (2004). "Characterization of a novel low-molecular-mass dual-specificity phosphatase-3 (LDP-3) that enhances activation of JNK and p38". Biochem. J. 383 (Pt. 3): 447–55. doi:10.1042/BJ20040498. PMC 1133737. PMID 15281913.
- Bailey SD, Xie C, Do R, et al. (2010). "Variation at the NFATC2 locus increases the risk of thiazolidinedione-induced edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) study". Diabetes Care. 33 (10): 2250–3. doi:10.2337/dc10-0452. PMC 2945168. PMID 20628086.
- Tang JP, Tan CP, Li J, et al. (2010). "VHZ is a novel centrosomal phosphatase associated with cell growth and human primary cancers". Mol. Cancer. 9: 128. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-128. PMC 2893100. PMID 20509867.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.