Cobalamin
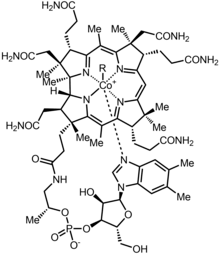
Cobalamin (Cbl) is a general term that is referred to a number of compounds, that have cobalt ion in the middle, hence the name of the compound. Cobalt ion is surrounded by four nitrogen atoms from four tetrapyrrolic corrin rings.[1]
Cobalamin is a vitamin from the vitamin B group.[2]
Cobalamin may refer to several chemical forms of vitamin B12, depending on the upper axial ligand of the cobalt ion. These are:
- Cyanocobalamin (R = –CN)
- Hydroxocobalamin (R = –OH)
- Methylcobalamin (R = –CH3), an active form of vitamin B12
- Adenosylcobalamin (R = –Ado), also an active form of vitamin B12
For dietary supplement purposes, the most commonly used form of B12 vitamin is cyanocobalamin (CNCbl) because it has superior stability, i.e., shelf-life. It was discovered as a factor against pernicious anemia, an illness which is also known as vitamin B12 deficiency anemia. There are also several physiological forms of cobalamin that differ only by the ligand that is attached to cobalt ion. For example, adenosylcobalamin (or cobamamide, AdoCbl) and methylcobalamin (MeCbl) are both cofactors: MeCbl is a cofactor for the Cytosolic methionine synthase; AdoCbl for mitochondrial methylmalonyl-CoA mutase. In physiological conditions an intermediate form of coblalamin is hydroxocobalamin (HOCbl)[1]
Cobalamin is susceptible to acid. During its biosynthesis, complexes are formed that protect it.
References
- 1 2 Obeid R, Fedosov SN, Nexo E (July 2015). "Cobalamin coenzyme forms are not likely to be superior to cyano- and hydroxyl-cobalamin in prevention or treatment of cobalamin deficiency". Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 59 (7): 1364–72. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201500019. PMC 4692085. PMID 25820384.
- ↑ Pubchem. "Cobalamin". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-03-09.