COP9 signalosome
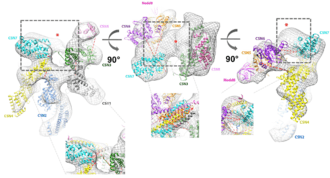
COP9 (Constitutive photomorphogenesis 9) signalosome (CSN) is a protein complex with isopeptidase activity. It catalyses the hydrolysis of NEDD8 protein from the cullin subunit of Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL). Therefore, it is responsible for CRL deneddylation – at the same time, it is able to bind denedyllated cullin-RING complex and retain them in deactivated form. COP9 signalosome thus serves as a sole deactivator of CRLs.[1] It was found in all eukaryotic organisms including human; it was first discovered in plants.[2][3] [4][5] Human COP9 signalosome (total size ~350 kDa) consists of 8 subunits - CSN1, CSN2, CSN3, CSN4, CSN5, CSN6, CSN7 (COPS7A, COPS7B), CSN8. All are essential for full function of the complex and mutation in some of them is lethal in mice.[1]
References
- 1 2 Lingaraju, GM; Bunker, RD; Cavadini, S; Hess, D; Hassiepen, U; Renatus, M; Fischer, ES; Thomä, NH (14 August 2014). "Crystal structure of the human COP9 signalosome". Nature. 512 (7513): 161–5. doi:10.1038/nature13566. PMID 25043011.
- ↑ Wei, Ning; Chamovitz, Daniel A.; Deng, Xing-Wang (1994). "Arabidopsis COP9 is a component of a novel signaling complex mediating light control of development". Cell. 78 (1): 117–124. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90578-9. ISSN 0092-8674.
- ↑ Chamovitz, Daniel A; Wei, Ning; Osterlund, Mark T; von Arnim, Albrecht G; Staub, Jeffrey M; Matsui, Minami; Deng, Xing-Wang (1996). "The COP9 Complex, a Novel Multisubunit Nuclear Regulator Involved in Light Control of a Plant Developmental Switch". Cell. 86 (1): 115–121. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80082-3. ISSN 0092-8674.
- ↑ Schwechheimer, C (29 November 2004). "The COP9 signalosome (CSN): an evolutionary conserved proteolysis regulator in eukaryotic development". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1695 (1–3): 45–54. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.023. PMID 15571808.
- ↑ Wei, N; Serino, G; Deng, XW (December 2008). "The COP9 signalosome: more than a protease". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 33 (12): 592–600. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2008.09.004. PMID 18926707.
Further reading
- Salmena, Leonardo; Hakem, Razqallah (2013). "From photomorphogenesis to cancer. A CSN journey". Cell Cycle. 12 (2): 205–206. doi:10.4161/cc.23422. PMC 3575449.
- Singer, R.; Atar, S.; Atias, O.; Oron, E.; Segal, D.; Hirsch, J. A.; Chamovitz, D. A. (2014). "Drosophila COP9 signalosome subunit 7 interacts with multiple genomic loci to regulate development". Nucleic Acids Research. 42 (15): 9761–9770. doi:10.1093/nar/gku723. PMC 4150811. PMID 25106867.
- Lingaraju, G. M.; Bunker, R. D.; Cavadini, S.; Hess, D.; Hassiepen, U.; Renatus, M.; Thomä, N. H. (2014). "Crystal structure of the human COP9 signalosome". Nature. 512 (7513): 161–165. doi:10.1038/nature13566. PMID 25043011.
- Birol, M.; Echalier, A.; Dumas, C.; Padilla, A.; Yang, Y.; Hoh, F. (2014). "The COP9 Signalosome: Activity and Regulation". Biophysical Journal. 106 (2): 463a. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2013.11.2622.
- Chamovitz, D. A. (2009). "Revisiting the COP9 signalosome as a transcriptional regulator". EMBO Reports. 10 (4): 352–358. doi:10.1038/embor.2009.33. PMC 2672896. PMID 19305390.
- Stratmann, Johannes W.; Gusmaroli, Giuliana (2012). "Many jobs for one good cop – The COP9 signalosome guards development and defense". Plant Science. 185–186: 50–64. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.10.004.
- Fang, L.; Kaake, R. M.; Patel, V. R.; Yang, Y.; Baldi, P.; Huang, L. (2012). "Mapping the Protein Interaction Network of the Human COP9 Signalosome Complex Using a Label-free QTAX Strategy". Cellular Proteomics. 11 (5): 138–147. doi:10.1074/mcp.M111.016352. PMC 3418852.