Asimina triloba
| Asimina triloba | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Asimina triloba in fruit | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Magnoliids |
| Order: | Magnoliales |
| Family: | Annonaceae |
| Genus: | Asimina |
| Species: | A. triloba |
| Binomial name | |
| Asimina triloba | |
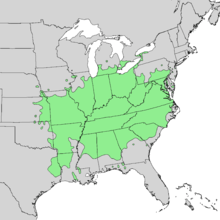 | |
| Natural range of Asimina triloba | |
Asimina triloba, the papaw,[1] pawpaw, paw paw, paw-paw, common pawpaw, Quaker delight, or hillbilly mango[2] is a small deciduous tree native to the eastern United States and Canada, producing a large, yellowish-green to brown fruit. It belongs to the genus Asimina in the same plant family (the Annonaceae) as the custard-apple, cherimoya, sweetsop, ylang-ylang and soursop.
The pawpaw is a patch-forming (clonal) understory tree found in well-drained, deep, fertile bottom-land and hilly upland habitat, with large, simple leaves. Pawpaw fruits are the largest edible fruit indigenous to the United States (not counting gourds, which are typically considered vegetables rather than fruit for culinary purposes, although in botany they are classified as fruit).[3]
Pawpaw fruits have a sweet, custardish flavor somewhat similar to banana, mango, and cantaloupe, and are commonly eaten raw, but are also used to make ice cream and baked desserts.
Names
This plant's scientific name is Asimina triloba. The genus name Asimina is adapted from the Native American (probably Miami-Illinois[4]) name assimin or rassimin[5] through the French colonial asiminier.[6] The epithet triloba in the species' scientific name refers to the flowers' three-lobed calices and doubly three-lobed corollas,[5] the shape not unlike a tricorne hat.
The common name of this species is variously spelled pawpaw, paw paw, paw-paw, and papaw. It probably derives from the Spanish papaya, an American tropical and sub-tropical fruit (Carica papaya) sometimes also called "papaw",[7][8] perhaps because of the superficial similarity of their fruits and the fact that both have very large leaves. The name Pawpaw or Papaw, first recorded in print in English in 1598,[9] originally meant the giant herb Carica papaya or its fruit (as it still commonly does in many English-speaking communities, including Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa). According to Douglas Harper's Online Etymology Dictionary, it began to be used [presumably in North America] "from 1760 to designate the papaw tree" [meaning not Carica papaya but Asimina triloba]. Daniel F. Austin's Florida Ethnobotany[10] states that
The original "papaw" . . . is Carica papaya. By 1598, English-speaking people in the Caribbean were calling these plants "pawpaws" or "papaws" . . . [yet later, when English-speakers settled in] the temperate Americas they found another tree with a similarly aromatic, sweet fruit. It reminded them of the "papaya", which had already become "papaw", so that is what they called these different plants. . . By 1760 the names "papaw" and "pawpaw" were being applied to A. triloba.
Yet Asimina triloba has had numerous local common names, many of which compare it to a banana rather than to pawpaw/papaya (i.e. to Carica papaya). These include: wild banana, prairie banana, Indiana banana, Hoosier banana, West Virginia banana, Kansas banana, Kentucky banana, Michigan banana, Missouri banana, the poor man’s banana, Ozark banana, banango, and asimoya.[11]
Description

Asimina triloba is a large shrub or small tree growing to a height of 35 feet (11 m) (rarely to 45 feet or 14 m) with a trunks 8-12 inches (20–30 cm) or more in diameter. The large leaves of pawpaw trees are clustered symmetrically at the ends of the branches, giving a distinctive imbricated appearance to the tree's foliage.[5][12]
The leaves of the species are simple, alternate and spirally arranged, entire, deciduous, obovate-lanceolate, 10-12 inches (25–30 cm) long, 4-5 inches (10–13 cm) broad, and wedge-shaped at the base, with an acute apex and an entire margin, with the midrib and primary veins prominent. The petioles are short and stout, with a prominent adaxial groove. Stipules are lacking. The expanding leaves are conduplicate, green, covered with rusty tomentum beneath, and hairy above; when fully grown they are smooth, dark green above, and paler beneath. When bruised, the leaves have a disagreeable odor similar to a green bell pepper. In autumn the leaves are a rusty yellow, which make spotting pawpaw groves possible from a long distance.[3][5][12]
Pawpaw flowers are perfect, about 1-2 inches (3–5 cm) across, rich red-purple or maroon when mature, with three sepals and six petals. They are borne singly on stout, hairy, axillary peduncles. The flowers are produced in early spring at the same time as or slightly before the new leaves appear, and have a faint fetid or yeasty smell.[3][5][12][13]

The fruit of the pawpaw is a large, yellowish-green to brown berry, 2–6 in (5–16 cm) long and 1–3 in (3–7 cm) broad, weighing from 0.7–18 oz (20–500 g), containing several brown/black seeds 1/2 to 1 in (15–25 mm) in diameter embedded in the soft, edible fruit pulp. The conspicuous fruits begin developing after the plants flower; they are initially green, maturing by September or October to yellow or brown. When mature, the heavy fruits bend the weak branches down.[3][5][12]
Other characteristics:
- Calyx: Sepals three, valvate in bud, ovate, acuminate, pale green, downy.[5][12]
- Corolla: Petals six, in two rows, imbricate in the bud. Inner row acute, erect, nectariferous. Outer row broadly ovate, reflexed at maturity. Petals at first are green, then brown, and finally become dull purple or maroon and conspicuously veiny.[5][12]
- Stamens: Indefinite, densely packed on the globular receptacle. Filaments short; anthers extrorse, two-celled, opening longitudinally.[12]
- Pistils: Several, on the summit of the receptacle, projecting from the mass of stamens. Ovary one-celled; stigma sessile; ovules many.[12]
- Branchlets: light brown, tinged with red, marked by shallow grooves.[12]
- Winter buds: Small, of two kinds, the leaf buds pointed and closely appressed to the twigs, and the flower buds round, brown, and fuzzy.[5]
- Bark: Light gray, sometimes blotched with lighter gray spots, sometimes covered with small excrescences, divided by shallow fissures. Inner bark tough, fibrous. The bark with a very disagreeable odor when bruised.[5][12]
- Wood: Pale, greenish yellow, sapwood lighter; light, soft, coarse-grained and spongy. Sp. gr., 0.3969; weight of cu ft 24.74 lb.[5][12]
Range and ecology

Asimina triloba, the pawpaw, is native to the Eastern, Southern, and Midwestern United States and adjacent Ontario, Canada, from New York west to southeastern Nebraska, and south to northern Florida and eastern Texas.[3][14][15]
The tree commonly grows in floodplains and shady, rich bottomlands, where it often forms a dense, clonally spreading undergrowth in the forest, often appearing as a patch or thicket of individual small slender trees. Pawpaws are not the first to colonize a disturbed site (arriving roughly four years after a clearcut), but may become dominant and slow the establishment of oaks and hickories. Although shade-tolerant, pawpaws do not persist in undisturbed old growth forest. Pawpaws spread locally primarily by root suckers; sexual reproduction by seed does also occur, but at a fairly low rate.[16]
Pawpaw flowers are insect-pollinated, but fruit production is sometimes limited as few if any pollinators are attracted to the flower's faint, or sometimes non-existent scent.[17] The flowers produce an odor similar to that of rotting meat to attract blowflies or carrion beetles for cross pollination. Other insects that are attracted to pawpaw flowers include scavenging fruit flies, carrion flies and beetles. Because of irregular fruit production, some believe pawpaw plants are self-incompatible, requiring cross-pollination between trees of different clones (patches).[17]
The fruits of the pawpaw are eaten by a variety of mammals, including raccoons, gray foxes, opossums, squirrels, and black bears.[16]
The disagreeable-smelling leaves, twigs, and bark of pawpaws contain natural insecticides known as acetogenins.[18] Pawpaw leaves and twigs are seldom consumed by rabbits, deer, or goats,[19] or by many insects.[3] However, mules have been seen eating pawpaw leaves in Maryland.[20]
Larvae of the zebra swallowtail (Protographium marcellus), a butterfly, feed exclusively on young leaves of Asimina triloba and various other pawpaw (Asimina) species, but never occur in great numbers on the plants.[19] Chemicals in the pawpaw leaves confer protection from predation throughout the butterfly's life, as trace amounts of acetogenins remain present, making them unpalatable to birds and other predators.[21]
Conservation status
On a global (range-wide) scale, the common pawpaw (Asimina triloba) has a NatureServe global conservation rank of G5 (very common).
In the United States, the species has a NatureServe national conservation rank of N5 (very common), but is considered a threatened species in New York, and an endangered species in New Jersey.
In Canada, where the species is found only in portions of southern Ontario, it has a NatureServe national conservation rank of N3 (vulnerable), and a NatureServe subnational conservation rank of S3 (vulnerable) in Ontario. The Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources has given the species a general status of "Sensitive", and its populations there are monitored.
In areas in which deer populations are dense, pawpaws appear to be becoming more abundant locally, since the deer avoid them but consume seedlings of most other woody plants.[20]
History
A candidate for the natural distribution of the common pawpaw (Asimina triloba) in North America, prior to the Ice Ages and lasting until roughly 10,000 years ago, were extant but now extinct megafauna.[22] Such animals became extinct during the Quaternary extinction event, and with the arrival of humans and subsequent extinction of such megafauna for distributing Asimina triloba, the probable distribution of these large fruit bearing plants was by humans.[22]
The earliest documented mention of pawpaws is in the 1541 report of the Spanish de Soto expedition, who found Native Americans cultivating it east of the Mississippi River.[23] The Lewis and Clark Expedition consumed pawpaws during their travels.[23] Chilled pawpaw fruit was a favorite dessert of George Washington,[13][23] and Thomas Jefferson planted it at Monticello, his home in Virginia.[23]
Cultivation
In cultivation, lack of successful pollination is the most common cause of poor fruiting. Cross-pollination of at least two different genetic varieties of the plant is recommended,[3] and growers often resort to hand pollination or to use of pollinator attractants such as spraying fish emulsion or hanging chicken necks or other meat near the open flowers to attract pollinators. While pawpaws are larval hosts for the zebra swallowtail butterfly, these caterpillars are usually present only at low density, and not detrimental to the foliage of the trees.[19]
Pawpaws have never been cultivated for their fruits on the scale of apples (Malus domestica) or peaches (Prunus persica), primarily because pawpaw fruits ripen to the point of fermentation soon after they are picked, and only frozen fruit will store or ship well. Other methods of preservation include dehydration, production of jams or jellies, and pressure canning (using the numerical values for bananas).
In recent years, cultivation of pawpaws for fruit production has attracted renewed interest, particularly among organic growers, as a native fruit with few to no pests, successfully grown without pesticides. The commercial cultivation and harvesting of pawpaws is strong in southeastern Ohio[24] and also being explored in Kentucky[3] and Maryland,[20] as well as various areas outside the species' native range, including California,[19] the Pacific Northwest,[19] and Massachusetts.[25]
The pawpaw is also gaining in popularity among landscapers and backyard gardeners because of the tree's distinctive growth habit, the appeal of its fresh fruit, and its relatively low maintenance needs once established. However, only container-grown pawpaws should be transplanted; use of bare-rooted pawpaws is not recommended, since their fragile root hairs tend to break off unless a cluster of moist soil is retained on the root mass.[13]
 First pawpaw leaf forming on stem above ground.
First pawpaw leaf forming on stem above ground.
Propagation
Trees are easily grown from seed. Germination is hypogeal and cotyledons remain within the seed coat. Strictly speaking, hypogeal means the cotyledons stay in the soil, acting as a food store for the seedling until the plumule emerges from the soil on the epicotyl or true stem. However, pawpaw seeds have occasionally been observed to emerge from the ground and form the true stem and plumule above ground. Desirable kinds (cultivars) of pawpaw are propagated by chip budding or whip grafting.
Seeds will lose viability if they dehydrate to 5% moisture.[26] The seeds need to be stratified, achieved by storage for 9 weeks at 5 degrees C, losing their viability if stored for 3 years or more. Some seeds survive if stored for 2 years.[26]
In one study, propagation using cuttings was not successful.[26]
Habitat restoration
Pawpaws are sometimes included in ecological restoration plantings since this tree grows well in wet soil and has a strong tendency to form well-rooted colonial thickets.
Uses

| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
|
18.8 g | |
| Dietary fiber | 2.6 g |
|
1.2 g | |
|
1.2 g | |
| Vitamins | Quantity %DV† |
| Vitamin A equiv. |
11% 87 μg |
| Thiamine (B1) |
1% 0.01 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
8% 0.09 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
7% 1.1 mg |
| Vitamin C |
22% 18.3 mg |
| Minerals | Quantity %DV† |
| Calcium |
6% 63 mg |
| Iron |
54% 7 mg |
| Magnesium |
32% 113 mg |
| Manganese |
124% 2.6 mg |
| Phosphorus |
7% 47 mg |
| Potassium |
7% 345 mg |
| Zinc |
9% 0.9 mg |
|
| |
| |
| †Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Fruits
As described by horticulturist Barbara Damrosch, the fruit of the pawpaw "looks a bit like mango, but with pale yellow, custardy, spoonable flesh and black, easy-to-remove seeds."[25] Wild-collected pawpaw fruits, ripe in late August to mid-September, have long been a favorite treat throughout the tree's extensive native range in eastern North America, and on occasion are sold locally at farmers' markets.[3][25] Pawpaw fruits have a sweet, custardish flavor somewhat similar to banana, mango, and cantaloupe,[3][5][27] varying significantly by source or cultivar,[3] with more protein than most fruits.[3] Nineteenth-century American agronomist E. Lewis Sturtevant described pawpaws as
... a natural custard, too luscious for the relish of most people[20]
Ohio botanist William B. Werthner noted that
The fruit ... has a tangy wild-wood flavor peculiarly its own. It is sweet, yet rather cloying to the taste and a wee bit puckery – only a boy can eat more than one at a time.[5]
Fresh fruits of the pawpaw are commonly eaten raw, either chilled or at room temperature. However, they can be kept only 2–3 days at room temperature, or about a week if refrigerated.[13] The easily bruised pawpaw fruits do not ship well unless frozen.[3][25] Where pawpaws grow, the fruit pulp is also often used locally in baked dessert recipes, with pawpaw often substituted with volumetric equivalency in many banana-based recipes. Pawpaws may also be blended into ice cream[13] or included in pancakes.[13]
Due to its potential for allergic reaction causing contact dermatitis and possible presence of pesticides,[28] pawpaw consumption may be harmful to humans.[29][30]
Nutrition
According to a report from the Kentucky State University Pawpaw Program (right table), raw pawpaw (with skin) in a 100 gram amount provides 80 Calories and is a rich source (20% or more of the Daily Value, DV) of vitamin C (22% DV), magnesium (32% DV), iron (54% DV) and manganese (124% DV). The fruit also contains a moderate amount (10–19% DV) of vitamin A (11% DV).
Phytochemicals
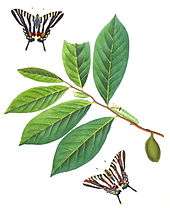
Phytochemical extracts of the leaves and fruit contain acetogenins, including the neurotoxin annonacin.[30] The seeds and bark contain the chemical asimitrin[31] and other acetogenins, including asimin, asiminacin and asiminecin.[30][32]
Effect on insects
Due to the presence of acetogenins, the leaves, twigs, and bark of pawpaw trees can be used to make an organic insecticide.[18] The one notable exception is the zebra swallowtail butterfly (Eurytides marcellus), whose larvae feed on the leaves of various species of Asimina, conferring protection from predation throughout the butterfly's life, as trace amounts of acetogenins remain present, making them unpalatable to birds and other predators.[21]
Historical uses
The tough, fibrous inner bark of the pawpaw was used by Native Americans and settlers in the Midwest for making ropes, fishing nets, mats,[5][20] and for stringing fish.[6]
Pawpaw logs have been used for split-rail fences in Arkansas.[5]
The hard, brown, shiny lima-bean-sized seeds were sometimes carried as pocket pieces in Ohio.[5]
Cultural significance
Old song
A traditional American folk song portrays wild harvesting of pawpaws; Arty Schronce of the Georgia Department of Agriculture gives these lyrics:[13]
Where, oh where is dear little Nellie?
Where, oh where is dear little Nellie?
Where, oh where is dear little Nellie?
Way down yonder in the pawpaw patch
Pickin' up pawpaws, puttin' 'em in your pocket
Pickin' up pawpaws, puttin' 'em in your pocket
Pickin' up pawpaws, puttin' 'em in your pocket
Way down yonder in the pawpaw patch
He notes that "picking up pawpaws" refers to gathering the ripe, fallen fruit from beneath the trees, and that the "pocket" in the song is that of an apron or similar tie-on pocket, not a modern pants or blue jeans pocket, into which pawpaws would hardly fit.[13] A "pawpaw patch" refers to the plant's characteristic patch-forming clonal growth habit.
Place names
The pawpaw (Asimina triloba) is the basis for various place and school names in the United States, almost all using the older spelling variant "paw paw".
Art
Nineteenth-century naturalist and painter John James Audubon included pawpaw foliage and fruits in the background of his illustration of the yellow-billed cuckoo (Coccyzus americanus) in his classic work, The Birds of America (1827–1838).
Pawpaw fruits and a pawpaw leaf are featured in the painting Still Life with Pawpaws (c. 1870-1875) by Edward Edmondson, Jr. (1830–1884), at the Dayton Art Institute in Dayton, Ohio.
Other
- The Paw Paw Formation, an Early Cretaceous geological formation in Texas where the Pawpawsaurus (pawpaw lizard), an herbivorous Cretaceous dinosaur, was found in Texas.[33]
- The Paw Paw Tunnel in Maryland on the historic Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, a 3118-foot (950-m) canal tunnel completed in 1850 bypassing the six-mile-long Paw Paw Bends in the Potomac River near the town of Paw Paw, West Virginia, all ultimately named after the pawpaw tree.[27]
- The Paw Paw Railroad (1857–1887), which constructed and operated a 4-mile (6.4 km) rail line between Lawton and Paw Paw, in Van Buren County, Michigan.[34]
- Paw Paws (or Paw Paw Bears), a 1985–1986 television cartoon series.[35]
- The pawpaw (Asimina triloba) was designated as Ohio's state native fruit in 2009.[36]
- Since 1999, The Ohio Pawpaw Growers' Association has sponsored an annual Ohio Pawpaw Festival at Lake Snowden, near Albany, Ohio.[37]
- Since 2012, Delaware's Alapocas Run State Park has hosted an annual Pawpaw Folk Festival featuring tastings of the fruit.[38]
References
- ↑ Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary (2009), as its main entry.
- ↑ "This Once-Obscure Fruit Is On Its Way To Becoming PawPaw-Pawpular". NPR. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Pawpaw Description and Nutritional Information". Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ↑ Chamberlain, Alexander F. (1 December 1902). "Algonkian Words in American English: A Study in the Contact of the White Man and the Indian". The Journal of American Folklore. American Folklore Society. 15 (59): 240–267. doi:10.2307/533199. ISSN 0021-8715. JSTOR 533199.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Werthner, William B. (1935). Some American Trees: An intimate study of native Ohio trees. New York: The Macmillan Company. pp. xviii + 398 pp.
- 1 2 Sargent, Charles Sprague (1933). Manual of the trees of North America (exclusive of Mexico). Boston and New York: Houghton Mifflin Company: The Riverside Press Cambridge. pp. xxvi + 910.
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "papaya". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 2012-10-28.
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "papaw". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 2012-10-28.
- ↑ http://historicalthesaurus.arts.gla.ac.uk/category/?type=search&qsearch=papaw&word=papaw&page=1#id=22012
- ↑ CRC Press, 2004, p.122.
- ↑ For "Asimoya" see http://rfcarchives.org.au/Next/Fruits/CustardApple/Asimoya11-96.htm
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Keeler, Harriet L. (1900). Our Native Trees and How to Identify Them. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 20–23.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Pawpaw". University of Georgia Cooperative Extension, College of Agricultural & Environmental Sciences, Athens, GA. 2012. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ↑ Robert Kral (1997). "Annonaceae". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee. Magnoliophyta: Magnoliidae and Hamamelidae. Flora of North America. 3. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-511246-7.
- ↑ "Asimina triloba (L.) Dunal". Plants Database, Natural Resources Conservation Service, US Department of Agriculture. 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
- 1 2 Asimina triloba, Fire Effects Information System, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory
- 1 2 "Asimina triloba - pawpaw". Apios Institute.
- 1 2 B. J. Sampson, J. L. McLaughlin, D. E. Wedge. 2003. PawPaw Extract as a Botanical Insecticide, 2002. Arthropod Management Tests, vol.28, p. L.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Pawpaw". California Rare Fruit Growers. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Bilton, Kathy. "Pawpaws: A paw for you and a paw for me". Retrieved 21 July 2011.
- 1 2 John M. Martin; Stephen R. Madigosky; Zhe-ming Gu; Dawei Zhou; Jinn Wu; Jerry L. McLaughlin (January 1999). "Chemical defense in the zebra swallowtail butterfly, Eurytides marcellus, involving annonaceous acetogenins". Journal of Natural Products. 62 (1): 2–4. doi:10.1021/np980308s. PMID 9917274.
- 1 2 Connie Barlow (2001). "Anachronistic Fruits and the Ghosts Who Haunt Them" (PDF). Harvard University Arboretum. Retrieved 5 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 Craig Summers Black (February 4, 2009). "America's forgotten fruit: The native pawpaw tastes like banana and grows close to home". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on March 14, 2009.
- ↑ "The 15th Annual Ohio Pawpaw Festival". Ohio Pawpaw Festival. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
- 1 2 3 4 Damrosch, Barbara (8 Sep 2011). "Return of the Native? Pawpaws' Proponents". The Washington Post (Local Living, p.9).
- 1 2 3 "Propagation of Pawpaw (Asimina triloba)". International Plant Propagators' Society. Combined Proceedings of Annual Meetings. 2000. Retrieved 17 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Paw Paw Tunnel". Town of Paw Paw, West Virginia. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ↑ Avalos, J; Rupprecht, J. K.; McLaughlin, J. L.; Rodriguez, E (1993). "Guinea pig maximization test of the bark extract from pawpaw, Asimina triloba (Annonaceae)". Contact Dermatitis. 29 (1): 33–5. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1993.tb04533.x. PMID 8365150.
- ↑ "Pawpaw uses, benefits & dosage". Drugs.com. 2016. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
- 1 2 3 Potts, L. F.; Luzzio, F. A.; Smith, S. C.; Hetman, M; Champy, P; Litvan, I (2012). "Annonacin in Asimina triloba fruit: Implication for neurotoxicity" (PDF). NeuroToxicology. 33 (1): 53–8. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2011.10.009. PMID 22130466.
- ↑ Eun Jung Kim; Kyung Mi Suh; Dal Hwan Kim; Eun Joo Jung; Chang Seob Seo; Jong Keun Son; Mi Hee Woo; Jerry L. McLaughlin (February 2005). "Asimitrin and 4-hydroxytrilobin, new bioactive annonaceous acetogenins from the seeds of Asimina triloba possessing a bis-tetrahydrofuran ring". Journal of Natural Products. 68 (2): 194–197. doi:10.1021/np040184l. PMID 15730242.
- ↑ Geng-Xian Zhao; Laura R. Miesbauer; David L. Smith; Jerry L. McLaughlin (June 1994). "Asimin, asiminacin, and asiminecin: novel highly cytotoxic asimicin isomers from Asimina triloba". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 37 (13): 1971–1976. doi:10.1021/jm00039a009. PMID 8027979.
- ↑ Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Early Cretaceous, North America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 553-556. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
- ↑ "RRHX - Railroad History Time Line - 1860". RRHX: Railroad History of Michigan. Archived from the original on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 6 August 2011.
- ↑ "IMDb - Paw Paws (TV Series 1985)". Internet Movie Database. Retrieved 6 August 2011.
- ↑ Ohio Revised Code 5.082
- ↑ Ohio Pawpaw Festival
- ↑ "Pawpaw Folk Festival set for Aug. 20 at the Blue Ball Barn". Retrieved 9 December 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Asimina triloba. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Asimina triloba |