Zaporizhia (region)
Zaporizhia (Ukrainian: Запоріжжя or Ukrainian: Запорожжя, Zaporozhia) is a historical region in central Ukraine below the Dnieper River rapids (Ukrainian: пороги porohy) - hence the name, literally "(territory) beyond the rapids".
Zaporizhia | |
|---|---|
.svg.png) Coat of arms | |
| Etymology: Beyond the Dnieper's rapids | |
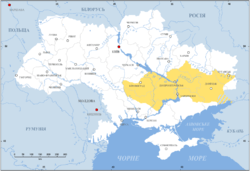 Zaporizhia (yellow) in modern Ukraine | |
| Countries | Ukraine Russia |
| Regions | Eastern Ukraine Southern Ukraine Southern Russia |
| Capital | Zaporizhian Sich |
| Parts | Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Kirovohrad Oblast, Zaporizhia Oblast, Donetsk Oblast, Luhansk Oblast, Kherson Oblast, Mykolaiv Oblast, Rostov Oblast |
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Ukraine |
 |
|
Early history
|
|
Modern history
|
|
Topics by history |
|
|
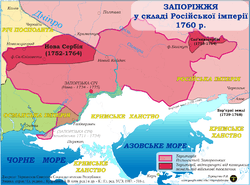

From the 16th to the 18th centuries the Zaporizhia region functioned as semi-independent quasi-republican Cossack territory centred on the Zaporizhian Sich. Sometimes the region is referred to as Zaporizhian Sich as well. Zaporizhia corresponds to modern Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, major parts of Zaporizhia and Kirovohrad Oblasts, as well as parts of Kherson and Donetsk Oblasts of Ukraine.
Names
The region was officially known as Free lands of the Lower Zaporizhia Host (Ukrainian: Вольності Війська Запорозького Низового, Polish: Zaporoże; Dzikie Pola (Wild Fields or Wild Plain), Russian: Запоро́жье, romanized: Zaporož'je). Among other names, it was called as Wild Fields, Novorossiya (in Russia), and others.
Origin
During the 1667 truce of Andrusovo, the region was under condominium of both the Tsardom of Muscovy and the Kingdom of Poland and in 1686 with signing of the Treaty of Perpetual Peace it passed into Russian suzerainty. In 1750s at the northwestern portion of the region the Russian authorities sanctioned the establishment of so-called New Serbia as a military frontier right on the border with the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Just before the Koliyivshchyna, the Russian authorities created Novorossiya Governorate centered in Kremenchuk which included territories of New Serbia, Slovianoserbia, and northern parts of Zaporizhian region.
History
Zaporizhia was the name of the territory of the Cossack state, the Zaporozhian Host, whose fortified capital was the Zaporizhian Sich. From the 15th century to the late 17th century it was fought over by Muscovy, the Polish Kingdom and the Ottoman Empire, as well as by the Hetmans of Central Ukraine (after 1648). For most of that time it was technically controlled by Poland, but it was rarely peaceful, and was widely regarded (from the perspective of the claimant governments) as turbulent and dangerous, the refuge of outlaws and bandits. In the eyes of the vast majority of the Ukrainian people, however, it was a promised land of heroes and free men (as later described in the poetry of Taras Shevchenko).In addition to many invasions by neighbouring countries, inhabitants of the Zaporozhe had to deal with an influx of new settlers from all directions and conflicts between the szlachta (Polish nobility) and independent Cossacks, who enjoyed a kind of autonomy in the region. Further, Cossacks often raided the nearby rich lands of the Ottoman Empire,retaliating for the constant slave raids of the Tatars against Ukrainian territories as far west as Galicia, in return provoking raids by Ottoman vassals, the Tatars.
The more independent Army of Lower Zaporozhia was centered at the Old Sich (Stara Sich). In 1709, Tsar Peter I ordered the destruction of the Old Sich, forcing the Zaporozhian Cossacks to flee to Oleshky, on the Black Sea in Ottoman territory. In 1734, the Russians allowed the Cossacks to re-establish their republic as the Free Lands of the Zaporozhian Host, based at the New Sich (Nova Sich), but brought in many foreign settlers, and destroyed the Sich for good in 1775, incorporating the territory into New Russia.
In the population Zaporozhye lands in the late 1970s to early 1980s of the XVIII century after liquidation Zaporizhian Sich (1775) prevailed Ukrainians. In 1779, they accounted for 64.36% of the total population of this region. On the second the place among others ethnic group was occupied by the Greeks (13.76%), followed by Armenians (10.61%) and Russian (8.09%).[1]
Economy
Some historians estimate, that an average peasant's hut did not last over 10 years.[2] In the years 1605-1633, for example, Red Ruthenian lands suffered 100,000 people taken captive by the Ottomans, and 24,000 dead; in the first half of the 17th century, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, controlling Zaporizhia, lost approximately 300,000 of people due to the Ottoman raids.[2]
Legacy
It was after this region, a city of Zaporizhia received its name in 1921 previously known as Aleksandrovsk.
See also
- Reply of the Zaporozhian Cossacks
- Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth#Voivodships of Lesser Poland
- Dmytro Yavornytsky, historian of the Zaporozhian Cossacks.
- Cossack with musket
Notes
- Vladymyr Kabuzan (1976). Заселение Новороссии (Екатеринославской и Херсонской губерний) в XVIII — первой половине XIX в. (1719—1858 гг.). Nauka. p. 133.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Podhorodecki, Leszek (1978). Stanisław Koniecpolski ok. 1592–1646. Wydawnictwo Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej. P.148-150
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zaporizhia. |
- Zaporizhia at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- Mytsyk, Yu. Free lands of the Zaporizhian Host, the Lower. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine.