Tripotassium phosphate
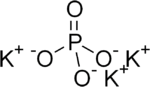
Tripotassium phosphate, also called potassium phosphate tribasic,[2] is a water-soluble salt which has the chemical formula K3PO4.(H2O)x (x = 0, 3, 7, 9)[3] Tripotassium phosphate is a strong base.
 | |
 Unit cell of tripotassium phosphate. | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium phosphate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Potassium tetraoxidophosphate(3−) | |
| Other names
Potassium phosphate, tribasic | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.006 |
| E number | E340(iii) (antioxidants, ...) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K3PO4 | |
| Molar mass | 212.27 g/mol |
| Appearance | White deliquescent powder |
| Density | 2.564 g/cm3 (17 °C) |
| Melting point | 1,380 °C (2,520 °F; 1,650 K) |
| 90 g/100 mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility in ethanol | Insoluble |
| Basicity (pKb) | 1.6 |
| Structure[1] | |
| Primitive orthorhombic | |
| Pnma, No. 62 | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| Safety data sheet | MSDS |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R36-R38 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26-S36 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Trisodium phosphate Triammonium phosphate Tricalcium phosphate |
Related compounds |
Monopotassium phosphate Dipotassium phosphate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production
Tripotassium phosphate can be produced by the reaction of ammonium phosphate () with potassium chloride ().[4]
Use in organic chemistry
Tripotassium phosphate has few applications except as a basic reagent in organic synthesis. It has been used as a catalyst for certain organic reactions.

K3PO4
Tripotassium phosphate has been used a catalyst for many organic reactions. It is cost-effective and has been used as an efficient catalyst to replace more expensive alternatives. Some of the reactions catalysed by are listed below:
- Hydrated tripotassium phosphate () can be used as a catalyst for the removal of BOC protecting group from secondary BOC amines using methanol as a solvent. Microwave radiation is used to aid the reaction.[5]
- is used as a catalyst for the synthesis of unsymmetrical diaryl ethers using [Bmim] as the solvent. Aryl methane-sulfonates are deprotected and then followed by a nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) with activated aryl halides.[6]
- was found to be one of the catalysts that aids in the coupling reaction of aryl halides with terminal alkynes. It also plays a role in the deacetonation of 4-aryl-2-methylbut-3-yn-2-ol intermediates.[7]
- can be used as one of the catalysts for the addition of aryl halides to phenols and aliphatic alcohols.[8]
Hazards
Tripotassium phosphate is strongly basic.
References
- Voronin, V. I.; Ponosov, Yu. S.; Berger, I. F.; Proskurnina, N. V.; Zubkov, V. G.; Tyutyunnik, A. P.; Bushmeleva, S. N.; Balagurov, A. M.; Sheptyakov, D. V.; Burmakin, E. I.; Shekhtman, G. Sh.; Vovkotrub, E. G. (2006). "Crystal structure of the low-temperature form of K3PO4". Inorganic Materials. 42 (8): 908–913. doi:10.1134/S0020168506080206.
- "Potassium phosphate tribasic P5629". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 2018-04-27.
- Klaus Schrödter; Gerhard Bettermann; Thomas Staffel; Friedrich Wahl; Thomas Klein; Thomas Hofmann (2012). "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3.
- Cyclic process for producing tripotassium phosphate and ammonium chloride, 1968-10-15, retrieved 2018-04-27
- Dandepally, Srinivasa Reddy; Williams, Alfred L. (2009-03-04). "Microwave-assisted N-Boc deprotection under mild basic conditions using K3PO4·H2O in MeOH". Tetrahedron Letters. 50 (9): 1071–1074. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.12.074. ISSN 0040-4039.
- Xu, Hui; Chen, Yang (2007-04-30). "C(aryl)-O Bond Formation from Aryl Methanesulfonates via Consecutive Deprotection and SNAr Reactions with Aryl Halides in an Ionic Liquid". Molecules. 12 (4): 861–867. doi:10.3390/12040861. PMC 6149384.
- Shirakawa, Eiji; Kitabata, Takaaki; Otsuka, Hidehito; Tsuchimoto, Teruhisa (2005-10-10). "A simple catalyst system for the palladium-catalyzed coupling of aryl halides with terminal alkynes". Tetrahedron. 61 (41): 9878–9885. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2005.07.099. ISSN 0040-4020.
- Niu, Jiajia; Zhou, Hua; Li, Zhigang; Xu, Jingwei; Hu, Shaojing (2008-10-03). "An Efficient Ullmann-Type C−O Bond Formation Catalyzed by an Air-Stable Copper(I)−Bipyridyl Complex". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 73 (19): 7814–7817. doi:10.1021/jo801002c. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 18771324.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
