Transport in Kosovo
Transport in Kosovo consists of transport by land and air.
Kosovo [lower-alpha 1] is complicated by political issues relating to international recognition. The country declared Independence in 2008 from Serbia. It currently has 110 diplomatic recognitions, of which 108 are members of the United Nations. Transport links to the north are fractured as Serbia does not recognise Kosovo's independence. Kosovo is recognised as sovereign by all other countries with which it shares a border. After the Independence, improvements to the road infrastructure, urban transport, and air travel have all led to a vast improvement in transportation. These upgrades have played a key role in supporting Kosovo's economy.
Road transport
The road transport in Kosovo has significantly improved following the independence of Kosovo. The government of Kosovo in recent years has focused the majority of investments on the construction of numerous motorways specifically on constructing the R6, R7 and R7.1 which connect Kosovo with its neighbouring countries.[1][2]
In recent years, two major road construction spree took place on the main state roads of Kosovo, involving the construction of new roadways, putting of contemporary signs, planting of trees, and related greening projects. Works on two highways are completed.
Motorways
| Motorway | District | Length | Description | Cities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferizaj, Pristina | 60 km (37 mi) | The R 6 (Albanian: Autostrada R 6, Serbian: Autoput R 6) is a four traffic lane motorway, spanning 60 km (37 mi).[3] The majority of the motorway is completed but still under construction. It connect the city of Pristina with the city of Skopje in North Macedonia at the border in Elez Han.[4] | Ferizaj, Kosovo Polje, Lipljan, Pristina | |
| Pristina, Prizren | 129.8 km (80.7 mi) | The R 7 (Albanian: Autostrada R 7, Serbian: Autoput R 9) is a four traffic lane motorway, spanning 129.8 km (80.7 mi). The majority of the motorway is completed but still under construction. It connect the city of Pristina with the city of Durrës in Albania at the border in Vërmica.[5] | Pristina, Prizren, Suva Reka | |
| Gjilan, Pristina | 47.1 km (29.3 mi) | The R 7.1 (Albanian: Autostrada R 7.1, Serbian: Autoput R 7.1) is a four traffic lane motorway, spanning 47.1 km (29.3 mi). The motorway is currently under construction and still under planning process and will connect the east with the west from Kosovo through the cities of Gjilan, Pristina and Kamenica. | Gjilan, Kamenica, Lipljan, Pristina, |
Air transport
Air transport in Kosovo started as early as 1936 when Yugoslav flag carrier Aeroput opened scheduled flights from Belgrade to Skopje through Podujevo airfield as mid stop.[6]
There are three Airports situated in Kosovo, the Gjakova Airport in the city of Gjakova, Batlava-Donja Penduha Airfield in the village of Dumosh and the only international Airport of Pristina in the capital of Kosovo, Pristina. Gjakova's Airport was built by the Kosovo Force (KFOR) following the Kosovo War, next to an existing airfield used for agricultural purposes, and was used mainly for military and humanitarian flights. The local and national government plans to offer Gjakova Airport for operation under a public-private partnership with the aim of turning it into a civilian and commercial airport.[7]
Pristina International Airport is located southwest of Pristina. It is Kosovo's only international airport that handles over 1.75 million passengers per year and the only port of entry for air travelers to Kosovo.
Airports: 10 ; *Airports with paved runways: 4 ; **2,438 to 3,047 m: 1 ; **1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 ; **Under 914 m: 2 ; *Airports with unpaved runways: 4 ; **Under 914 m: 4 ; *Heliports: 2
Rail transport
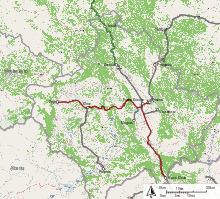
The first railway line was built under Turkish guidance for the Compagnie des Chemins de Fer Orientaux (CO), led by Maurice de Hirsch. It started in Thessaloniki, went on north to Skopje and reached Kosovska Mitrovica in 1873. Before the First World War it was used by the Serbian Railways which operated as Yugoslav Railways between 1918 and 1992, and stopped their operations in Kosovo after the NATO intervention in 1999. In 2008 Serbian Railways restored some of its routes in Northern Kosovo region.
Trainkos operates 430 km (267 mi) of railway in Kosovo, of which 333 km (207 mi) serve both freight and passenger and 97 km (60 mi) only serve freight traffic. The non-electrified network originally consisted of two lines crossing at Kosovo Polje railway station in Kosovo Polje: A main line going from Kraljevo in western Serbia via Mitrovica and Kosovo Polje to Skopje in North Macedonia, and a branch line in east-west direction from Niš in southern Serbia via Pristina railway station in the capital Pristina and Kosovo Polje with one branch leading to Peć and the other one to Prizren. Of these lines, the one from Pristina to Peć and the one from Kosovo Polje to Macedonia are still served by passenger trains. Some more parts of the network are occasionally served by freight trains, like Kosovo Polje - Obilić; the other parts of the network are currently unused. For years, there have been plans to extend the branch to Prizren across the border to Albania, to create a link to the network of the Hekurudha Shqiptare. However, these projects are no more than letters of intent.
- Total: 430 km ; *Country comparison to the world: 115 ; *Standard gauge: 430 km 1.435-m gauge
See also
- Economy of Kosovo
- Geography of Kosovo
- Transport in Prishtina
- Vehicle registration plates of Kosovo
Notes
- Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo unilaterally declared independence on 17 February 2008, but Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. The two governments began to normalise relations in 2013, as part of the 2013 Brussels Agreement. Kosovo is currently recognized as an independent state by 97 out of the 193 United Nations member states. In total, 112 UN member states recognized Kosovo at some point, of which 15 later withdrew their recognition.
References
- "Sectorial Strategy and Multimodal Transport 2015-2025 and the Action Plan for 5 years" (PDF). kryeministri-ks.net. October 2015. p. 9.
However, due to the commitment of MI, and related structures, we have achieved significant results. Proof of this are the construction of new highways, linking the Republic of Kosovo with neighbouring countries
- "The Assessment of the First 100 Days of Government" (PDF). legalpoliticalstudies.org. p. 18.
On the other hand, the Government successfully organized and handled the State Visit of Zoran Zaev, Prime Minister of Macedonia, in which a number of mutually important questions were discussed, such as bilateral trade and the new highway between Prishtina and Skopje.
- "MILOT – MORINE HIGHWAY PROJECT REQUEST FOR QUALIFICATION" (PDF). businesshungary.gov.hu. p. 8.
- "ROUTE 6: HIGHWAY PRISHTINA - SKOPJE" (PDF). kfos.org. 2015. pp. 29–35.
- "ROUTE 6: HIGHWAY PRISHTINA - SKOPJE" (PDF). kfos.org. 2015. pp. 13–28.
- Drustvo za Vazdusni Saobracaj A D – Aeroput at europeanairlines.no
- "Aktivitetet e Ministrisë së Tregtisë dhe Industrisë: Themelohet Ndërmarrja Publike "Aeroporti i Gjakovës"". Ministria e Tregtisë dhe Industrisë. Archived from the original on 2015-02-27.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Transport in Kosovo. |
- Civil Aviation Authority of Kosovo Official Website



