Sans Souci Cabaret
The Sans Souci was a night club within a natural environment and located in the outskirts seven miles outside of Havana. It had a restaurant and floor shows nightly that attracted a great number of tourists. Its greatest profits came from an amusement arcade operating located in a small room next door to the Sans Souci that was not advertised since there was no official license for its exploitation.[1]
| Sans Souci Cabaret | |
|---|---|
 Sans Souci | |
| |
| General information | |
| Type | Commercial |
| Location | Arroyo Arenas |
| Address | 15 Avenida 51 |
| Town or city | |
| Country | |
| Coordinates | 23.0457°N 82.4653°E |
| Closed | 1959 |
| Client | Santo Trafficante Jr. |
1956 Cabaret yearbook
Sans Souci Cabaret, Arroyo Arenas Highway (BO-7979). "Usually run by Americans, Sans Souci Cabaret is located in a Spanish-type villa. Stage, dance floor and tables are under the moonlight. Shows, like at the other Big Three nightclubs, are production numbers with name acts. Good-looking U.S. showgirls are an added attraction. Sans Souci, as well as Tropicana and Montmartre, has a gambling room with roulette, craps and chemin de fer, etc. Located even further out than Tropicana, Sans Souci usually opens only for the winter season."[2]
Remodel
Remodeling of the Sans Souci Cabaret started in 1955 at an approximate cost of one million dollars. The management of Norman “Roughneck” Rothman, a mafia member who was married to the Cuban Olga Chaviano, a star at the Sans Souci between 1953 and 1955, preceded the management of William G. Buschoff, known as Lefty Clark, from Miami Beach; one of the men of Santo Trafficante Jr.. A report by the Department of the Treasury written in Havana considered Buschoff a suspect of drug trafficking; Santo Trafficante was also a suspect.
American tourists

Because the Havana gambling tables are played mainly by American tourists, it was the tourists who were losing heavily. One American reportedly lost $30,000 in a single night. Another lost $17,000. Complaints poured into the American embassy and into the Cuban Tourist Institute. The Cuban government warned the night-club operators, but razzle continued. The warning took the form of a five-hour shutdown of all casinos on New Year's Eve, but still razzle continued. The Tourist Institute imported a U.S. gambling expert, Fred Freed, to clean up the casinos, but so much pressure was brought to bear that within a few days of his arrival Freed had to go into hiding. He soon fled the country, and the president of the Tourist Institute resigned.
But the golden flood could not continue indefinitely. The cries against razzle inevitably reached the Presidential Palace, where the unfavorable publicity Cuba was getting was noted, and soon President Fulgencio Batista ordered the police to clean out razzle once and for all. This they did with rapid dispatch. Shortly afterwards eleven U.S. gamblers were deported from Cuba.
So widespread was the effect of razzle that it even made the United States newspapers headlines. A political figure allegedly lost more than $4,000 at the game and paid with a bad check. A suit was filed in an effort to make good the check.When new management took over in 1955, it considered renaming the San Souci to Capacabana or Copahabana, in order to get away from the lingering taint. Finally it was decided, however, that Sans Souci is almost a Havana landmark, its name is a fixture, and the best way to restore it to respectability would simply be to operate it respectably.
Razzle game
Sometime in 1952 Sans Souci Cabaret installed a razzle game and it was so successful that within a few months virtually every Cuban nightclub in Havana had one. The game made as much money for the clubs as all their other games combined: an average of $7,000 nightly.[3]
Razzle (or Razzle-Dazzle) is a scam sometimes presented as a gambling game on carnival midways and historically, in the casinos of Havana, Cuba.[4] The player throws a number of marbles onto a grid of holes, and the numbers of those holes award points which it is suggested can be converted into prizes. In reality, it is almost impossible for a player to win enough points for the prize. According to gaming expert Darwin Ortiz, the Razzle is seldom, if ever, run honestly.[5]
This generic name of Razzle is seldom known to players, as it is generally presented under a name such as Football, Baseball, Ten Points Win, Mo-Co, Indian Poker or Cajun Bingo, selected to generate interest for the locals. The nature of the game makes it a particular money-maker for dishonest carnies.[6]
Play
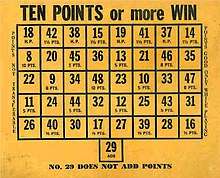
Razzle consists of a large playing board with over a hundred holes numbered 1 through 6. A player makes a bet by spilling eight marbles onto the board from a cup, and the numbers of the holes they land in are added together and referenced on a chart that looks something like a calendar, telling the player how many points they have won for that roll. Around half of the squares on the chart show a point bonus, while the other half are empty and score nothing. In football-themed versions of the game, points scored are "yards". Significant prizes can be on offer, valued in the hundreds of dollars,[7] but they can only be won when a player has reached a particular point or yard total.[6] In most Razzle set-ups, the player must bet one unit of currency (dollar, pound, Euro) per roll. Whenever the player throws a total of 29, the game is "doubled": the player must pay twice as much for all future rolls, but will receive an extra prize at the end of the game.
Jay Mallin records the game being played with eight dice instead of marbles and holes, in Cuban nightclubs and casinos in the 1950s.[8]
Scam
The points-per-number chart is the secret. The scattered order of the chart obscures the fact that the point-scoring squares are exclusively among the higher and lower throws.
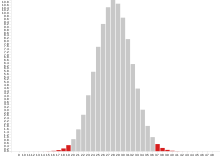
A chart might list numbers from 8 through to 48, where a result in a middle range of 20 through 36 is shown as scoring the player nothing, while results 8 through 19 and 37 through 48 all payout. Visually this would mean that more than half of the squares on the chart showed a payout (with 22 winning squares and only 16 losing ones), and a player might instinctively conclude that more than half of their throws will payout. In reality, more than 98% of a player's throws would land in the 20-to-36 range.
Further to this, around 10% of throws will total to 29,[9] and although this is presented as penalty for both sides ("Player and Operator must Double on Number 29") it merely accelerates the rate at which the player hands over their money: the operator will never lose, so doubling the size of the prize is meaningless.
Even if the game were run honestly, the mathematical nature of the razzle board makes it extremely unlikely that a player would ever win before running out of money, or that the value of the prizes won would ever equal the amount of money spent chasing them. The game operator conceals this from the player by using a fast and incorrect count to, when it suits the operator, pretend that a throw scored when it did not. This is used initially to hook the player into the game by giving the player a generous number of wins in the opening throws of the game, taking them some way to the prize point total and giving the impression that the remaining points can be obtained just as easily. Once the player has become invested in the game, the operator will switch to counting the throws accurately, with nearly all of them being losses. If the player starts to show reluctance to continue, the operator will dole out just enough miscounted points to keep them at the table.[10] Increasingly the player believes that walking away would be a disaster - they only need one or two more points to win the prize. Unfortunately for the player, they will only get those points if the operator allows it. According to Darwin Ortiz, most Razzle operators are not satisfied until they get their mark's last dollar.
The Razzle is such a devastatingly effective scam that some crooked booth operators have been known to even abandon their store's theme and "bring out the razzle". On a block in New Orleans in the early 2000s, tourists had reported losses of up to $18,000 to the scam.[11]
Notes
References
- "THE CUBAN CASINO CHIPS". Retrieved 2020-02-17.
- GUIDE TO AFTER-DARK HAVANA 1956 Cabaret Yearbook, Winter Resort Number, Volume One, poss 1956, p68
- "SANS SOUCI Havana Night Club & Casino, Cabaret, April 1957, p36". Retrieved 2020-02-17.
- English, T. J. (2008). Havana Nocturne: how the mob owned Cuba -- and then lost it to the revolution. New York: William Morrow.
- Ortiz, Darwin (1984). Gambling Scams. Mead.
- Berry, Donald A.; Regal, Ronald R. (Nov 1978). "Probabilities of Winning a Certain Carnival Game". The American Statistician. 32 (4): 126. doi:10.2307/2682938. JSTOR 2682938.
- Du, Susan. "Minnesota State Fair goer confronts Razzle scam artists and gets his revenge". City Pages. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- "Razzle Dazzle". www.goodmagic.com. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- "Ask the Wizard #260 - Wizard of Odds". wizardofodds.com. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- Gryczan, Matthew L. (1988). Carnival Secrets: How to Win at Carnival Games, Which Games to Avoid, How to Make Your Own Games. Zenith Press.
- Perlstein, Michael; TheTimes-Picayune, Copyright 2004 (8 May 2004). "Role of New Orleans police in rigged game investigated". Houston Chronicle. Retrieved 4 May 2019.