Sagarmatha Zone
Sagarmāthā (Nepali: सगरमाथा अञ्चल![]()
Sagarmāthā सगरमाथा अञ्चल | |
|---|---|
Zone | |
Lower Pangboche village in Khumbu, Nepal | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Time zone | UTC+5:45 (Nepal Time) |
It includes mountain districts of the Himalayas (including Mount Everest)[2] in the north, hill districts in the center, and valley districts of the Terai in the south. It is bordered by China to the north, India to the south, the Koshi Zone to the east and the Janakpur Zone to the west.
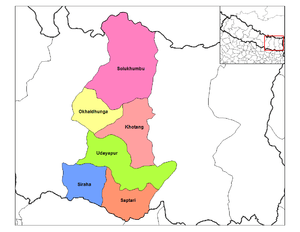
Sagarmāthā is divided into six districts:
| District | Type | Headquarters | Since 2015 part of Province |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khotang | Hill | Diktel | Province No. 1 |
| Okhaldhunga | Hill | Okhaldhunga | |
| Solukhumbu | Mountain | Salleri | |
| Udayapur | Inner Terai | Triyuga | |
| Saptari | Outer Terai | Rajbiraj | Province No. 2 |
| Siraha | Outer Terai | Siraha |
The main city of the Sagarmāthā Zone was Rajbiraj which was also the headquarters. Other towns of the Sagarmāthā hill area were Katari, Okhaldhunga, Diktel, Salleri and Namche Bazaar; while Kathauna, Lahan, Fatepur, Rajbiraj and Siraha are in the outer Terai. Triyuga is an emerging city in the zone.[3]
Sagarmāthā Zone took its name from the Nepalese name for Mount Everest, which is located in the very north of the zone within the Sagarmatha National Park (1,148 km²) in the Solu Khumbu district. Sagarmāthā means "the Head in the Great Blue Sky".[4]
See also
- Development Regions of Nepal (Former)
- List of zones of Nepal (Former)
- List of districts of Nepal
- Sagarmatha National Park
References
- "Sacred Himalayan Landscape". 2013-06-12. Retrieved 2018-09-03.
- yukesh0007 (2019-02-17). "Undisputed glory tales of Mt.Everest". SOUL OF HIMALAYAS. Retrieved 2020-01-28.
- "Triyuga Municipality proposes river land for Sagarmatha Airport". My Republica. Retrieved 2018-09-03.
- Exceed English Series 1 New Edition 2006 pg 48