Redhill–Tonbridge line
The Redhill–Tonbridge line is a railway line going from Redhill, Surrey to Tonbridge, Kent in southeast England. It branches off the Brighton Main Line at Redhill and, after 20 miles (32 km), joins the South Eastern main line at Tonbridge.[1]
| Redhill–Tonbridge line | |
|---|---|
 Looking east towards the Bletchingley Tunnel | |
| Overview | |
| Type | Suburban rail, Heavy rail |
| System | National Rail |
| Status | Operational |
| Locale | Kent Surrey South East England |
| Termini | Tonbridge, Kent Redhill, Surrey |
| Stations | 7 |
| Operation | |
| Opened | c. 1836 |
| Owner | Network Rail |
| Operator(s) | Southern |
| Rolling stock | Class 377 Electrostar |
| Technical | |
| Number of tracks | 2 |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 750 V DC Third rail |
| Operating speed | 100 mph (160 km/h) |
Redhill– Tonbridge line | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
It was originally part of the South Eastern Railway having been sanctioned by Act of Parliament in 1836 as part of the first railway line from London to Dover. This may explain why the route runs perfectly straight: serving the settlements en route was a secondary consideration. Following the completion of the new South Eastern main line in 1868, along which services run a more direct route between London and Tonbridge, the Redhill–Tonbridge line's function as the trunk route between London and Dover became part of the new line.
Aircraft coming into London's Croydon Airport in the early 20th century used this line as a source of navigation. All the stations along this route had their names written in bold white paint on the roof of the station buildings.
It starts with an initial curve just outside Redhill where it passes over the Quarry line which is inside the Redhill tunnel (649 yards). The Bletchingley Tunnel (grid reference TQ340486), about 1 mile (1.6 km) southeast of Bletchingley is about 1⁄2 mile (0.8 km) long. At grid reference TQ400480 the "Crowhurst Spur"[2] connected with the East Grinstead branch of the Oxted line but this was lifted in the early 1970s. Just west of Edenbridge, in a hamlet called Troy Town it crosses, but does not connect with, the Uckfield branch of the Oxted line.[3]
The line was electrified with 750 V DC third rail in 1993 and services started to run through to London rather than being an extension of the Reading to Redhill North Downs Line service. The electrification also created a diversionary route for the Eurostar services until 2007 from Waterloo International through Tonbridge and Ashford International.
Stations and services on the line are operated by Southern using Class 377 units. They provide a service between Tonbridge and London Victoria.
Accidents and incidents
- On 28 July 1845, a passenger train was run into by a steam locomotive at Penshurst, injuring about 30 people.[4]
- On 21 January 1846, a bridge over the River Medway collapsed in a flood. The driver of a freight train was killed when he tried to jump clear of the train.[5]
- On 1 April 1852, a passenger train was derailed at Edenbridge.[6]
- On 22 December 2019, a landslip between Edenbridge and Godstone caused the line to be temporarily closed to traffic.[7] The line reopened and normal services resumed in March 2020.[8]
Gallery
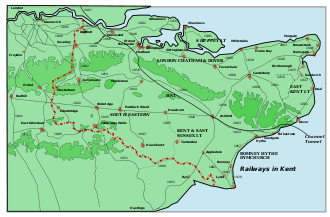 The Redhill–Tonbridge line, shown with other railway lines in Kent. Note the line's relation with the South Eastern Main Line.
The Redhill–Tonbridge line, shown with other railway lines in Kent. Note the line's relation with the South Eastern Main Line._Waterloo_RJD_126.jpg) A 1910 Railway Clearing House map of the interaction of the Oxted lines and the Redhill–Tonbridge line.
A 1910 Railway Clearing House map of the interaction of the Oxted lines and the Redhill–Tonbridge line.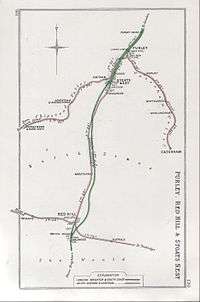 A 1905 Railway Clearing House map of the western end of the Redhill–Tonbridge line.
A 1905 Railway Clearing House map of the western end of the Redhill–Tonbridge line.
References
- Rail Maps - National Rail. Retrieved on 7 March 2009.
- Southern E-Group article on the Crowhurst Spur
- Collins Road Atlas Britain 2008 (Paperback) ISBN 0-00-725047-9
- "Accident on the Dover Railway". The Times (18988). London. 29 July 1845. col A, p. 5.
- "Fearful and Fatal Accident on the South Eastern Railway". The Times (19139). London. 21 January 1846. col D, p. 5.
- "Accident to the Dover Express Train". The Standard (8626). London. 2 April 1852.
- "'Significant landslip' between Redhill and Tonbridge disrupts rail services". BBC News online. 28 December 2019. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- "Landslip repairs: Redhill-Tonbridge railway to reopen in March". Network Rail. 22 January 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
