Moorfields
Moorfields was an open space, partly in the City of London, lying adjacent to – and outside – its northern wall, near the eponymous Moorgate. It was known for its often marshy conditions, which may have been a result of the defensive wall acting like a dam, impeding the flow of the River Walbrook and its tributaries.[1]
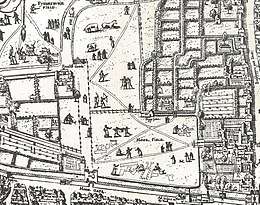

Moorfields gives its name to the Moorfields Eye Hospital which occupied a site on the former fields from 1822–1899, and is still based close by, in the St Luke's area of the London Borough of Islington.[2]
Setting
Moorfields was contiguous with Finsbury Fields, Bunhill Fields and other open spaces, and until its eventual loss in the 19th century, was the innermost part of a green wedge of land which stretched from the wall, to the open countryside which lay close by. Moorfields separated the western and eastern growth of London beyond the city wall – with the eastern extension being better known as the East End.
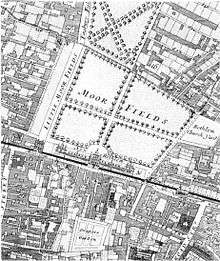
The fields were divided into four areas; the Little Moorfields, Moorfields proper, Middle Moorfields and Upper Moorfields.
The Little Moorfields and Moorfields proper (also known as Lower Moorfields) were just north of London's wall, and from 1676-1815 included the Bethlem Hospital. Little Moorfields was the element that was left lying just west of Moorgate Street after gap had been made in the wall to create the Moorgate, and the associated road from the north, in the 15th century. These parts were inside the City boundaries, lying in the Coleman Street Ward.
The Walbrook, known at this point as Deepditch and running on the line of modern Blomfield Street, seems to have formed the eastern boundary of Moorfields proper. It also formed an administrative boundary,[3] with Coleman Street Ward to the west (including the open spaces of Little Moorfields and Moorfields proper); while on the East End side lay the urbanised extra-mural ward of Bishopsgate Without, and also the parish of Shoreditch.
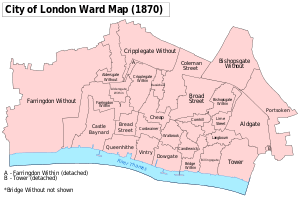
Middle Moorfields and Upper Moorfields lay outside the City, to the north-west of Moorfields proper, in the Manor of Finsbury. The manor was coterminous with the parish of St Luke's (a late sub-division of the parish of St Giles-without-Cripplegate).[4]
The Metropolitan Borough of Shoreditch (which replaced the parish of Shoreditch, being based on the same boundaries), had an electoral ward named Moorfields, this was adjacent to the former Moorfields (and also the famous Moorfields Eye Hospital) with only a small part of the area ever having been part of Moorfields, and only at an early date.
History
An early name for Moorfields proper appears to have been Moor Mead.[5] The Moor place-name element usually refers to fen environments,[6] and the wet nature of the area persisted at least until the area was drained in 1572.[7]
Development in the area became more feasible after a small nearby postern gate was replaced with the last of the city gates, Moorgate, in 1415, and enlarged in 1472 and 1511. The gate remained poorly connected as there was no direct approach road from the south until 1846, long after the gate and wall were demolished.
After the Great Fire of London in 1666, refugees from the fire evacuated to Moorfields and set up temporary camps there. King Charles II of England encouraged the dispossessed to move on and leave London, but it is unknown how many newly impoverished and displaced persons instead settled in the Moorfields area.
In the early 18th century, Moorfields was the site of sporadic open-air markets, shows, and vendors/auctions. Additionally, the homes near and within Moorfields were places of the poor, and the area had a reputation for harbouring highwaymen, as well as brothels. James Dalton and Jack Sheppard both retreated to Moorfields when in hiding from the law. Parts of the area were known as public cruising areas for gay men.[8] A path in the Upper Moorfields, beside a wall that separated the Upper and Middle Moorfields was known as Sodomites Walk: the wall was removed in 1752 but the path remains as the south side of Finsbury Square.[9]
In 1780 it was the site of some of the most violent rioting during the Gordon Riots.
The district was once the site of The Foundery, a centre of Wesleyan Methodism.[10]
A fashionable carpet manufactory was established here by Thomas Moore (c. 1700–1788) in the mid-eighteenth century. Moore's carpet manufactory at Moore Place made a number of fine carpets commissioned by the architect and interior designer, Robert Adam, for the grand rooms he designed for his wealthy clients. Thomas Moore lived at his home on Chiswell Street until his death. His Moore Park factory remained in operation until 1793, when his daughter, Jane, and her husband, Joseph Foskett, sold the lease to another carpet manufacturer.
Demise and legacy
Much of Moorfields was developed in 1777, when Finsbury Square was developed; the remainder succumbed within the next few decades, notably when Moorfields proper was replaced by the modern Finsbury Circus after 1812.

Today the name survives in the names of Moorfields Eye Hospital (since moved to another site); St Mary Moorfields; Moorfields the short street (on which stands the headquarters of the British Red Cross) parallel with Moorgate (and containing some entrances to Moorgate station); and Moorfields Highwalk, one of the pedestrian "streets" at high level in the Barbican Estate. Moorfields Highwalk is featured in the music video to Robbie Williams' song "No Regrets".
References
- on the wall eventually becoming an inadvertent? dam to hold back the walbrook https://www.british-history.ac.uk/rchme/london/vol3/pp10-18
- History from the hospital's own web page https://www.moorfields.nhs.uk/content/our-history
- BHO source on the Moorfields area https://www.british-history.ac.uk/survey-london/vol8/pp88-90
- Records of St Giles without Cripplegate, Chapter 6 see https://archive.org/stream/recordsstgilesc01dentgoog/recordsstgilesc01dentgoog_djvu.txt
- https://www.british-history.ac.uk/survey-london/vol8/pp88-90
- Concise Oxford Dictionary of Place Names, Eilert Ekwall, fourth edition. He doesn't refer to Moorfields, only the place name element.
- The London Encyclopaedia, Weinreb and Hibbert
- Norton, Rictor (1992). Mother Clap's Molly House: The Gay Subculture in England 1700–1830. London: Gay Men's Press. pp. 71–90. ISBN 0854491880.
- Homosexuality in 18th century England, Rictor Norton, http://rictornorton.co.uk/eighteen/brown.htm
- "List of publications published or distributed at the Foundry". Copac. Retrieved 28 January 2010.
