Königswinter
Königswinter (Low Franconian: Keuningswintjer) is a city and summer resort in the Rhein-Sieg district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany.
Königswinter | |
|---|---|
 Front of St. Remigius (2009) | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Königswinter within Rhein-Sieg-Kreis district 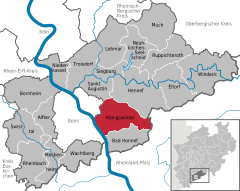  | |
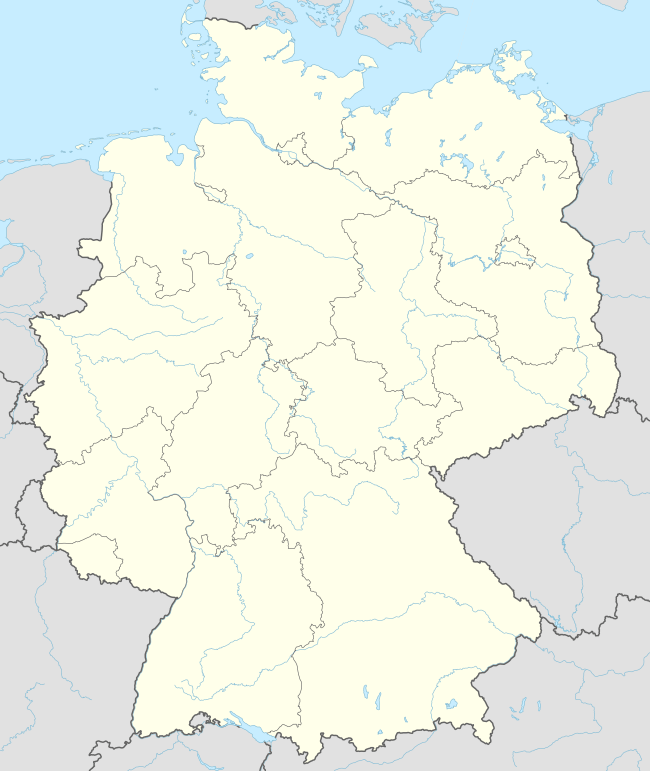 Königswinter 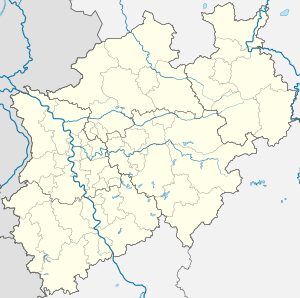 Königswinter | |
| Coordinates: 50°40′25″N 7°11′41″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Köln |
| District | Rhein-Sieg-Kreis |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Peter Wirtz (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 76.19 km2 (29.42 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 460 m (1,510 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 51 m (167 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 41,243 |
| • Density | 540/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 53639 |
| Dialling codes | 02223, 02242, 02244, 0228 |
| Vehicle registration | SU |
| Website | www.koenigswinter.de |
Geography
Königswinter is situated on the right bank of the Rhine, opposite Bad Godesberg, at the foot of the Siebengebirge. It covers an area of 76.19 square kilometres which makes it the fourth-largest conurbation in the Rhein-Sieg district. It contains over 80 townships and boroughs, divided over the municipal districts of Stieldorf, Niederdollendorf, Oberdollendorf, Heisterbacherrott, Ittenbach, Oberpleis, Eudenbach, Thomasberg and Königswinter proper.
Main sights
Drachenfels
The Drachenfels, crowned by the ruins of a castle built in the early 12th century by the archbishop of Cologne, rises behind the town. From the summit, which can be accessed by the Drachenfels Railway, there is a view celebrated by Lord Byron in Childe Harold's Pilgrimage.
A cave in the hill is said to have sheltered the dragon (German: Drachen) which was slain by the hero Siegfried. The mountain is quarried, and from 1267 onward supplied stone (trachyte) for the building of Cologne Cathedral. The Schloss Drachenburg, built in 1883, is on the north side of the hill.
Petersberg and Heisterbach
The Petersberg mountain also overlooks Königswinter. This was formerly the home of an Augustinian and, later, Cistercian monastery. Around 1195 the monks moved to the foot of the mountain and founded the Abbey of Heisterbach, which was destroyed in 1803. The ruins can still be seen.
Today the peak of the Petersberg is occupied by the Hotel Petersberg, a grand hotel which serves as a guest house for the German Government. Many world leaders have stayed there, and conferences are regularly held. Like the Drachenfels, the Petersberg was once served by its own railway, the Petersberg Railway, but this closed in 1958 and the hotel is now reached by road or helicopter.
The town
Königswinter has a Catholic (St Remigius) and a Protestant church, some small manufactures and a little shipping. It has a monument to the poet Wolfgang Müller.
Transport

The town is served by Königswinter and Niederdollendorf stations on the Rhine East Bank Railway between Cologne and Wiesbaden, as well as by several stops on line 66 of the Bonn Stadtbahn, which takes a different route through the town. The tourist-oriented Drachenfels Railway does not connect direct with either of these lines but instead relies on a steam-outline road train for connection to the town centre and stations.[2]
Several ferries cross the Rhine between Königswinter and the west bank.
Gallery
 Lithography of St. Remigius (August Karstein, 1850)
Lithography of St. Remigius (August Karstein, 1850) Homes in Königswinter
Homes in Königswinter Königswinter town hall
Königswinter town hall
References
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2018" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "Drachenfelsbahn Königswinter". Drachenfelsbahn Königswinter. Archived from the original on 2015-03-16. Retrieved 2012-02-20.
![]()
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Königswinter. |

- Official site (in German)
- View at Terraserver