Geography of Uganda
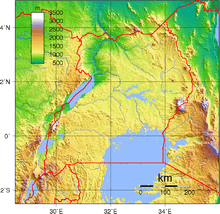
Uganda is located in eastern Africa, west of Kenya, south of South Sudan, east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and north of Rwanda and Tanzania. It is in the heart of the Great Lakes region, and is surrounded by three of them, Lake Edward, Lake Albert, and Lake Victoria. While much of its border is lakeshore, Uganda is landlocked with no access to the sea.
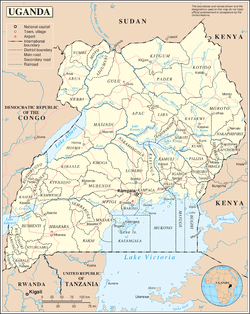
The country is mostly plateau with a rim of mountains.[1]
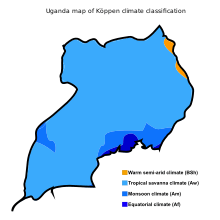
The climate is tropical and generally rainy with two dry seasons (December to February, June to August).[1] It is semiarid in the northeast.[1]
Statistics
Area:[2]
total: 241,551 square kilometres (93,263 sq mi)
land: 200,523 square kilometres (77,422 sq mi)
water: 41,028 square kilometres (15,841 sq mi)
Land boundaries:[1]
total: 2,729 kilometres (1,696 mi)
border countries: Democratic Republic of the Congo 877 kilometres (545 mi), Kenya 814 kilometres (506 mi), South Sudan 475 kilometres (295 mi), Tanzania 391 kilometres (243 mi), Rwanda 172 kilometres (107 mi)
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: 614 metres (2,014 ft) Albert Nile at border with South Sudan[1]
highest point: 5,111 metres (16,768 ft)[2] Margherita Peak on Mount Stanley[1]
Natural resources:
copper, cobalt, hydropower, limestone, salt, arable land, gold[1]
Land use: (2012)[3]
arable land: 69,000 square kilometres (27,000 square miles) 34.41%
permanent crops: 22,500 square kilometres (8,700 square miles) 11.22%
forest cover: 28,100 square kilometres (10,800 square miles) 14.01%
other: 80,931 square kilometres (31,248 sq mi) 40.36%
Irrigated land: (2012)[3]
140 square kilometres (54 square miles)
Total renewable water resources:
66 cubic kilometres (16 cu mi) (2011)[4] or 60 cubic kilometres (14 cu mi) (2012)[5]
Environment - current issues:
draining of wetlands for agricultural use, deforestation, overgrazing, soil erosion, water hyacinth infestation in Lake Victoria, widespread poaching[1]
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
- Convention on the International Maritime Organization
- Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage
- Agreement on the Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer
- Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
- Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
- Convention on Biological Diversity
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification in Those Countries Experiencing Serious Drought and/or Desertification, Particularly in Africa
- International Plant Protection Convention
- Convention on Wetlands of International Importance, especially as Waterfowl Habitat
signed, but not ratified:
- Convention on the Prohibition of Military or Any Other Hostile Use of Environmental Modification Techniques
Geography - note: Uganda is one of six African states that lies on the equator. Most of Uganda is north of the equator.
Population geography
Uganda's population density is 172.44 person/km2. Uganda's most populated cities are located in the Central and Eastern regions of the country.
Kampala is Uganda's most populated city, also its national and commercial capital. Its population is around 1,353,189.
Uganda Top 10 Cities (By Population)
- Kampala (1,353,189)
- Gulu (146,858)
- Lira (119,323)
- Mbarara (97,500)
- Jinja (93,061)
- Bwizibwera (79,157)
- Mbale (76,493)
- Mukono (76,290)
- Kasese (67,269)
- Masaka [6]
Climate
Uganda has a warm tropical climate with temperatures falling in the 25–29°C (77–84°F) range on an average. The months from December to February are the hottest, but even during this season the evenings can be chilly with temperatures in the 17–18°C (63–64°F) range.[7]
Uganda receives an annual rainfall of 1,000mm to 1,500mm. The rainy seasons are from March to May and from September to November. During these months, heavy rains can make roads and terrains hard to traverse. The period from January to February and again from June to August are dry.[7]
See also
- List of Protected Areas in Uganda
References
- "Uganda". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 2018-10-12.
- ""2014 Statistical Abstract", Uganda Bureau of Statistics, accessed 16 July 2015" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 November 2015. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- Uganda, Country Profile, FAO Stat, Food and Agriculture Organization, accessed 16 July 2015
- TOTAL RENEWABLE WATER RESOURCES, "The World Factbook", United States Central Intelligence Agency, 2011, accessed 16 July 2015 Archived 12 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- "Uganda - Total Renewable Water Resources - Water resources: total renewable (natural)", World Data Atlas, knoema, based on FAO Aquastat, 2014, accessed 16 July 2015
- "Biggest Cities Uganda". www.geonames.org. Retrieved 2018-11-19.
- "Uganda".
