Domestic rabbit
A domestic or domesticated rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus domesticus)—more commonly known as a pet rabbit, a bunny, a bun, or a bunny rabbit—is a subspecies of European rabbit. A domestic rabbit kept as a pet may be considered a pocket pet, depending on its size. A male rabbit is known as a buck, a female is a doe, and a young rabbit is a kit, or kitten.
| Domestic rabbit | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A pet rabbit eating in a bowl | |
Domesticated | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | O. c. domesticus |
| Trinomial name | |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus domesticus | |
Rabbits were first used by the Romans as sources of food and fur, and have been kept as pets in Western nations since the 19th century.[1] Beginning in the 1980s, the idea of the domestic rabbit as a house companion, a so-called house rabbit, was promoted. Rabbits can be litter box-trained and come when called, but they need exercise and can damage a house that is not "rabbit proof." Unwanted rabbits end up in animal shelters, especially after the Easter season.[2] Because they have become invasive in Australia, pet rabbits are banned in the state of Queensland.[3]
History
Phoenician sailors visiting the coast of Spain c. 12th century BC, mistaking the European rabbit for a species from their homeland (the rock hyrax Procavia capensis), gave it the name i-shepan-ham (land or island of hyraxes). [4]
The captivity of rabbits as a food source is recorded as early as the 1st century BC, when the Roman writer Pliny the Elder described the use of rabbit hutches, along with enclosures called leporaria.[1] A controversial theory is that a corruption of the rabbit's name used by the Romans became the Latin name for the peninsula, Hispania.[5] In Rome, rabbits were raised in large walled colonies with walls extended underground.[6] According to Pliny, the consumption of unborn and newborn rabbits, called laurices, was considered a delicacy.[7]
Evidence for the domestic rabbit is rather late. In the Middle Ages, wild rabbits were often kept for the hunt. Monks in southern France were crossbreeding rabits at least by the 12th century AD. Domestication was probably a slow process that took place from the Roman period (or earlier) until the 1500s.[8]

In the 19th century, as animal fancy in general began to emerge, rabbit fanciers began to sponsor rabbit exhibitions and fairs in Western Europe and the United States. Breeds of various domesticated animals were created and modified for the added purpose of exhibition, a departure from the breeds that had been created solely for food, fur, or wool. The rabbit's emergence as a household pet began during the Victorian era.[9]
The keeping of the rabbit as a pet commencing from the 1800s coincides with the first observable skeletal differences between the wild and domestic populations, even though captive rabbits had been exploited for over 2,000 years.[1] Domestic rabbits have been popular in the United States since the late 19th century. What became known as the "Belgian Hare Boom" began with the importation of the first Belgian Hares from England in 1888 and, soon after, the founding of the American Belgian Hare Association, the first rabbit club in America. From 1898 to 1901, many thousands of Belgian Hares were imported to America.[10] Today, the Belgian Hare is one of the rarest breeds, with only 132 specimens found in the United States in a 2015 census.[11]

The American Rabbit Breeders Association (ARBA) was founded in 1910 and is the national authority on rabbit raising and rabbit breeds having a uniform Standard of Perfection, registration and judging system. The domestic rabbit continues to be popular as a show animal and pet. Many thousand rabbit shows occur each year and are sanctioned in Canada and the United States by the ARBA. Today, the domesticated rabbit is the third most popular mammalian pet in Britain after dogs and cats.
Rabbits have been, and continue to be, used in laboratory work such as the production of antibodies for vaccines and research of human male reproductive system toxicology. The Environmental Health Perspective, published by the National Institute of Health, states, "The rabbit [is] an extremely valuable model for studying the effects of chemicals or other stimuli on the male reproductive system." According to the Humane Society of the United States, rabbits are also used extensively in the study of bronchial asthma, stroke prevention treatments, cystic fibrosis, diabetes, and cancer. Animal rights activists have opposed animal experimentation for non-medical purposes, such as the testing of cosmetic and cleaning products, which has resulted in decreased use of rabbits in these areas.[12]
Terminology
Male rabbits are called bucks; females are called does. An older term for an adult rabbit is coney, while rabbit once referred only to the young animals.[13] Another term for a young rabbit is bunny, though this term is often applied informally (especially by children and rabbit enthusiasts) to rabbits generally, especially domestic ones. More recently, the term kit or kitten has been used to refer to a young rabbit. A young hare is called a leveret; this term is sometimes informally applied to a young rabbit as well. A group of rabbits is known as a "colony" or a "nest."[14]
Biology
Genetics
The study of rabbit genetics is of interest to fanciers, the fiber & fur industry, medical researchers, and the meat industry. Among rabbit fanciers, the genetics of rabbit health and diversity are paramount. The fiber & fur industry focuses on the genetics of coat color and hair properties. In the biomedical research community and the pharmaceutical industry, rabbit genetics are important in model organism research, antibody production, and toxicity testing. The meat industry relies on genetics for disease resistance, feed conversion ratios, and reproduction potential in rabbits.
The rabbit genome has been sequenced and is publicly available.[15] The mitochondrial DNA has also been sequenced.[16] In 2011, parts of the rabbit genome were re-sequenced in greater depth in order to expose variation within the genome.[17]
- Rabbit Coat Pattern & Color Genes

Gene = En
Pattern: English
Gene = A- B- C- D- E-
Color: Chestnut
Gene = du
Pattern: Dutch
Gene = B
Color: Black (on white)
Gene = e(j)
Pattern: HarlequinGene = Enen
Pattern: Broken
Gene = D
Color: Chocolate (on white)
Gene = si
Silvering of the hair shaft
There are 11 color gene groups (or loci) in rabbits. A rabbit's coat has either two pigments (pheomelanin for yellow, and eumelanin for dark brown) or no pigment (for an albino rabbit). Clusters of color genes plus their modifiers control such aspects as coat patterns (e.g. Dutch or English markings), color hues and their intensity or dilution, and the location of color bands on the hair shaft (e.g., silvering).
Diet
As a refinement of the diet of the wild rabbit, the diet of the domestic rabbit is often a function of its purpose. Show rabbits are fed for vibrant health, strong musculoskeletal systems, and—like rabbits intended for the fur trade—optimal coat production and condition. Rabbits intended for the meat trade are fed for swift and efficient production of flesh, while rabbits in research settings have closely controlled diets for specific goals. Nutritional needs of the domestic rabbit may also be focused on developing a physique that allows for the safe delivery of larger litters of healthy kits. Optimizing costs and producing feces that meet local waste regulations may also be factors.[18] The diet of a pet rabbit, too, is geared toward its purpose—as a healthy and long-lived companion.
Hay is an essential part of the diet of all rabbits and it is a major component of the commercial food pellets that are formulated for domestic rabbits and available in many areas. Pellets are typically fed to adult rabbits in limited quantities once or twice a day, to mimic their natural behavior and to prevent obesity. It is recommended only a teaspoon to an egg cup full of pellets is fed to adult rabbits each day. Most rabbit pellets are alfalfa-based for protein and fiber, with other grains completing the carbohydrate requirements. "Muesli" style rabbit foods are also available; these contain separate components—e.g., dried carrot, pea flakes and hay pellets as opposed to a uniform pellet. These are not recommended as rabbits will choose favored parts and leave the rest. Muesli style feeds are often lower in fiber than pelleted versions of rabbit food. Additionally numerous studies have found they increase the risk of obesity and dental disease. Minerals and vitamins are added during production of rabbit pellets to meet the nutritional requirements of the domestic rabbit. Along with pellets, many commercial rabbit raisers also feed one or more types of loose hay, for its freshness and important cellulose components. Alfalfa in particular is recommended for the growth needs of young rabbits.[19]
Digestion
Rabbits are hindgut fermenters and therefore have an enlarged cecum. This allows a rabbit to digest, via fermentation, what it otherwise would not be able to metabolically process.
After a rabbit ingests food, the food travels down the esophagus and through a small valve called the cardia. In rabbits, this valve is very well pronounced and makes the rabbit incapable of vomiting. The food enters the stomach after passing through the cardia. Food then moves to the stomach and small intestine, where a majority of nutrient extraction and absorption takes place. Food then passes into the colon and eventually into the cecum. Peristaltic muscle contractions (waves of motion) help to separate fibrous and non-fibrous particles. The non-fibrous particles are then moved backwards up the colon, through the illeo-cecal valve, and into the cecum. Symbiotic bacteria in the cecum help to further digest the non-fibrous particles into a more metabolically manageable substance. After as little as three hours, a soft, fecal "pellet," called a cecotrope, is expelled from the rabbit's anus. The rabbit instinctively eats these grape-like pellets, without chewing, in exchange keeping the mucous coating intact. This coating protects the vitamin- and nutrient-rich bacteria from stomach acid, until it reaches the small intestine, where the nutrients from the cecotrope can be absorbed.[20][21]
The soft pellets contain a sufficiently large portion of nutrients that are critical to the rabbit's health. This soft fecal matter is rich in vitamin B and other nutrients. The process of coprophagy is important to the stability of a rabbit's digestive health because it is one important way that which a rabbit receives vitamin B in a form that is useful to its digestive wellness.[22] Occasionally, the rabbit may leave these pellets lying about its cage; this behavior is harmless and usually related to an ample food supply.
When caecal pellets are wet and runny (semi-liquid) and stick to the rabbit and surrounding objects, they are called intermittent soft cecotropes (ISCs). This is different from ordinary diarrhea and is usually caused by a diet too high in carbohydrates or too low in fiber. Soft fruit or salad items such as lettuce, cucumbers and tomatoes are possible causes.
Reproduction
Rabbits have a reputation as prolific breeders, and deservedly so, in part because rabbits reach breeding age quickly. To prevent unwanted offspring and to possibly benefit the rabbit's behavior, rabbits may be spayed or neutered at sexual maturity: 4–5 months for small breeds (e.g., Mini Rex, Netherland Dwarf), 5–6 months for medium-sized breeds (e.g., Rex, New Zealand), and 6–7 months for large breeds (e.g., Flemish Giant). Bucks usually require more time to sexually mature than does, and they normally reach adult sperm counts at 6–7 months.
Rabbits, like all mammals, produce milk for their young. Female rabbits have six to eight nipples and produce milk for four weeks after birthing.[23] Rabbit milk is relatively high in fat, as a percentage by mass. While most species produce approximately 5% milk fat, rabbits produce 12%. The excerpted table below compares milk characteristics among mammals.[24]
| Species | Fat % | Protein % | Lactose % | Ash % | Total Solids % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gray Seal | 53.2 | 11.2 | 2.6 | 0.7 | 67.7 |
| Polar Bear | 31.0 | 10.2 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 42.9 |
| Rabbit | 12.2 | 10.4 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 26.4 |
| Bison | 1.7 | 4.8 | 5.7 | .96 | 13.2 |
| Donkey | 1.2 | 1.7 | 6.9 | .45 | 10.2 |
Health

Disease is rare when rabbits are raised in sanitary conditions and provided with adequate care. Rabbits have fragile bones, especially in their spines, and need support on the belly or bottom when they are picked up.
Spayed or neutered rabbits kept indoors with proper care may have a lifespan of 8 to 12 years, with mixed-breed rabbits typically living longer than purebred specimens, and dwarf breeds having longer average lifespans than larger breeds.[25] The world record for longest-lived rabbit is 18 years.[25]
Rabbits will gnaw on almost anything, including electrical cords (possibly leading to electrocution), potentially poisonous plants, and material like carpet and fabric that may cause life-threatening intestinal blockages, so areas to which they have access need to be pet-proofed.[26][27][28]
Spaying and neutering
Rabbit fancier organizations and veterinarians recommend that pet rabbits be made infertile by spaying or neutering by a rabbit-experienced veterinarian.[29][30]:123 Health advantages of surgically altering a rabbit include increased longevity and (for females) a reduced risk of ovarian and uterine cancers or of endometritis.[30]:195–9[31][25] For both rabbit sexes, spaying or neutering reduces aggression toward other rabbits, as well as territorial marking (especially in males).[31][32][33] Rabbits are at high risk for complications from anesthesia and infection of the surgical site is another top concern.[34] Since un-altered animals are not as likely to form agreeable social bonds, spaying and neutering promotes less stressful interactions.
Vaccinations
In most jurisdictions, including the United States (except where required by local animal control ordinances), rabbits do not require vaccination. Vaccinations exist for both rabbit hemorrhagic disease and myxomatosis.[35] These vaccinations are usually given annually, two weeks apart. If there is an outbreak of myxomatosis locally, this vaccine can be administered every six months for extra protection.[36] Myxomatosis immunizations are not available in all countries, including Australia, due to fears that immunity will pass on to feral rabbits. However, they are recommended by some veterinarians as prophylactics, where they are legally available.[30]:182 In the UK a combined vaccination exists for myxomatosis and VHD1 made by Nobivac called Myxo-RHD, this is given yearly. Due to increasing cases of VHD2 it is now recommended rabbits receive an additional vaccination for RHD2 one brand for this is filovac, the vaccination is given yearly 2 weeks apart from other vaccinations, it may be given 6 monthly at rabbit believed to be at higher risk.
Declawing
A rabbit cannot be declawed. Lacking pads on the bottoms of its feet, a rabbit requires its claws for traction. Removing its claws would render it unable to stand.[37][38]
Tonic immobility
Coping with stress is a key aspect of rabbit behavior, and this can be traced to part of the brain known as ventral tegmental area (VTA). Dopaminergic neurons in this part of the brain release the hormone dopamine. In rabbits, it is released as part of a coping mechanism while in a heightened state of fear or stress, and has a calming effect. Dopamine has also been found in the rabbit's medial prefrontal cortex, the nucleus accumbens, and the amygdala.[39] Physiological and behavioral responses to human-induced tonic immobility (TI, sometimes termed "trancing" or "playing dead") have been found to be indicative of a fear-motivated stress state, confirming that the promotion of TI to try to increase a bond between rabbits and their owners—thinking the rabbits enjoy it—is misplaced.[40] However, some researchers conclude that inducing TI in rabbits is appropriate for certain procedures, as it holds less risk than anesthesia.[40]
Sore hocks
The formation of open sores on the rabbit's hocks, commonly called sore hocks, is a problem that commonly afflicts mostly heavy-weight rabbits kept in cages with wire flooring[41] or soiled solid flooring. The problem is most prevalent in rex-furred rabbits and heavy-weight rabbits (over 9 pounds (4.1 kg)), as well as those with thin foot bristles.
The condition results when, over the course of time, the protective bristle-like fur on the rabbit's hocks thins down. Standing urine or other unsanitary cage conditions can exacerbate the problem by irritating the sensitive skin. The exposed skin in turn can result in tender areas or, in severe cases, open sores, which may then become infected and abscessed if not properly cared for.
Gastrointestinal stasis

Gastrointestinal stasis (GI stasis) is a serious and potentially fatal condition that occurs in some rabbits in which gut motility is severely reduced and possibly completely stopped. When untreated or improperly treated, GI stasis can be fatal in as little as 24 hours.
GI stasis is the condition of food not moving through the gut as quickly as normal. The gut contents may dehydrate and compact into a hard, immobile mass (impacted gut), blocking the digestive tract of the rabbit. Food in an immobile gut may also ferment, causing significant gas buildup and resultant gas pain for the rabbit.
The first noticeable symptom of GI stasis may be that the rabbit suddenly stops eating. Treatment frequently includes intravenous or subcutaneous fluid therapy (rehydration through injection of a balanced electrolyte solution), pain control, possible careful massage to promote gas expulsion and comfort, drugs to promote gut motility, and careful monitoring of all inputs and outputs. The rabbit's diet may also be changed as part of treatment, to include force-feeding to ensure adequate nutrition. Surgery to remove the blockage is not generally recommended and comes with a poor prognosis.[42]
Some rabbits are more prone to GI stasis than others. The causes of GI stasis are not completely understood, but common contributing factors are thought to include stress, reduced food intake, low fiber in the diet, dehydration, reduction in exercise or blockage caused by excess fur or carpet ingestion. Stress factors can include changes in housing, transportation, or medical procedures under anesthesia. As many of these factors may occur together (poor dental structure leading to decreased food intake, followed by a stressful veterinary dental procedure to correct the dental problem) establishing a root cause may be difficult.[43]
GI stasis is sometimes misdiagnosed as "hair balls" by veterinarians or rabbit keepers not familiar with the condition.[44][45] While fur is commonly found in the stomach following a fatal case of GI stasis, it is also found in healthy rabbits. Molting and chewing fur can be a predisposing factor in the occurrence of GI stasis, however, the primary cause is the change in motility of the gut.
Dental problems
Dental disease has several causes, namely genetics, inappropriate diet, injury to the jaw, infection, or cancer.
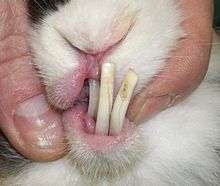
- Malocclusion: Rabbit teeth are open-rooted and continue to grow throughout their lives. In some rabbits, the teeth are not properly aligned, a condition called malocclusion. Because of the misaligned nature of the rabbit's teeth, there is no normal wear to control the length to which the teeth grow. There are three main causes of malocclusion, most commonly genetic predisposition, injury, or bacterial infection. In the case of congenital malocclusion, treatment usually involves veterinary visits in which the teeth are treated with a dental burr (a procedure called crown reduction or, more commonly, teeth clipping) or, in some cases, permanently removed. In cases of simple malocclusion, a block of wood for the rabbit to chew on can rectify this problem.
- Molar spurs: These are spurs that can dig into the rabbit's tongue and/or cheek causing pain. These should be filed down by an experienced exotic veterinarian specialised in rabbit care, using a dental burr, for example.
- Osteoporosis: Rabbits, especially neutered females and those that are kept indoors without adequate natural sunlight, can suffer from osteoporosis, in which holes appear in the skull by X-Ray imaging. This reflects the general thinning of the bone, and teeth will start to become looser in the sockets, making it uncomfortable and painful for the animal to chew hay. The inability to properly chew hay can result in molar spurs, as described above, and weight loss, leading into a downward spiral if not treated promptly. This can be reversible and treatable. A veterinary formulated liquid calcium supplement[46] with vitamin D3 and magnesium can be given mixed with the rabbit's drinking water, once or twice per week, according to the veterinarian's instructions. The molar spurs should also be trimmed down by an experienced exotic veterinarian specialised in rabbit care, once per 1–2 months depending on the case.
Signs of dental difficulty include difficulty eating, weight loss and small stools and visibly overgrown teeth. However, there are many other causes of ptyalism, including pain due to other causes.[47]
Respiratory and conjunctival problems
An over-diagnosed ailment amongst rabbits is respiratory infection, known colloquially as "snuffles". Pasteurella, a bacterium, is usually misdiagnosed and this is known to be a factor in the overuse of antibiotics among rabbits.[48] A runny nose, for instance, can have several causes, among those being high temperature or humidity, extreme stress, environmental pollution (like perfume or incense), or a sinus infection. Options for treating this is removing the pollutant, lowering or raising the temperature accordingly, and medical treatment for sinus infections.[48] Pasteurella does live naturally in a rabbit's respiratory tract, and it can flourish out of control in some cases. In the rare event that happens, antibiotic treatment is necessary.
Sneezing can be a sign of environmental pollution (such as too much dust) or a food allergy.
Runny eyes and other conjunctival problems can be caused by dental disease or a blockage of the tear duct. Environmental pollution, corneal disease, entropion, distichiasis, or inflammation of the eyes are also causes. This is easy to diagnose as well as treat.[48]
Viral diseases
Rabbits are subject to infection by a variety of viruses. Some have had deadly and widespread impact.

Myxomatosis
Myxomatosis is a virulent threat to all rabbits but not to humans.[49] The intentional introduction of myxomatosis in rabbit-ravaged Australia killed an estimated 500 million feral rabbits between 1950 and 1952. The Australian government will not allow veterinarians to purchase and use the myxomatosis vaccine that would protect domestic rabbits, for fear that this immunity would be spread into the wild via escaped livestock and pets.[50] This potential consequence is also one motivation for the pet-rabbit ban in Queensland.[51]
In Australia, rabbits caged outdoors in areas with high numbers of mosquitoes are vulnerable to myxomatosis. In Europe, fleas are the carriers of myxomatosis. In some countries, annual vaccinations against myxomatosis are available.
Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD)
Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD), also known as viral hemorrhagic disease (VHD) or rabbit calicivirus disease (RCD),[52] is caused by a rabbit-specific calicivirus known as RHDV or RCV. Discovered in 1983, RHD is highly infectious and usually fatal. Initial signs of the disease may be limited to fever and lethargy, until significant internal organ damage results in labored breathing, squealing, bloody mucus, and eventual coma and death. Internally, the infection causes necrosis of the liver and damages other organs, especially the spleen, kidneys, and small intestine.
RHD, like myxomatosis, has been intentionally introduced to control feral rabbit populations in Australia and (illegally) in New Zealand, and RHD has, in some areas, escaped quarantine. The disease has killed tens of millions of rabbits in China (unintentionally) as well as Australia, with other epidemics reported in Bolivia, Mexico, South Korea, and continental Europe. Rabbit populations in New Zealand have bounced back after developing a genetic immunity to RHD, and the disease has, so far, had no effect on the genetically divergent native wild rabbits and hares in the Americas.
In the United States, an October 2013 USDA document[53] stated:
RHD has been found in the United States as recently as 2010, and was detected in Canada in 2011. Thus far, outbreaks have been controlled quickly through quarantine, depopulation, disease tracing, and cleaning and disinfection; however, rabbit losses have been in the thousands. An RHD vaccine exists, but it is not recommended for use where the disease is not widespread in wildlife, as it may hide signs of disease and is not considered a practical response for such a rapidly spreading disease.
In the UK, reports of RHD (as recently as February 2018) have been submitted to the British Rabbit Council's online "Notice Board".[54] Vaccines for RHD are available—and mandatory—in the UK.
West Nile virus
West Nile virus is another threat to domestic as well as wild rabbits.[55] It is a fatal disease, and while vaccines are available for other species, there are none yet specifically indicated for rabbits.[56]
Wry neck & parasitic fungus
Wry neck (or head tilt) is a condition in rabbits that can be fatal, due to the resulting disorientation that causes the animal to stop eating and drinking. Inner ear infections or ear mites, as well as diseases or injuries affecting the brain (including stroke) can lead to wry neck. The most common cause, however, is a parasitic microscopic fungus called Encephalitozoon cuniculi (E. cuniculi). Note that: "despite approximately half of all pet rabbits carrying the infection, only a small proportion of these cases ever show any illness".[57] Some vets now recommend treating rabbits against E. cuniculi. The usual drugs for treatment and prevention are the benzimidazole anthelmintics, particularly fenbendazole (also used as a deworming agent in other animal species). In the UK, fenbendazole (under the brand name Panacur Rabbit), is sold over-the-counter in oral paste form as a nine-day treatment. Fenbendazole is particularly recommended for rabbits kept in colonies and as a preventive before mixing new rabbits with each other.[57]
Fly strike
Fly strike, or blowfly strike, (Lucilia sericata) is a condition that occurs when flies (particularly botflies) lay their eggs in a rabbit's damp or soiled fur, or in an open wound. Within 12 hours, the eggs hatch into the larval stage of the fly, known as maggots. Initially small but quickly growing to 15 millimetres (0.59 in) long, maggots can burrow into skin and feed on an animal's tissue, leading to shock and death. The most susceptible rabbits are those in unsanitary conditions, sedentary ones, and those unable to clean their excretory areas. Rabbits with diarrhea should be inspected for fly strike, especially during the summer months.[58] The topical treatment Rearguard® (from Novartis) is approved in the United Kingdom for 10-week-per-application prevention of fly strike.[59]
Breeds

As of 2017, there were at least 305 breeds of domestic rabbit in 70 countries around the world.[60] The American Rabbit Breeders Association currently recognizes 49 rabbit breeds[61] and the British Rabbit Council recognizes 106.[62] Selective breeding has produced rabbits ranging in size from dwarf to giant. Across the world, rabbits are raised as livestock (in cuniculture) for their meat, pelts, and wool, and also by fanciers and hobbyists as pets.
Rabbits have been selectively bred since ancient times to achieve certain desired characteristics.[63] Variations include size and body shape, coat type (including hair length and texture), coat color, ear carriage (erect or lop), and even ear length.[64] As with any animal, domesticated rabbits' temperaments vary in such factors as energy level and novelty seeking.
Most genetic defects in the domestic rabbit (such as dental problems in the Holland Lop breed) are due to recessive genes.[65] Genetics are carefully tracked by fanciers who show rabbits, to breed out defects.
As pets

Rabbits have been kept as pets in Western nations since the 19th century, but because of the destructive history of feral rabbits in Australia, domestic rabbits are illegal as pets in Queensland.[3] Depending upon its size, a rabbit may be considered a type of pocket pet. Rabbits can bond with humans,[66] can learn to follow simple voice commands and to come when called,[30]:166 and are curious and playful.
Rabbits do not make good pets for small children because rabbits are fragile and easily injured by rough handling, can bite when hurt or frightened, and are easily frightened by loud noises and sudden motions.[67] With the right guidance, rabbits can be trained to live indoors perfectly.[68]
Rabbits are especially popular as pets in the United States during the Easter season, due to their association with the holiday. However, animal shelters that accept rabbits often complain that during the weeks and months following Easter, there is a rise in unwanted and neglected rabbits that were bought as Easter gifts, especially for children.[69] Similar problems arise in rural areas after county fairs and the like, in jurisdictions where rabbits are legal prizes in fairground games.
Thus, there are many humane societies, animal shelters, and rescue groups that have rabbits available for pet adoption. Fancy rabbit breeds are often purchased from pet stores, private breeders, and fanciers.
House rabbits

Rabbits may be kept as small house pets and "rabbit-proofed" spaces reduce the risks associated with their intrinsic need to chew.[26][27] Rabbits are easily litter box trained[70] and a rabbit that lives indoors may be less exposed to the dangers of predators, parasites, diseases, adverse weather, and pesticides, which in turn increases their lifespan.[26] Rabbits are often compatible with others of their kind, or with birds or guinea pigs, but opinion differs regarding the dangers of housing different species together. For example, while rabbits can synthesize their own Vitamin C, guinea pigs cannot, so the two species should not be fed the same diet. Also, most rabbits tend to be stronger than guinea pigs, so this may cause deliberate or inadvertent injury.[71] Some people consider rabbits a pocket pet even though they are rather large.
Keeping a rabbit as a house companion was popularised by Sandy Crook in her 1981 book Your French Lop. In 1983, at the American Family Pet Show in Anaheim, California (attended by 35,000), Crook presented her personal experiences living with an indoor rabbit as evidence of a human-rabbit bond.[72] In the late 1980s, it became more common to litter box train a rabbit and keep it indoors, after[73] the publication of Marinell Harriman's House Rabbit Handbook: How to Live with an Urban Rabbit in 1985. (The book's fifth edition was published in 2013.)[74]
As the domestic descendants of wild prey animals, rabbits are alert, timid creatures that startle fairly easily, and many of their behaviors are triggered by the fight-or-flight response to perceived threats. According to the House Rabbit Society, the owner of a pet rabbit can use various behavioral approaches to gain the animal's trust and reduce aggression, though this can be a long and difficult process.[33]
In addition, there is evidence to suggest that young rabbits that occupy the periphery of the "litter huddle" obtain less milk from the mother and, as a result, have a lower weight. It has been suggested that this factor may contribute to behavioural differences in litter mates during adolescence.[75]
Care
Not all veterinarians will treat rabbits, and pet owners may have to seek out an Exotic Animal Veterinarian for their rabbit's care. Rabbits need regular checkups at the veterinarian because they may hide signs of illness or disease. Additionally, rabbits need regular maintenance in the form of being able to chew on something and having their nails trimmed regularly.
Advantages and disadvantages

The advantages of keeping rabbits as pets is that they are clean, smart, cute, soft and have a low carbon footprint.[77] They may or may not react favorably to handling and petting depending on their personality and how they were raised. There are also many different sizes and characteristics available, owing to a long history of breeding. Rabbits are friendly to each other and are often compatible with other pets. Rabbits are herbivores and their diet is relatively simple. Compared to other small animals kept as pets, rabbits are physically robust creatures with strong hind legs that enable them to run fast, and they have powerful teeth. Rabbits should never be picked up by the ears or the "scruff" on the back of their neck because "their skeletons are light compared to their bodies, and they susceptible to trauma from falling, twisting, and kicking".[78] Rabbits breed rapidly and so it is often easy, and affordable, to find one to buy or adopt.
Some disadvantages of keeping rabbits as pets is that they may chew many things in the house. Unneutered male rabbits may spray their territory with a strong-smelling urine, unspayed female urine is also pungent, and so the litter box may smell. Rabbits can bite and scratch, and may do so to communicate displeasure, or if ignored; it is a part of normal communication and cannot be stopped entirely. They have to be picked up and handled properly to avoid injury to the rabbit or the owner. They may leave faeces around the house and are not always that conscious of leaving their droppings in the litter box. Rabbits can potentially be aggressive and territorial. Some rabbits may also be unfriendly, and then would be unsuitable as pets for children.
Rabbits have a different body language to the most common domestic pets: cats and dogs. If someone wants a rabbit and is only familiar with those pet animals, then they would have to learn a lot about caring for this species and the behaviour of rabbits. They are often compared to guinea pigs but they may be as similar, in care and behaviour, to guinea pigs as they are to cats. Like cats, they are smart and can be litterbox trained. They also use their teeth and claws as weapons of defense and they can jump like a cat. They are quiet like a cat and independent, but they are also quite curious. Another animal they might be compared to is a chinchilla.
As livestock
Rabbits have been kept as livestock since ancient times for their meat, wool, and fur. In modern times, rabbits are also utilized in scientific research as laboratory animals.
Meat rabbits

Breeds such as the New Zealand and Californian are frequently utilized for meat in commercial rabbitries. These breeds have efficient metabolisms and grow quickly; they are ready for slaughter by approximately 14 to 16 weeks of age.
Rabbit fryers are rabbits that are between 70 and 90 days of age, and weighing between 3 and 5 lb (1 to 2 kg) live weight. Rabbit roasters are rabbits from 90 days to 6 months of age weighing between 5 and 8 lb (2 to 3.5 kg) live weight. Rabbit stewers are rabbits from 6 months on weighing over 8 lb.
Any type of rabbit can be slaughtered for meat, but those exhibiting the "commercial" body type are most commonly raised for meat purposes. Dark fryers (any other color but albino whites) are sometimes lower in price than albino fryers because of the slightly darker tinge of the fryer (purely pink carcasses are preferred by consumers) and because the dark hairs are easier to see than if there are residual white hairs on the carcass. There is no difference in skinability.
Wool rabbits
Rabbits such as the Angora, American Fuzzy Lop, and Jersey Wooly produce wool. However, since the American Fuzzy Lop and Jersey Wooly are both dwarf breeds, only the much larger Angora breeds such as the English Angora, Satin Angora, Giant Angora, and French Angoras are used for commercial wool production. Their long fur is sheared, combed, or plucked (gently pulling loose hairs from the body during molting) and then spun into yarn used to make a variety of products. Angora sweaters can be purchased in many clothing stores and is generally mixed with other types of wool. Rabbit wool, called Angora, is 2.5 times warmer than sheep's wool.[79]

Fur rabbits
Rabbit breeds that were developed for their fur qualities include the Rex with its plush texture, the Satin with its lustrous color, and the Chinchilla for its exotic pattern. White rabbit fur may be dyed in an array of colors that aren't produced naturally. Rabbits in the fur industry are fed a diet focused for robust coat production and pelts are harvested after the rabbit reaches prime condition, which takes longer than in the meat industry. Rabbit fur is used in local and commercial textile industries throughout the world. China imports much of its rabbit fur from Scandinavia (80%) and some from North America (5%), according to the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service GAIN Report CH7607.
Laboratory rabbits
Rabbits have been and continue to be used in laboratory work such as production of antibodies for vaccines and research of human male reproductive system toxicology. In 1972, around 450,000 rabbits were used for experiments in the United States, decreasing to around 240,000 in 2006.[80] The Environmental Health Perspective, published by the National Institute of Health, states, "The rabbit [is] an extremely valuable model for studying the effects of chemicals or other stimuli on the male reproductive system."[81] According to the Humane Society of the United States, rabbits are also used extensively in the study of bronchial asthma, stroke prevention treatments, cystic fibrosis, diabetes, and cancer.
The New Zealand White is one of the most commonly used breeds for research and testing.

The use of rabbits for the Draize test, a method of testing cosmetics on animals,[82][83] has been cited as an example of cruelty in animal research by animal rights activists.[84][85] Albino rabbits are typically used in the Draize tests because they have less tear flow than other animals, and the lack of eye pigment makes the effects easier to visualize.[86]
Housing
Rabbits can live outdoors in properly constructed, sheltered hutches, which provide protection from the elements in winter and keep rabbits cool in summer heat. To protect from predators, rabbit hutches are usually situated in a fenced yard, shed, barn, or other enclosed structure, which may also contain a larger pen for exercise.[87] Rabbits in such an environment can alternatively be allowed to roam the secured area freely, and simply be provided with an adapted doghouse for shelter. A more elaborate setup is an artificial warren. However, because of stress related to being inside confined spaces too small for a rabbit, it is recommended that instead of a cage, domestic rabbits free-roam indoors.[88]
Show jumping
Rabbit show jumping, a form of animal sport between rabbits, began in the 1970s and has since become popular in Europe, particularly Sweden and the United Kingdom. When rabbit jumping was first starting out, the rules of competition were the same as horse jumping rules. However, rules were later changed to reflect a rabbit's abilities. The first national championship for rabbit show jumping was held in Stockholm, Sweden in 1987.[89] Any rabbit, regardless of breed, may participate in this kind of competition, as it is based on athletic skill.
See also
References
- Irving-Pease, Evan K.; Frantz, Laurent A.F.; Sykes, Naomi; Callou, Cécile; Larson, Greger (2018). "Rabbits and the Specious Origins of Domestication". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 33 (3): 149–152. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2017.12.009. ISSN 0169-5347. PMID 29454669.
- Lovett, Ian (19 April 2014). "When Delight Turns to Reality, It's Goodbye, Easter Bunny". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- "Rabbit Laws in QLD: Real life threat". Greencross Vets. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- Plummer, D. Brian (David Brian) (2001). In pursuit of Coney. [Place of publication not identified]: Coch-y-Bonddu Books. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-9533648-8-6. OCLC 786137135.
- Anthon, Charles (1850). A System of Ancient and Mediæval Geography for the Use of Schools and Colleges. Harper. p. 14.
A System of Ancient and Mediæval Geography for the Use of Schools and Colleges.
- Moore, Lucile C. (2005). A House Rabbit Primer: Understanding and Caring for your Companion Rabbit. Santa Monica, CA: Santa Monica Press, LLC. pp. 19–20. ISBN 1595808736.
- Pliny, the Elder, , Natural history, 8.81 (55) The different species of hares, online: http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.02.0137%3Abook%3D8%3Achapter%3D81
- Irving-Pease, Evan K.; Frantz, Laurent A. F.; Sykes, Naomi; Callou, Cécile; Larson, Greger (2018-03-01). "Rabbits and the Specious Origins of Domestication". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 33 (3): 149–152. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2017.12.009. ISSN 0169-5347. PMID 29454669.
- Amato, Sarah (2015). Beastly Possessions : Animals In Victorian Consumer Culture. Toronto, Canada: University Of Toronto Press. pp. 31–32. ISBN 978-1-4426-1760-5. OCLC 1124537499.
- "Heritage Rabbits - Belgian Hare". The Livestock Conservancy. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
Status: Threatened
- "Hare Survey - Submitted by the Rare Breed Rabbits Group". American Belgian Hare Club. Archived from the original on 21 February 2018. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- Franco, Nuno (19 March 2013). "Animal Experiments in Biomedical Research: A Historical Perspective". Animals. 3 (1): 238–273. doi:10.3390/ani3010238. PMC 4495509. PMID 26487317.
- Online Etymology Dictionary
- "The Collective Noun Page". Retrieved January 30, 2008.
- "Genome of Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)". Washington, DC: United States National Institutes of Health. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- Gissi, C.; Gullberg, A.; Arnason, U. (1998). "The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the rabbit, Oryctolagus cuniculus". Genomics. 50 (2): 161–169. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5282. PMID 9653643.
- Carneiro, Miguel; Afonso, Sandra; Geraldes, Armando; Garreau, Hervé; Bolet, Gerard; Boucher, Samuel; Tircazes, Aurélie; Queney, Guillaume; Nachman, Michael W.; Ferrand, Nuno (2011). "The Genetic Structure of Domestic Rabbits". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 28 (6): 1801–1816. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr003. PMC 3695642. PMID 21216839.
- Maertens, L. (1999). "Towards reduced feeding costs, dietary safety and minimal mineral excretion in rabbits: A review". World Rabbit Science. 7 (2): 65–74. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- "Hay and Pellets: What do you feed a bunny?". IndianaHRS.org. House Rabbit Society, Indiana Chapter. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- Official Guidebook to Raising Better Rabbits and Cavies. Bloomington, Illinois: American Rabbit Breeders Association. 1991.
- Rees Davies, R.; Rees Davies, J. A. E. (2003). "Rabbit Gastro-intestinal Physiology" (PDF). Vet. Clin. Exot. Anim. 6 (1): 139–153. doi:10.1016/S1094-9194(02)00024-5. PMID 12616837.
- "Rabbit – Nutrition & Management". RabbitChow.com. Purina Mills. April 19, 2011.
- Maertens, L.; Labas, F.; Szendro, Z. S. (2006). "Rabbit Milk: A review of quantity, quality, and non-dietary affecting factors". Official Journal of the World Rabbit Science Association. 14 (4). doi:10.4995/wrs.2006.565. hdl:10251/9560.
- Bremel (University of Wisconsin), Robert D.; Jensen (Handbook of Milk Composition), R.G. "Milk Composition - Species Table". Lactation Biology. University of Illinois - Department of Animal Sciences. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- "What's the Lifespan of a Rabbit?". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society. Retrieved October 2, 2015.
- "Outdoor and Indoor Hazards". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society.
- "Chewing". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society. Retrieved February 25, 2010.
- Dawson, Bronwyn (July 10, 2011). "Dealing with Medical Emergencies". House Rabbit Journal. House Rabbit Society. II (4). Retrieved October 2, 2015. A differently formatted version is also available here.
- Krempels, Diana. "Rabbit Health: Spay or Neuter My Rabbit?". Bio.Miami.edu. Miami University College of Arts and Sciences, Department of Biology. Archived from the original on December 7, 2014. Retrieved October 3, 2015.
- Pavia, Audrey (2003). Rabbits for Dummies. New York: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-7645-0861-5.
- "Spaying and Neutering". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society. Retrieved October 29, 2007.
- "Litter Training". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society. Retrieved October 3, 2015.
- Davis, Susan (2 April 2013). "Aggression". House Rabbit Society. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
- "Health Concerns". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
- British Veterinary Association Rabbit Care Downloads http://www.link2content.co.uk/uploads/bva/rabbit.pdf%5B%5D
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-02-25. Retrieved 2008-05-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Intervet vaccination literature.
- "Why Rabbits Should Not Be Declawed". www.rabbit.org.
- "Rabbit Care: Rabbit Never Do's". www.rabbitwise.org.
- Guarraci, F.; Knapp, B. (1999). "An electrophysiological characterization of ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons during differential pavlovian fear conditioning in the awake rabbit" (PDF). Behavioural Brain Research. 99 (2): 169–179. doi:10.1016/S0166-4328(98)00102-8. PMID 10512583.
- McBride, Anne; Day, Simone; McAdie, Tina; Meredith, Anna; Barley, Jasmine; Hickman, Janice; Lawes, Lesley (2006). "Trancing rabbits: Relaxed hypnosis or a state of fear?". Proceedings of the VDWE International Congress on Companion Animal Behaviour and Welfare. Sint-Niklaas, Belgium: Vlaamse Dierenartsenvereniging (VDV): 135–137. Archived from the original on July 12, 2016. HopperHome PDF archived November 24, 2010.
- "Housing". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Society.
- Harkness, John E. (2010). Biology and Medicine of Rabbits and Rodents (5th ed.). Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 306–308. ISBN 978-0-8138-1531-2.
- Jenkins, Jeffery (1997). "Gastrointestinal Diseases". In Hillyer, E. V.; Quesenberry, K. (eds.). Ferrets, Rabbits and Rodents: Clinical Medicine and Surgery. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co. pp. 178–179. ISBN 978-0-7216-4023-5.
- House Rabbit Society: Sluggish Motility in the Gastrointestinal Tract
- University of Miami Department of Biology: Gastrointestinal Stasis, The Silent Killer
- "Zolcal D liquid calcium". www.vetark.co.uk. Retrieved 2016-12-16.
- "Differential diagnosis for ptyalism". www.medirabbit.com.
- Respiratory Disease by Susan A. Brown
- "Myxomatosis (Chapter 2.6.1)" (PDF). Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals ("Terrestrial Manual 2014"). World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) (Lagomorpha (Chapter 2.6)): 1–18. May 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 March 2018. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- "A Statement from the Chief Veterinary Officer (Australia) on myxomatosis vaccine availability in Australia". Australian Government - Department of Agriculture and Water Resources. 12 September 2017. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- "Restricted Invasive Animals - Rabbit". Queensland [Australia] Government - Business Queensland. 22 November 2017. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- Center for Food Security & Public Health; Institute for International Cooperation in Animal Biologics (September 2007). "Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease: Viral Hemorrhagic Disease of Rabbits, Rabbit Calicivirus Disease" (PDF). CFSPH.IAState.edu. Iowa State University College of Veterinary Medicine. Retrieved October 3, 2015.
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service - Veterinary Services (October 2013). "Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease: Standard Operating Procedures: 1. Overview of Etiology and Ecology" (PDF). Foreign Animal Disease Preparedness and Response Plan (FAD PReP). United States Department of Agriculture: 1–11. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- "Notice Board". The British Rabbit Council. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- Mancinelli, Elisabetta; Cousquer, Glen. "West Nile virus infection (Lapis)". Vetstream. ISSN 2398-2969. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- Suen, Willy W.; et al. (2015). "Experimental West Nile Virus Infection in Rabbits: An Alternative Model for Studying Induction of Disease and Virus Control". Pathogens. 4 (3): 529–558. doi:10.3390/pathogens4030529. PMC 4584271. PMID 26184326.
- "Rabbits and E. cuniculi (Encephalatizoon cuniculi)". Rabbit Welfare Association & Fund. 4 May 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- Harriman, Marinell. "Fly Strike". House Rabbit Society. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- "Summary of [Rearguard] Product Characteristics (AN. 01134/2015)" (MS Word document). Veterinary Medicines Directorate. Government of the United Kingdom (gov.uk). 15 December 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- "Data export". DAD-IS (Domestic Animal Diversity Information System). FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). 21 November 2017. Retrieved 30 March 2018.
- "ARBA Recognized Breeds". American Rabbit Breeders Association. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- "Breed Standards 2016-2020" (PDF). The British Rabbit Council. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- Whitman, Bob D. (October 2004). Domestic Rabbits & Their Histories: Breeds of the World. Leawood KS: Leathers Publishing. ISBN 978-1585972753.
- "Longest ears on a rabbit". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- Botha, Mariette; Petrescu-Mag, Ioan Valentin; Hettig, Andrea (2014). "Genetic disorders in domestic rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus)". Rabbit Genetics. 4 (1): 7–47 – via https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Genetic-disorders-in-domestic-rabbits-(Oryctolagus-Botha-Petrescu-Mag/9a18d0b44369cbeca57c3322000b38093f8924d9.
- Ramnaraine, Amy (12 January 2017). "Bonding With Your Rabbit". House Rabbit Society. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
- Mixon, Carolyn (10 July 2011). "Children and Rabbits". House Rabbit Society. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- "Rabbit Facts - Top 20 Facts about Rabbits".
- "Easter Rabbits". ABC7 News. Chicago: WLS-TV. April 4, 2007. Archived from the original on February 2, 2009.
- "Litter Training". House Rabbit Society. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- Rubins, Suzanne. "Guinea Pigs as Rabbit Buddies". Rabbit.org. House Rabbit Network. Archived from the original on September 10, 2012. Retrieved June 10, 2009.
- Crook, Sandy (1986). Lop Rabbits as Pets. T.F.H. Publications. p. 8.
- DeMello, M. (2010). "Becoming rabbit: Living with and knowing rabbits". Spring: a journal of archetype and culture. 83: 237–252 – via https://animalstudiesrepository.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1009&context=acwp_habr.
- Harriman, Marinell (2013). House Rabbit Handbook: How to Live with an Urban Rabbit (5th ed.). Drollery Press. ISBN 978-0940920187.
- Reyes-Meza, Veronica; Hudson, Robyn; Martínez-Gómez, Margarita; Nicolás, Leticia; Rödel, Heiko G.; Bautista, Amando (2011-10-24). "Possible contribution of position in the litter huddle to long-term differences in behavioral style in the domestic rabbit". Physiology & Behavior. 104 (5): 778–785. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.07.019. PMID 21803066.
- "Hiding places | rspca.org.uk". www.rspca.org.uk. RSPCA. Retrieved 29 December 2019.
- nzcpe (2020-04-27). "Bunnies are Better". Planetary Ecology. Retrieved 2020-04-28.
- O'Meara, Holly (10 February 2013). "An Uplifting Experience". House Rabbit Journal (Fall 1998). 3 (11). Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- Kulpa-Eddy, Jodie; Snyder, Margaret; Stokes, William (2008). "A review of trends in animal use in the United States (1972–2006)" (PDF). AATEX. Japanese Society for Alternatives to Animal Experiments (14, Special Issue: Proceedings of the 6th World Congress on Alternatives & Animal Use in the Life Sciences, August 21–25, 2007): 163–165. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 13, 2012. Retrieved October 3, 2015.
- Morton, Daniel (April 1988). "The use of rabbits in male reproductive toxicology". Environmental Health Perspectives. U.S. National Institutes of Health. 77: 5–9. doi:10.2307/3430622. JSTOR 3430622. PMC 1474531. PMID 3383822.
- Prinsen, M. K. (2006). "The Draize Eye Test and in vitro alternatives:A left-handed marriage?". Toxicology in Vitro. 20 (1): 78–81. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2005.06.030. PMID 16055303.
- "Special Senses". ScienceDirect. 2018-01-01. pp. 673–747. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-809841-7.00022-8. Retrieved 2020-06-11.
- "Rabbits in Laboratories". PETA. 2010-06-23. Retrieved 2020-06-11.
- "Do Cosmetic Companies Still Test on Live Animals?". Scientific American. 2009-08-06. Retrieved 2020-06-11.
- Dawn, Karen (2008). Thanking the Monkey: Rethinking the Way we Treat Animals. New York: HarperCollins. pp. 239–40. ISBN 978-0-06-135185-3. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- "Rabbit Housing Options". IndianaHRS.org. House Rabbit Society, Indiana Chapter.
- https://www.rspca.org.uk/adviceandwelfare/pets/rabbits/behaviour
- Hopping versus Agility. (n.d.).
External links
- The American Rabbit Breeders Association – the oldest and largest rabbit specialist organization in the United States
- The Livestock Conservancy – a registry of the rarest breeds of domestic rabbits
- World Rabbit Science Association – an international science organization dedicated to rabbit health research
- The British Rabbit Council – recognized breeds with photographs and more
- MediRabbit – a site dedicated to spreading the knowledge of rabbit medicine and safe medication in rabbits, for the owner and the vet professional
- Rabbit Breeds - directory of ARBA-recognized breeds of rabbit
- Complete Guide of Rabbit Breeds - List of rabbit breeds approved by American Rabbit Breeders Association
- RabbitPedia.com - Source for information about rabbit care.
- House Rabbit Society – a US-based educational and advocacy organization for rabbit pet-keepers, founded in 1988
- Domestic rabbit at Curlie