Barium cyanide
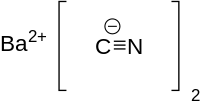
Barium cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula Ba(CN)2. It is synthesized by the reaction of hydrogen cyanide and barium hydroxide in water or petroleum ether.[1] This white crystal reacts with water and carbon dioxide in air slowly, producing highly toxic hydrogen cyanide gas.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Barium dicyanide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.021 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Ba(CN)2 | |
| Molar mass | 189.362 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystal |
| Melting point | 600 °C (1,112 °F; 873 K) |
| 18 g/100 mL (14 °C) | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Smith, R P; Gosselin, R E (1976). "Current Concepts about the Treatment of Selected Poisonings: Nitrite, Cyanide, Sulfide, Barium, and Quinidine". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 16: 189–99. doi:10.1146/annurev.pa.16.040176.001201. PMID 779614.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.