Anglo-Russian Convention
The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907, or Convention between the United Kingdom and Russia relating to Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet[1], was signed on August 31, 1907, in St. Petersburg, Russia. It ended the longstanding rivalry in Central Asia and enabled the two countries to outflank the Germans, who were threatening to connect Berlin to Baghdad with a new railroad that would probably align the Ottoman Empire with Germany.
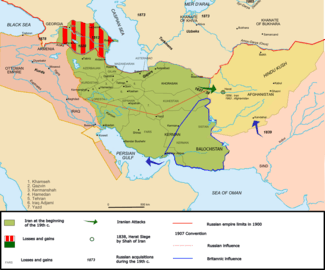 Map of southwest Asia, showing British and Russian areas of rule or influence. | |
| Signed | 31 August 1907 |
|---|---|
| Location | Saint Petersburg, Russia |
| Signatories | |
The Convention ended the long dispute over Persia. Great Britain promised to stay out of northern Persia, and Russia recognized southern Persia as part of the British sphere of influence. Russia also promised to stay out of Tibet and Afghanistan. In exchange, London extended loans and some political support. [2][3] The convention brought shaky British–Russian relations to the forefront by solidifying boundaries that identified respective control in Persia,[4][5] Afghanistan and Tibet. It delineated spheres of influence in Persia, stipulated that neither country would interfere in Tibet's internal affairs and recognized Britain's influence over Afghanistan.[6][7] The agreement led to the formation of the Triple Entente.[7]
Background
During the last third of the nineteenth century, the Russian Empire's advances into Central Asia and the consolidation of Great Britain's domination of South Asia led to intense rivalry between the two European powers. The conflicting interests centered on Afghanistan, Iran, and Tibet, three states that constituted buffers between the two powers. The emergence of the German Empire as a world power and the defeat in 1905 of Russia by a nascent Asian power, the Empire of Japan, in the Russo-Japanese War, helped to persuade some British and Russian officials of a need to resolve their respective differences in Asia.[8] There was talk of an entente during the 1880s and 1890s, especially after Britain's occupation of Egypt in 1882. However stiff resistance in Britain to a deal with Russia.[9] In the leadup to the convention, there were discussions on the Straits question.
[[Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs}Foreign Minister]] Sir Edward Grey, thought entente with Russia a good idea. On 20 October 1905, during the election, he said:[10]
...if Russia accepts, cordially and whole-heartedly, our intention to preserve the peaceable possession of our Asiatic possessions, then I am quite sure that in this country no government will make it its business to thwart or obstruct Russia's policy in Europe. On the contrary, it is urgently desirable that Russia's position and influence be re-established in the councils of Europe.
and later, writing to his ambassador to Russia Sir Arthur Nicolson:[9]
It is not for us to propose changes with regard to the treaty conditions of the Dardanelles. I think some change in the direction desired by Russia would be admissible and we should be prepared to discuss the question if Russia introduces it.
In early 1907, Alexander Izvolsky, the Russian ambassador at Paris, raised the question. and talks were carried on in London with Russian Ambassador Count Alexander Benckendorff. Little is known but the "suggestion appears to have been made that Russia should have free egress from the Black Sea through the Straits, while other powers should have the right to send their vessels of war into the Straits without going into the Black Sea" together with some talk of "Russia's occupying the Bosphorus and England the Dardanelles, after which the Straits might be opened to other warships as well." In the event nothing came of the discussions at the time.[9]
Rise of Germany
| Events leading to World War I | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
On May 20, 1882, Germany entered into the Triple Alliance with Italy and Austria-Hungary, complementing its industrial and socio-political climb in the world arena. Furthermore, Germany dramatically increased its military output from the early 1900s up to the outbreak of World War I. Under the new German empire, Chancellor Otto von Bismarck worked to increase the nation's wealth and reach what was then the zenith of German power. While Britain and Russia were hostile to Germany's imperialistic motives, members of the Triple Alliance were in turn somewhat threatened by Britain's and Russia's aggressive foreign policy tactics and wealth derived from their colonies. Thus, military and territorial expansion was Germany's key to making itself a major player in the international arena of power. Germany's interest in the Middle East took a secondary position, one subordinate to Germany's primary policy toward Europe, throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries. While of secondary importance, it was a tool that was used to manipulate the Middle Eastern attempt to play off the Western powers against each other. Berlin peacefully penetrated the Ottoman Empire and had few colonial aspirations in the region.[11]
Trouble in Persia
In 1905, revolutionary activity spread throughout Tehran, forcing the shah to accept a constitution, allow the formation of a majles (parliamentary assembly), and hold elections. Major figures in the revolution had secular goals, which then created rifts in the clergy to the advantage of the monarchy. Neither Britain nor Russia approved of the new liberal, unstable, political arrangement, as preferred a stable puppet government that submitted to foreign concessions and worked well with their imperialist goals.
To facilitate the situation in Persia, Britain and Russia discussed splitting it “into three zones. The agreement they wanted would allocate the north, including Isfahan, to Russia; the south-east, especially Kerman, Sistan, and Baluchistan to Britain; and demarcate the remaining land between the two powers as a "neutral zone." The division of Persia reinforced Great Power control over these respective territorial and economic interests in the country as well as allowed for contrived interference in Persia's political system. With foreign influence, revolution was outflanked by a combination of European and monarchist activities. As a result, Persians learned "that however predatory the two 'neighbors' were, they were even more dangerous when they put aside their rivalries."
Consequently, in 1907, Britain and Russia signed an agreement to regulate their economic and political interests.
Terms
With respect to Iran, the agreement recognized the country's strict independence and integrity but then divided it into three separate zones. The agreement designated all of northern Iran, which bordered Russia's possessions in Transcaucasia and Central Asia, as an exclusive sphere of influence for Russian interests. The northern zone was defined as beginning at Qasr-e Shirin in the west, on the border with the Ottoman Empire, and running through Tehran, Isfahan and Yazd to the eastern border, where the frontiers of Afghanistan, Iran, and Russia intersected.
A smaller zone in southeastern Iran, which bordered British India, was recognized as an exclusive sphere for Britain. The British zone extended west as far as Kerman in the south central and Bandar Abbas in the south. The area separating these two spheres, including part of central Iran and the entire southwest, was designated a neutral zone in which both countries and their respective private citizens could compete for influence and commercial privileges.
For Britain and Russia, the agreement was important in establishing a diplomatic alignment that endured until World War I. The government of Iran, however, had not been consulted about the agreement but was informed after the fact. Although not in a position to prevent Britain and Russia from implementing the agreement, the Iranian government refused to recognize the accord's legitimacy since it threatened the country's integrity and independence.
Iranian nationalists, in particular, felt aggravated by Britain, a country that they had considered as a democratic beacon during the Constitutional Revolution. Thus, an important legacy of the agreement was the growth of anti-British sentiment and other anti-Western attitudes as strong components of Iranian nationalism.
The agreement did not eliminate all competition between the two powers with respect to their policies in Iran, but after 1907, broad co-operation was fostered, often to the detriment of Iranian interests. In particular, Britain and Russia intervened in Iran's domestic politics by supporting the royalists in their contest with the constitutionalists.
The agreement lapsed in 1918, after it was renounced by the new revolutionary Soviet Russia.[12][13][14]
See also
- Dogger Bank Incident
- Entente Cordiale
- Franco-Russian Alliance
- The Great Game
- Persian Campaign
References
- See text in British Documents on the Origins of the War 1898-1914, Volume IV, The Anglo-Russian Rapprochement 1903-7. Edited by G. P. Gooch and H Temperley. Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London 1929. pp 618-621. Appendix I - Full Text of Convention between the United Kingdom and Russia relating to Persia (Iran), Afghanistan, and Tibet, Signed At St Petersburgh, August 31, 1907 (in French)
- Barbara Jelavich, St. Petersburg and Moscow: Tsarist And Soviet Foreign Policy, 1814-1974 (1974), pp 247-49, 254-56.
- Ewen W. Edwards, "The Far Eastern Agreements of 1907." Journal of Modern History 26.4 (1954): 340-355. Online
- British Documents on the Origins of the War 1898-1914, Volume IV, The Anglo-Russian Rapprochement 1903-7. Edited by G.P. Gooch and H Temperley. Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London 1929. p618-621. Appendix IV - Revised Draft of Agreement Concerning Persia, Sent to Sir A. Nicholson by Sir Edward Grey on June 6, 1907
- Yale Law School: "Agreement concerning Persia" (in English)
- The Major International Treaties of the Twentieth Century, Volume 1. Edited by J.A.S. Grenville and B. Wasserstein. Routledge London 2001. p45. Conventions between Russia and the United Kingdom relating to Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet, St Petersburgh, August 31, 1907
- Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. Anglo-Russian Entente
- Professor of History Jennifer Siegel; Siegel, Jennifer L. Siegel; Jennifer Siegel (6 September 2002). Endgame: Britain, Russia and the Final Struggle for Central Asia. I.B.Tauris. p. 177. ISBN 978-1-85043-371-2.
- Langer 1927, p. 68.
- Langer 1927, p. 67.
- Erich Eyck, Bismarck and the German Empire (1963) pp 261–297. online.
- Kazemzadeh, Firuz. Russia and Britain in Persia, 1864–1914: A Study in Imperialism. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1968.
- Siegel, Jennifer. Endgame: Britain, Russia, and the Final Struggle for Central Asia. London and New York: Tauris, 2002.
- White, John Albert. Transition to Global Rivalry: Alliance Diplomacy and the Quadruple Entente, 1895–1907. Cambridge, U.K., and New York: Cambridge University Press, 1995.
Further reading
- "The Recent Anglo-Russian Convention" The American Journal of International Law (1907) pp 979–984 online
- Abrahamiam, Ervand, A History of Modern Iran (Cambridge University Press, 2008)
- Adelson, Roger, London and the Invention of the Middle East: Money, Power, and War, 1902–1922 (St. Edmundsbury Press, 1995)
- Churchill, Platt Rogers. The Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 (1939).
- Habberton, William. Anglo-Russian Relations Concerning Afghanistan, 1837-1907 (U. of Illinois, 1937).
- Klein, Ira. "The Anglo-Russian Convention and the Problem of Central Asia, 1907-1914," Journal of British Studies (1971) 11#1 pp. 126–147 in JSTOR
- Langer, William L. (January 1929). "Russia, the Straits Question, and the European Powers, 1904-8". The English Historical Review. 44 (173): 59–85. JSTOR 552495.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Mahajan, Sneh. British foreign policy 1874-1914: The role of India (Routledge, 2003).
- Sicker, Martin. The Bear and the Lion: Soviet Imperialism and Iran (Praeger Publishers, 1988).
- Siegel, Jennifer, Endgame: Britain, Russia and the Final Struggle for Central Asia (New York: I.B. Tauris, 2002)
- Soroka, Marina. //Britain, Russia and the Road to the First World War: The Fateful Embassy of Count Aleksandr Benckendorff (1903–16) (Routledge, 2016).
- Tomaszewski, Fiona K. A Great Russia: Russia and the Triple Entente (Greenwood Publishing Group, 2002)