Solar eclipse of October 3, 1986
| Solar eclipse of October 3, 1986 | |
|---|---|
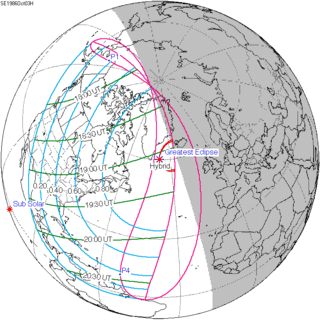 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Hybrid |
| Gamma | 0.9931 |
| Magnitude | 1 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 0 sec (0 m 0 s) |
| Coordinates | 59°54′N 37°06′W / 59.9°N 37.1°W |
| Max. width of band | 1 km (0.62 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 19:06:15 |
| References | |
| Saros | 124 (53 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9479 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on October 3, 1986. It was a hybrid event (normally, an eclipse which is annular for most of its duration, but with totality either at the beginning, end or at sometime during the eclipse) that did not officially satisfy the definition of totality. Totality occurred for a very short time (calculated at 0.2 seconds) in an area in the Atlantic Ocean, just east of the southern tip of Greenland. The path, on the surface of the Earth, was a narrow, tapered, horse-shoe, and visible only from a thin strip between Iceland and Greenland. At maximum eclipse the solar elevation was about 6°.
This eclipse was the last central eclipse of saros 124 and the only hybrid eclipse of that saros.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1986-1989
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1986-1989 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |
| 119 | 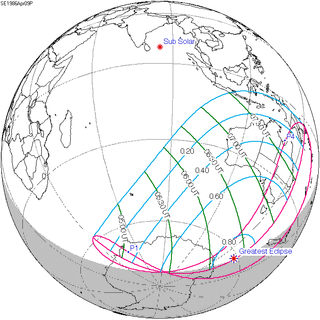 April 9, 1986 Partial |
124 |  October 3, 1986 Hybrid | |
| 129 |  March 29, 1987 Hybrid |
134 |  September 23, 1987 Annular | |
| 139 | 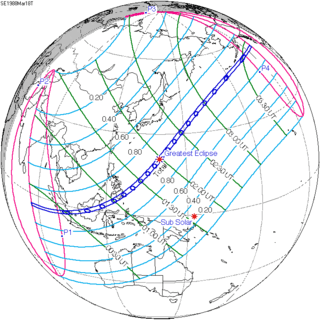 March 18, 1988 Total |
144 | 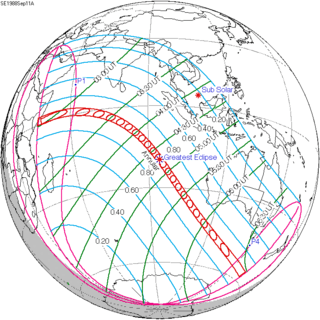 September 11, 1988 Annular | |
| 149 |  March 7, 1989 Partial |
154 |  August 31, 1989 Partial | |
Metonic cycle
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 events between July 22, 1971 and July 22, 2047 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 21-22 | May 9-11 | February 26-27 | December 14-15 | October 2-3 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 22, 1971 |
 May 11, 1975 |
 February 26, 1979 |
 December 15, 1982 |
 October 3, 1986 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 22, 1990 |
 May 10, 1994 |
 February 26, 1998 |
 December 14, 2001 |
 October 3, 2005 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 22, 2009 |
 May 10, 2013 |
 February 26, 2017 |
 December 14, 2020 |
 October 2, 2024 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
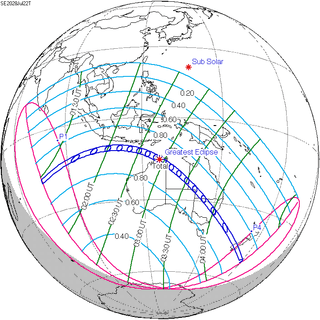 July 22, 2028 |
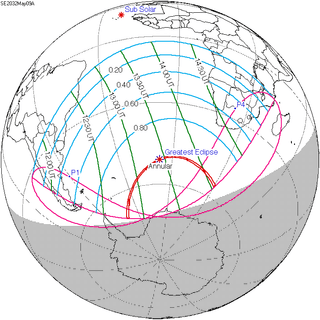 May 9, 2032 |
 February 27, 2036 |
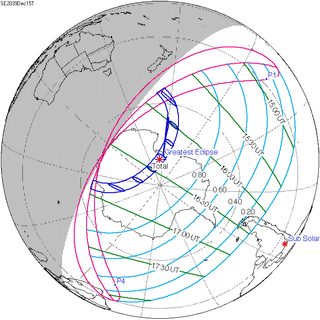 December 15, 2039 |
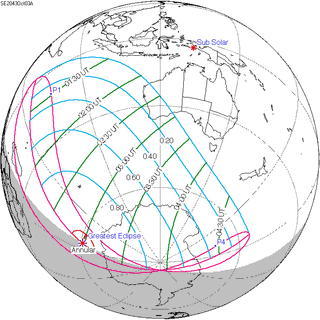 October 3, 2043 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 22, 2047 | ||||
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1986 October 3. |
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
