Solar eclipse of December 14, 1917
| Solar eclipse of December 14, 1917 | |
|---|---|
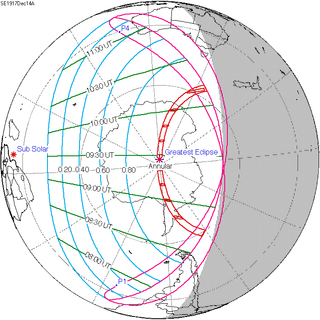 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | -0.9157 |
| Magnitude | 0.9791 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 77 sec (1 m 17 s) |
| Coordinates | 88°00′S 124°48′E / 88°S 124.8°E |
| Max. width of band | 189 km (117 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 9:27:20 |
| References | |
| Saros | 121 (55 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9323 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 14, 1917. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
This annular eclipse is notable in that the path of annularity passed over the South Pole.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1916-1920
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1916–1920 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| 111 | December 24, 1916 Partial |
116 | June 19, 1917 Partial | |
| 121 | December 14, 1917 Annular |
126 | June 8, 1918 Total | |
| 131 | December 3, 1918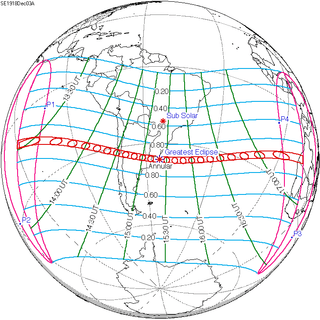 Annular |
136 | May 29, 1919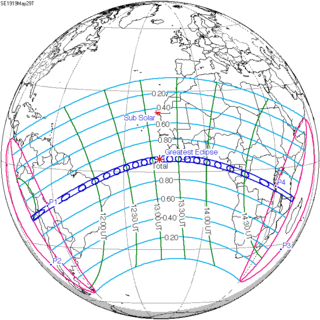 Total | |
| 141 | November 22, 1919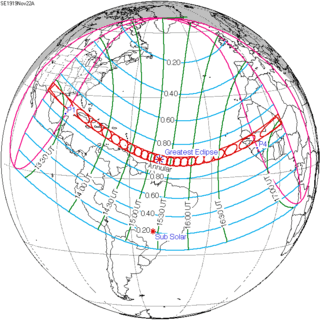 Annular |
146 | May 18, 1920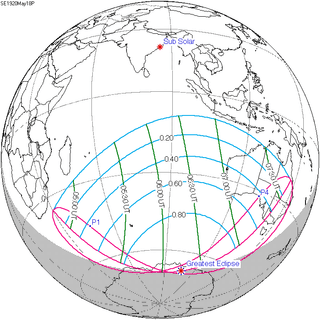 Partial | |
| 151 | November 10, 1920 Partial | |||
Notes
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1917 December 14. |
