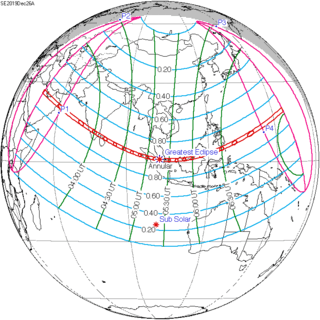
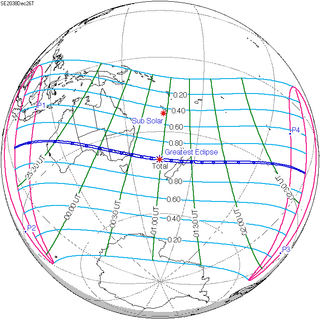
Solar eclipse of December 26, 2019
| Solar eclipse of December 26, 2019 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.4135 |
| Magnitude | 0.9701 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 220 sec (3 m 40 s) |
| Coordinates | 1°00′N 102°18′E / 1°N 102.3°E |
| Max. width of band | 118 km (73 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 5:18:53 |
| References | |
| Saros | 132 (46 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9552 |
An annular solar eclipse will occur on December 26, 2019. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The total annular eclipse will be visible in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Oman, southern India, Sri Lanka, Sumatra, Malaysia, Maldives, Indonesia, Singapore, parts of Borneo, other parts of Southeast Asia, some parts of Australia, and Guam. Population centers in the path of the total annular eclipse include Kozhikode, Coimbatore, Jaffna, Trincomalee, Sibolga, Batam, Singapore, Singkawang and Guam. Cities such as Doha, Madurai, Pekanbaru, Dumai and Kuching will narrowly miss the annular path.
Images

Animated path
Related eclipses
Astronomers Without Borders collected eclipse glasses for redistribution to Latin America and Asia for their 2019 eclipses from the Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017.[1]
Solar eclipses 2018-2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018, and August 11, 2018, occur during the previous semester series.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2018–2021 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | ||||
117.jpg) Partial from Melbourne, AU | July 13, 2018 Partial |
122 | January 6, 2019 Partial | ||
| 127 | July 2, 2019 Total |
132 | December 26, 2019 Annular | ||
| 137 | June 21, 2020 Annular |
142 | December 14, 2020 Total | ||
| 147 | June 10, 2021 Annular |
152 | December 4, 2021 Total | ||
Saros 132
It is a part of Saros cycle 132, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on August 13, 1208. It contains annular eclipses from March 17, 1569 through March 12, 2146, hybrid on March 23, 2164 and April 3, 2183 and total eclipses from April 14, 2200 through June 19, 2308. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on September 25, 2470. The longest duration of annular was 6 minutes, 56 seconds on May 9, 1641, and totality will be 2 minutes, 14 seconds on June 8, 2290.[3]
| Series members 40-50 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 40 | 41 | 42 |
 October 22, 1911 |
 November 1, 1929 |
 November 12, 1947 |
| 43 | 44 | 45 |
 November 23, 1965 |
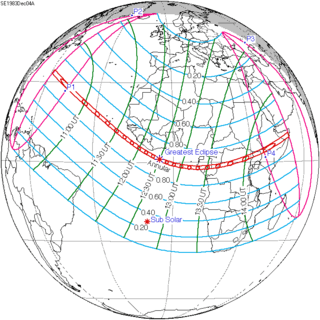 December 4, 1983 |
 December 14, 2001 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 |
 December 26, 2019 |
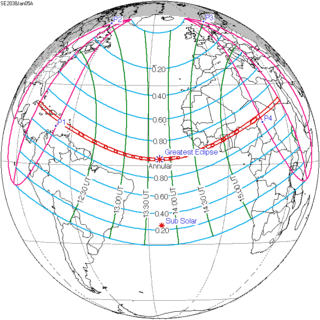 January 5, 2038 |
 January 16, 2056 |
| 49 | 50 | |
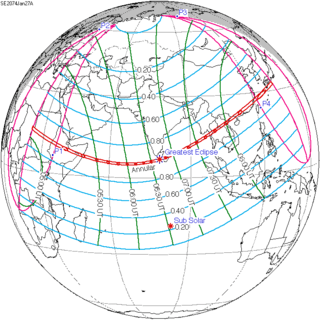 January 27, 2074 |
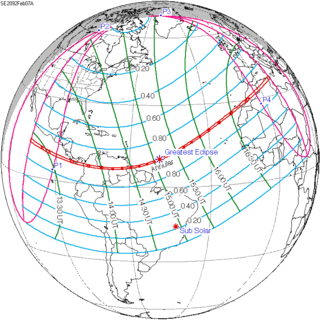 February 7, 2092 | |
Metonic series
This eclipse is a member of the Octon eclipse series, which includes 21 eclipses occurring in approximately 4 year intervals from May 21, 1993 to August 2, 2065.[4]
| Octon series with 21 events between May 21, 1993 and August 2, 2065 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 20–21 | March 9 | December 25–26 | October 13–14 | August 1–2 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
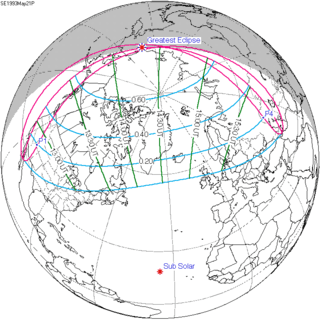 May 21, 1993 |
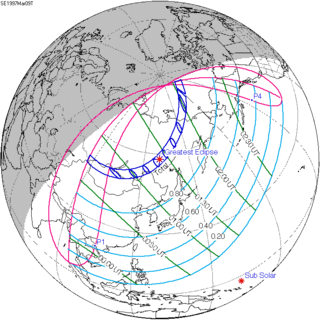 March 9, 1997 |
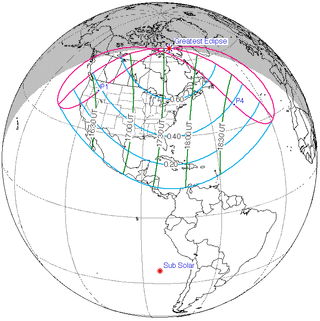 December 25, 2000 |
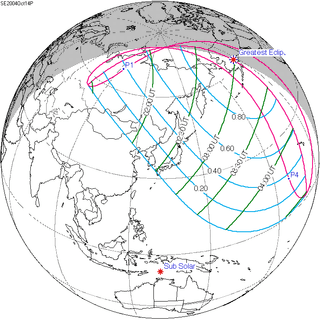 October 14, 2004 |
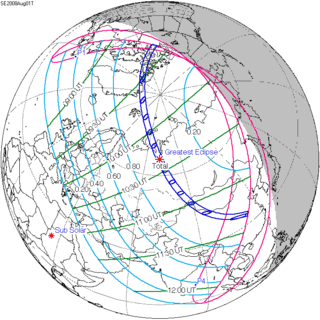 August 1, 2008 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
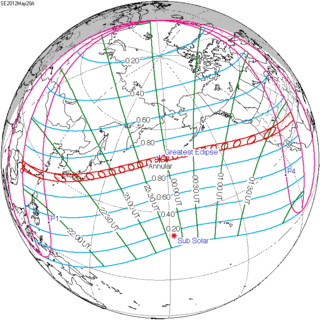 May 20, 2012 |
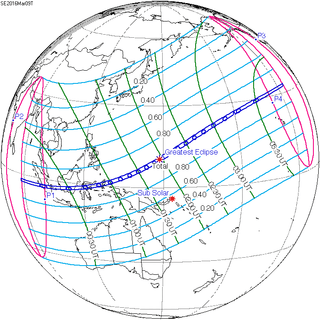 March 9, 2016 |
 December 26, 2019 |
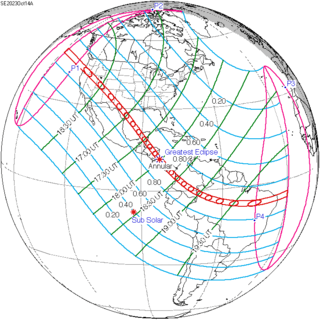 October 14, 2023 |
 August 2, 2027 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
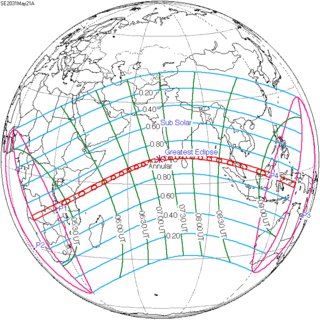 May 21, 2031 |
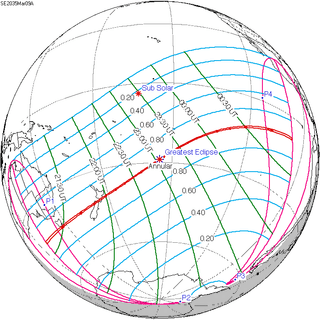 March 9, 2035 |
 December 26, 2038 |
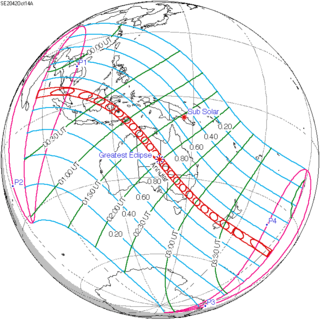 October 14, 2042 |
 August 2, 2046 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 20, 2050 |
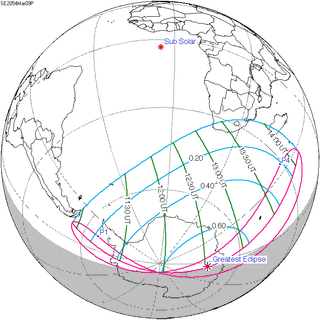 March 9, 2054 |
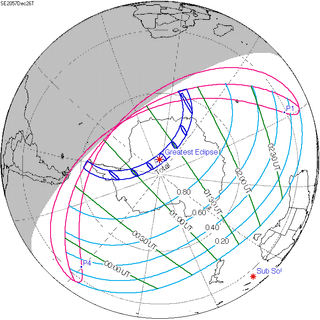 December 26, 2057 |
 October 13, 2061 |
 August 2, 2065 |
| 158 | ||||
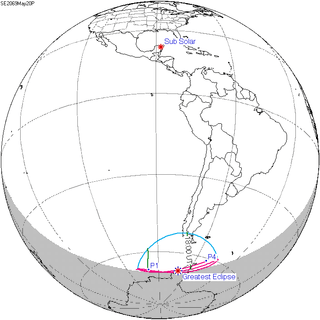 May 20, 2069 | ||||
Notes
- ↑ Cooper, Gael (2017-08-22). "Wait! Dig those eclipse glasses out of the garbage Here comes the sun. Astronomers Without Borders will be collecting the protective eyewear for use in future eclipses worldwide". Retrieved 2017-08-27.
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsaros/SEsaros132.html
- ↑ Freeth, Tony. "Note S1: Eclipses & Predictions". plos.org. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2019 December 26. |
