Solar eclipse of July 20, 1963
| Solar eclipse of July 20, 1963 | |
|---|---|
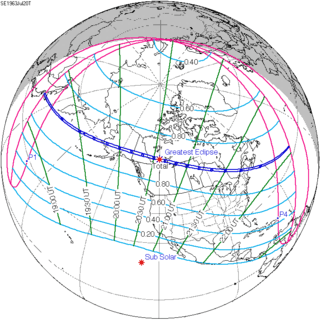 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.6571 |
| Magnitude | 1.0224 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 100 sec (1 m 40 s) |
| Coordinates | 61°42′N 119°36′W / 61.7°N 119.6°W |
| Max. width of band | 101 km (63 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 20:36:13 |
| References | |
| Saros | 145 (19 of 77) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9427 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on Saturday, July 20, 1963. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is the same size as the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Hokkaido in Japan and Kuril Islands in Soviet Union (now belonging to Russia) on July 21, and Alaska, and Maine in the United States and also Canada on July 20. Astronomer Charles H. Smiley observed the eclipse from a U.S. Air Force F-104D Starfighter supersonic aircraft that was "racing the moon's shadow" at 1,300 mph (2,100 km/h) extending the duration of totality to 4 minutes 3 seconds.[1]
In popular culture
The eclipse was featured in the comic strip Peanuts (July 15–20, 1963), with Linus demonstrating a safe way of observing the eclipse as opposed to looking directly at the eclipse. On the day the eclipse passed over his area, Linus was left helplessly standing in the rain with cloud cover entirely too thick to witness the eclipse.
It also served an important function in the plots of two Stephen King novels, Gerald's Game (1992) and Dolores Claiborne (1992) and was featured in a season 3 episode of Mad Men titled "Seven Twenty Three" (2009).[2]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1961-1964
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[3]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1961-1964 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |||
| 120 | 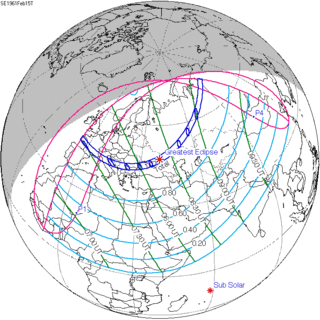 February 15, 1961 Total |
125 |  August 11, 1961 Annular | |||
| 130 | 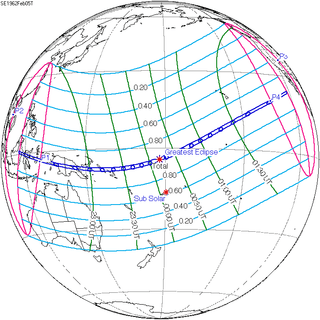 February 5, 1962 Total |
135 | 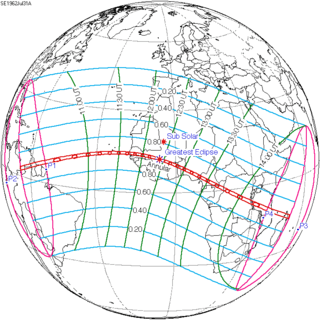 July 31, 1962 Annular | |||
| 140 |  January 25, 1963 Annular |
145 |  July 20, 1963 Total | |||
| 150 |  January 14, 1964 Partial |
155 |  July 9, 1964 Partial | |||
| Partial solar eclipses of June 10, 1964 and December 4, 1964 belong in the next lunar year set. | ||||||
Saros 145
This solar eclipse is a part of Saros cycle 145, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, 8 hours, containing 77 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on January 4, 1639, and reached a first annular eclipse on June 6, 1891. It was a hybrid event on June 17, 1909, and total eclipses from June 29, 1927, through September 9, 2648. The series ends at member 77 as a partial eclipse on April 17, 3009. The longest eclipse will occur on June 25, 2522, with a maximum duration of totality of 7 minutes, 12 seconds.[4]
| Series members 16–26 occur between 1901 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 16 | 17 | 18 |
 June 17, 1909 |
 June 29, 1927 |
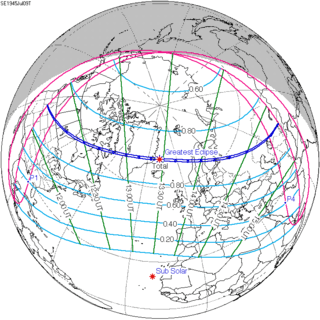 July 9, 1945 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 |
 July 20, 1963 |
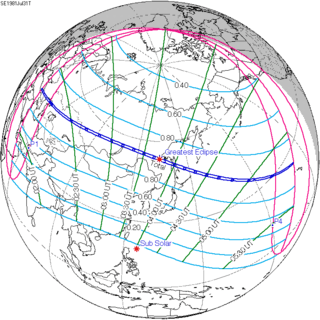 July 31, 1981 |
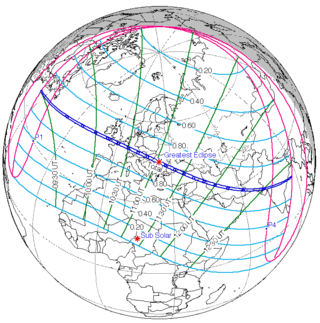 August 11, 1999 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 |
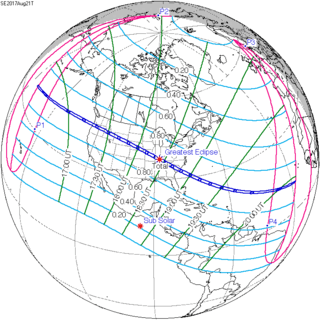 August 21, 2017 |
 September 2, 2035 |
 September 12, 2053 |
| 25 | 26 | |
 September 23, 2071 |
 October 4, 2089 | |
Notes
- ↑ Smiley, Charles H. (February 1964). "Racing the Moon's Shadow on July 20, 1963". Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. 58 (1): 10–12. Bibcode:1964JRASC..58...10S.
The United States Air Force provided an F-104D, a Starfighter made by Lockheed, and Major William A. Cato piloted the plane from Kirkland Air Force Base in New Mexico to Uplands Airport, Ottawa. Since the duration of totality depends on the difference between the speed of the plane and the speed of the moon's shadow, we elected to fly north-west to meet the shadow, then turn and increase speed so that we would reach our maximum speed at 42,000 feet as the shadow overtook us and continue to climb, attaining 48,000 feet as the shadow left us.
- ↑ Episode 7: Seven Twenty Three (Details tab) http://www.amctv.com/shows/mad-men/episodes/season-3/seven-twenty-three
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ Espenak, Fred (September 26, 2009). "Statistics for Solar Eclipses of Saros 145". NASA. Archived from the original on September 30, 2009.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1963 July 20. |
