Solar eclipse of August 30, 1905
| Solar eclipse of August 30, 1905 | |
|---|---|
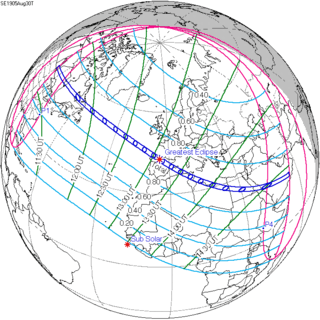 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.5708 |
| Magnitude | 1.0477 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 226 sec (3 m 46 s) |
| Coordinates | 42°30′N 4°18′W / 42.5°N 4.3°W |
| Max. width of band | 192 km (119 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 13:07:26 |
| References | |
| Saros | 143 (17 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9293 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on August 30, 1905. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Canada, Newfoundland Colony (now belonging to Canada), Spain, French Algeria (now Algeria), French Tunisia (now Tunisia), Ottoman Tripolitania (now Libya) include the capital Tripoli, Egypt, Ottoman Empire (the parts now belonging to Saudi Arabia) include Mecca, Emirate of Jabal Shammar (now belonging to Saudi Arabia), Aden Protectorate (now belonging to Yemen), and Muscat and Oman (now Oman).
Scientists came from all over the world to Alcalà de Xivert in Spain to watch the eclipse on August 30, 1905.[1]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1902–1907
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1902-1907 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||
| 108 | April 8, 1902 Partial |
118 | March 29, 1903 Annular | |
| 123 | September 21, 1903 Total |
128 | March 17, 1904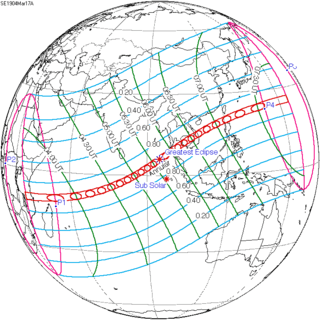 Annular | |
| 133 | September 9, 1904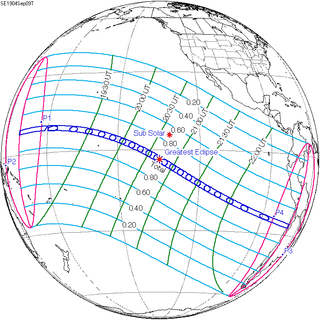 Total |
138 | March 6, 1905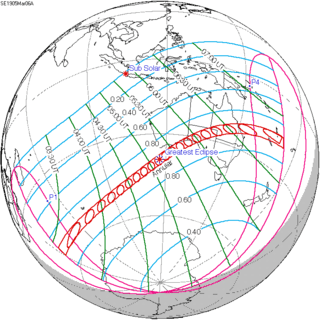 Annular | |
| 143 | August 30, 1905 Total |
148 | February 23, 1906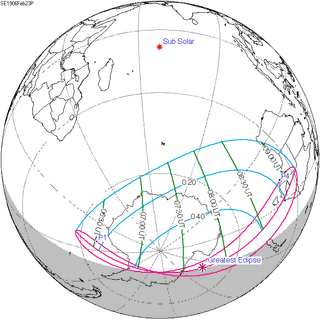 Partial | |
| 153 | August 20, 1906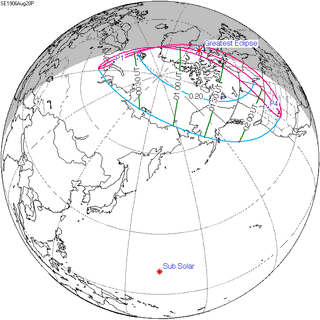 Partial | |||
Solar 143
It is a part of Saros cycle 143, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 72 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 7, 1617 and total event from June 24, 1797 through October 24, 1995. It has hybrid eclipses from November 3, 2013 through December 6, 2067, and annular eclipses from December 16, 2085 through September 16, 2536. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on April 23, 2873. The longest duration of totality was 3 minutes, 50 seconds on August 19, 1887.[3]
| Series members 17–28 occur between 1901 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 18 | 19 |
 August 30, 1905 |
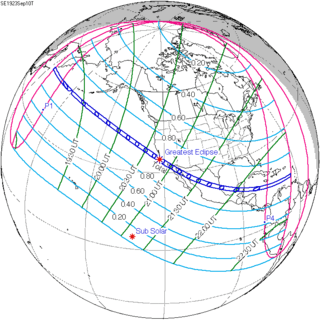 September 10, 1923 |
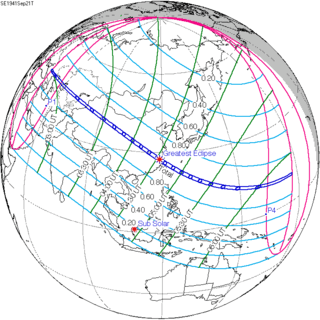 September 21, 1941 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 |
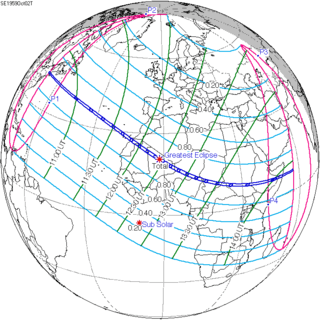 October 2, 1959 |
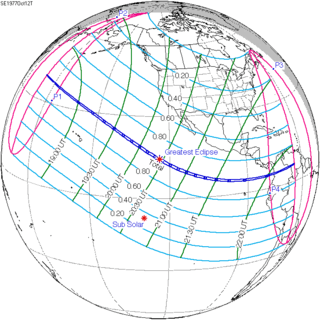 October 12, 1977 |
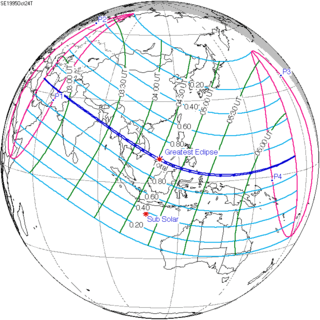 October 24, 1995 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 |
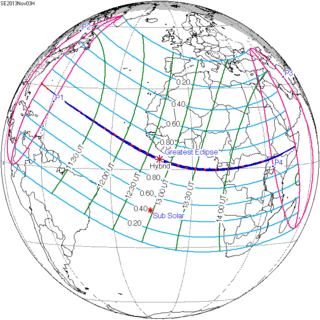 November 3, 2013 |
 November 14, 2031 |
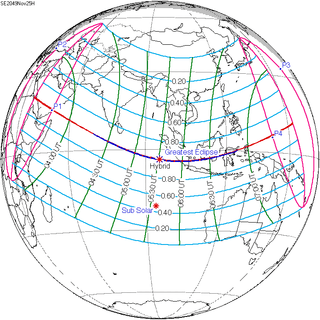 November 25, 2049 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 December 6, 2067 |
 December 16, 2085 | |
Notes
- ↑ Fabricio Cardenas, Vieux papiers des Pyrénées-Orientales, Eclipse solaire de 1905 à Perpignan, 20 March 2015
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ Espenak, F. "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 143". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- The total solar eclipse 1905: Reports of observations made by members of the ... By British Astronomical Association, Frederick William Levander
- Report of the solar eclipse expedition to Palma, Majorca, August 30, 1905 ... By Solar Physics Committee, Norman Lockyer
- Sketchs of Solar Corona August 30, 1905
- Sketchs from Russia expedition for solar Corona August 30, 1905 (2)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1905 August 30. |
