Hürth
| Hürth | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Saint Catherine parish church | ||
| ||
 Hürth Location of Hürth within Rhein-Erft-Kreis district 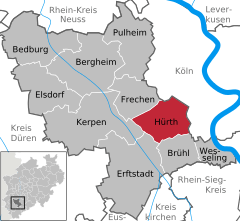  | ||
| Coordinates: 50°52′39″N 6°52′34″E / 50.87750°N 6.87611°ECoordinates: 50°52′39″N 6°52′34″E / 50.87750°N 6.87611°E | ||
| Country | Germany | |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Admin. region | Köln | |
| District | Rhein-Erft-Kreis | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Dirk Breuer (CDU) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 51.173 km2 (19.758 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 54 - 154 m (−500 ft) | |
| Population (2016-12-31)[1] | ||
| • Total | 59,272 | |
| • Density | 1,200/km2 (3,000/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | |
| Postal codes | 50354 | |
| Dialling codes | 02233 | |
| Vehicle registration | BM | |
| Website | www.huerth.de | |
Hürth is a town in the Rhein-Erft-Kreis, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Hürth shares borders with the city of Cologne.
Geography
Hürth is situated about 6 km to the southwest of Cologne city centre, at the northeastern slope of the natural preserve Kottenforst-Ville.
The town, consisting of thirteen formerly independent villages, is essentially made up of numerous subdivisions and commercial centres distributed over a relatively large area. The municipal area is interspersed with lakes and stretches of forest.
Coat of arms
Hürth's coat of arms shows an eagle from the family coat of arms belonging to the knight Hurth von Schönecken, the cross of Cologne and a cogwheel that refers to the heavy industry. It was awarded to the community on October 26, 1934, by a verdict of the Prussian Ministry of State.
Districts
- Alstädten/Burbach
- Alt-Hürth
- Berrenrath
- Efferen
- Fischenich
- Gleuel
- Hermülheim
- Hürth-Mitte
- Kalscheuren
- Kendenich
- Knapsack
- Sielsdorf
- Stotzheim
History
On April 1, 1930, the rural communities of Hürth (with Alstädten and Knapsack), Berrenrath, Fischenich, Gleuel (with Sielsdorf and Burbach), Hermülheim and Kendenich (with Kalscheuren) were united into a new country community called Hürth. After same year's failed attempt by the city of Cologne, with its then-mayor Konrad Adenauer, to incorporate Efferen, Efferen was associated to Hürth in 1933, in tandem with Stotzheim. This made Hürth the largest rural community of Germany until 1978, when Hürth ceased being a rural community and became a suburb of Cologne as new developments in Efferen closed the gap between the city of Cologne and Hürth.
The country administration of the rural district Cologne was seated in Hürth on November 22, 1963. From 1816, it had been seated in the city of Cologne itself. The administration moved to Bergheim on September 3, 1993.
Hürth is home to the Bundessprachenamt, which was founded on July 4, 1969.
Alstädten
Alstädten was first mentioned documentarily in 1185.
Burbach
Burbach was first mentioned documentarily in 1233. Nowadays, Alstädten and Burbach are one district named Alstädten-Burbach.
Berrenrath
Berrenrath was first mentioned documentarily in 922. The resettlement of Berrenrath onto a now-abandoned brown coal mine was decided on February 27, 1952. This was necessary due to mining plans of the Roddergrube AG. The resettlement was completed in the September 1995.
Efferen
The Efferen district had its first documentary mention as a pastoral town in 1189. The Catholics first humbled themselves with a plain wooden church. On June 6, 1869, this church was replaced with a solid building, consecrated by auxiliary bishop Baudri.
On October 31, 1944, large parts of Efferen, including the church and the hospital, were destroyed in an air raid; thirty-six people died.
On December 20, 1953, Boue, a member of the church assembly, consecrated the newly built Evangelic church, designed by architect Jürgen Körber. Two years later, on November 25, 1956, a new Roman Catholic church, which was designed by the Cologne architects Wolfram Borgard and Fritz Volmer, was consecrated by auxiliary bishop Wilhem Cleven.
Fischenich
Fischenich was first mentioned documentarily in 1189.
Gleuel
Gleuel was first mentioned documentarily in 898.
Hermülheim
Hermülheim was first mentioned documentarily in 943.
In Hermülheim the town's two grammar schools are located: the Ernst-Mach-Gymnasium and the Albert-Schweizer-Gymnasium.
Hürth (Alt-Hürth)
Hürth was first mentioned documentarily in 1185.
Hürth-Mitte
The building of the residential area Hürth-Mitte, that was begun in 1964 according to a decision by the municipal council in 1960, had the aim of establishing a "city centre" in the approximate geographic centre of Hürth. The decision was evidently benefitted by the constantly raising population in those times. This was partially completed by 1985, with the new town hall and community centre having been erected. Hürth-Mitte is also the site of the Hürth Park, a shopping mall, which serves as the town's economic and social centre. Hürth-Mitte is not a district for itself, but officially belongs to Hermülheim.
Kalscheuren
Kalscheuren was first mentioned documentarily in 1305.
Kendenich
Kendenich was first mentioned documentarily in 941.
Knapsack
Knapsack, its first documentary mention in 1566, started to emerge into a notable town after 1900 due to establishment and development of industry (1906 the Knapsack-Griesheim AG, later known as the Hoechst AG; 1913 construction of the brown coal power plant Goldenberg-Werk)
Due to environmental constraints, 4000 citizens had to be resettled between the years 1969 and 1979.
Sielsdorf
Sielsdorf was first mentioned documentarily in 898.
Stotzheim
Stotzheim was first mentioned documentarily in 1223.
Sights
In former times, the Eifel Aqueduct, a Roman aqueduct which supplied the city of Cologne with drinking water, went through Hürth. A couple of springs and streams in today's municipal area were used for that purpose before the Eifel aqueduct was built. Remnants of the aqueducts can still be found in the underground of the city.
Personages
Famous people from Hürth
- Ferdinand von Lüninck (1755-1825), Prince-Bishop of Corvey and Bishop of Münster
- Paul Henckels (1885-1967), actor
- Josef Metternich (1915-2005), opera singer, music and singing teacher
- Wolfgang von Trips, (1928-1961), Formula One driver
- Jean Breuer (born 1951), cyclist (World Championship 1972)
- Michael Schumacher, (born 1969), Formula One driver
- Reinhard Kleist (born 1970), comic artist and graphic designer
- Ralf Schumacher, (born 1975), Formula One driver
Other
- Anne Will, (born 1966), television journalist and moderator, went to school in Hürth
- Karl-Josef Assenmacher, former football league judge
- André Greipel, German cyclist, winner of several Tour de France stages and German champions 2013 and 2014
- Ralf Grabsch, cyclist
- Sarah Engels, second place in the 8th season of Germany is the superstar, currently resides in Hürth
- Dennis from Hürth (Deutsch: Dennis aus Hürth), is a comedian who often describes himself as son of efferen and adds his origin in his performances
Public transport
Since September 29, 1997, Hürth has a bus network that covers most of the city's area. There are six bus lines, labelled 711 through 720, by the city's public transport corporation,[2] and another five lines that are not associated with the SVH, having only a number of bus stops in Hürth.
Hürth-Kalscheuren station is located in Kalscheuren and operated by Deutsche Bahn. Two Regionalbahn services stop each hour, connecting to Cologne, Bonn and Euskirchen, while other Intercity and Regional-Express pass through without stopping.
Additionally, Hürth is connected to Cologne and Bonn via the Stadtbahn line 18 of the Cologne Stadtbahn.
All local public transport, including that of the Deutsche Bahn, is subject to the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Sieg, which is a combine of public transport organizations, setting unified prices for the whole of the combine.
Twin towns
- Argelès-sur-Mer, France (since 1988)
- Burhaniye, Turkey (since 2011)
- Kabarnet, Kenya (since 1988)
- Skawina, Poland (since 1996)
- Spijkenisse, Netherlands (since 1966)
- Thetford, England (since 1966)
Literature
- Clemens Klug: "Hürth - wie es war, wie es wurde" (1961)
- Herbert Sinz: "Auf der grünen Wiese"
- Herbert Sinz, Heinrich Schnitzler: "Hürth in alten Bildern" (1980), ISBN 3-88265-052-4
- Heinrich Schnitzler: "50 Jahre Ortsgemeinschaft Hürth-Gleuel" (1985)
- Helmut Neßeler: "Hürth wie es früher war" (1999), ISBN 3-86134-585-4
- Manfred Faust: "Geschichte der Stadt Hürth" (2009), ISBN 978-3-7616-2282-7
- Raymund Gottschalk: "Römer und Franken in Hürth" (2014), ISBN 978-3-7749-3928-8
External links
![]()
- ↑ "Amtliche Bevölkerungszahlen" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 2018-02-24.
- ↑ Stadtverkehr Hürth
