Pampanga River
| Pampanga River | |
| Rio Grande de Pampanga | |
Pampanga River with Mount Arayat in the background | |
| Country | Philippines |
|---|---|
| Region | Central Luzon |
| City | Cabanatuan, Palayan |
| Source | |
| - location | Sierra Madre, Central Luzon |
| Mouth | Manila Bay |
| - location | Hagonoy, Bulacan, Central Luzon |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 14°46′N 120°39′E / 14.767°N 120.650°ECoordinates: 14°46′N 120°39′E / 14.767°N 120.650°E |
| Length | 190 km (118 mi) [1] |
| Basin | 10,434 km2 (4,029 sq mi) [2] |
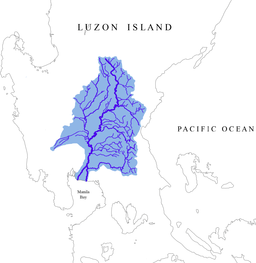 Drainage area of Pampanga River | |
Pampanga River is the second largest river on the island of Luzon in the Philippines (next to Cagayan River) and the country's fourth longest river.[3][4] It is in the Central Luzon region and traverses the provinces of Pampanga, Bulacan, and Nueva Ecija.
Topography
Its headwaters are at the Sierra Madre and runs a south and southwesterly course for about 260 kilometers until it drains into Manila Bay.
The river's basin covers an area of 10,540 km², including the allied basin of Guagua River. The basin is drained through the Pampanga River and via the Labangan Channel into the Manila Bay.
Its main tributaries are Peñaranda and the Coronel-Santor Rivers on the eastern side of the basin and the Rio Chico River from the northwest side. The Angat River joins the Pampanga River at Calumpit, Bulacan via the Bagbag River. Mount Arayat (elevation: 1,026) stands in the middle of the basin.
Southeast of Mount Arayat and the Pampanga River is the Candaba Swamp, covering an area of some 250 km² absorbing most of the flood flows from the western slopes of a portion of the Sierra Madre and the overflowing of the Pampanga River via the Cabiao Floodway. This area is submerged during the rainy season but is relatively dry during summer.
Flooding
The basin experiences, on an average, at least one flooding in a year. The dry season generally occurs from December to May and wet the rest of the year. The wettest months are from July to September. The Pampanga River Basin could handle between 100-130mm of 24-hour rainfall.
Extensive flooding occurred at the Pampanga River Basin in July 1962, May 1966, May 1976, October 1993, August 2003, August 2004, late September–October 2009, and August 2012.
The flooding in September 2011 associated with Pedring (Typhoon Nesat (2011)) nearly swallowed all of Pampanga and southern parts of Bulacan
Very catastrophic and exceptionally severe flooding in the river basin that engulfed the Central Luzon provinces of Pangasinan, Pampanga, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija and Tarlac occurred in July and August 1972. The 1972 flooding was so extensive that it flooded out 14 provinces in throughout Northern and Central Luzon, plus Metro Manila and Southern Tagalog. The Pampanga River Basin and the Agno River Basin converged over Tarlac, submerging that province.
Economic importance
At the higher sections of the basin, dams — especially the Pantabangan Dam in Pantabangan, Nueva Ecija — provide irrigation for farms in the province of Nueva Ecija.
At the lower sections of the basin, where the Pampanga delta lies, the Pampanga River system divides into small branches, crisscrossed with fishponds to form a network of sluggish, tidal flats and canals, which eventually find their way to Manila Bay.
With the anticipated completion of the Pampanga Delta Project (DPWH), it is expected that flood flows at the lower section of the Pampanga River will recede at a much faster rate.
References
- ↑ "Pampanga River - River, Philippines". www.britannica.com. Encyclopedia Britannica. July 20, 1998. Retrieved 10 April 2017.
- ↑ Vicente B. Tuddao Jr. (September 21, 2011). "Water Quality Management in the Context of Basin Management: Water Quality, River Basin Management and Governance Dynamics in the Philippines" (PDF). www.wepa-db.net. Department of Environment and Natural Resources. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- ↑ Kundel, Jim (June 7, 2007). "Water profile of Philippines". Encyclopedia of Earth. Retrieved 2008-09-30.
- ↑ "The Pampanga River Basin". Retrieved 2008-10-24.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pampanga River. |