List of earthquakes in Pakistan
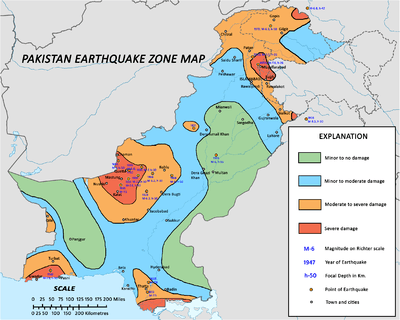 Earthquake zones of Pakistan. (<6.0 in green, 6.0–6.9 in blue, 7.0–7.9 in orange, 8.0+ in red) | |
| Largest | 8.1 Mw 1945 Balochistan earthquake |
|---|---|
Pakistan is one of the most seismically active countries in the world, being crossed by several major faults. As a result, earthquakes in Pakistan occur often and are destructive.
Geology
Pakistan geologically overlaps both the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. Balochistan, the Federally Administered Tribal Areas, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Gilgit-Baltistan provinces lie on the southern edge of the Eurasian plate on the Iranian Plateau. Sindh, Punjab and Azad Jammu & Kashmir provinces lie on the north-western edge of the Indian plate in South Asia. Hence this region is prone to violent earthquakes, as the two tectonic plates collide.
Earthquakes
| Date | Locality, district, or province | Mag. | MMI | Deaths | Injuries | Notes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-01-31 | Badakhshan Province | 6.1 Mw | 1 | 9-11 | ||||
| 2015-12-25 | Gilgit-Baltistan Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
6.3 Mw | V | 4 | 100 | |||
| 2015-10-26 | Badakhshan Province | 7.5 Mw | VII | 399 | 2,536 | |||
| 2014-05-08 | Sindh | 4.5 Mw | 2 | 50 | ||||
| 2013-09-28 | Awaran District, Balochistan | 6.8 Mw | 400 | |||||
| 2013-09-24 | Awaran District, Balochistan | 7.7 Mw | VII | 825 | 700 | |||
| 2011-01-18 | Dalbandin, Balochistan | 7.2 Mw | VI | 3 | some | |||
| 2008-10-29 | Ziarat District, Balochistan | 6.4 Mw | 215 | 200 | ||||
| 2005-10-08 | Azad Kashmir | 7.6 Mw | VIII | 86,000–87,351 | 69,000–75,266 | |||
| 1992-05-20 | Kohat Division, North West Frontier | 6.0 Mw | 36 | 100 | Moderate | NGDC [1] | ||
| 1983-12-31 | Gilgit-Baltistan | 7.2 Mw | VII | 12–26 | 60–483 | Severe | NGDC | |
| 1974-12-28 | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | 6.2 Mw | 5,300 | 17,000 | ||||
| 1945-11-28 | Makran Coast, British Baluchistan | 8.1 Mw | X | 300–400 | Tsunami | |||
| 1935-05-31 | Ali Jaan, Balochistan | 7.7 | X | 30,000–60,000 | ||||
| 1931-08-27 | Mach, Balochistan | 7.4 | [2] | |||||
| 1931-08-24 | Sharigh Valley, Balochistan | 7 | [2] | |||||
| 1909-10-21 | Sibi, Balochistan | 7 | 100 | [2] | ||||
| 1892-12-20 | Qilla Abdullah, Balochistan | 6.8 | Chaman Fault | [3] | ||||
| 1865-01-22 | Peshawar | 6 | [3] | |||||
| 1852-01-24 | Kahan, Balochistan | 8 | [4] | |||||
| 1827-09-24 | Lahore, Punjab | 7.8 | 1,000 | [4] | ||||
| 1819-06-16 | Allahbund, Sindh | 7.7–8.2 Mw | XI | >1,543 | Tsunami | |||
| 1668-05-02 | Shahbandar, Sindh | 7.6 | 50,000 | [5] | ||||
| The inclusion criteria for adding events are based on WikiProject Earthquakes' notability guideline that was developed for stand alone articles. The principles described are also applicable to lists. In summary, only damaging, injurious, or deadly events should be recorded. | ||||||||
See also
References
- ↑ Satyabala, S. P.; Yang, Zhaohui; Bilham, R. (2012), "Stick–slip advance of the Kohat Plateau in Pakistan", Nature Geoscience, Nature Publishing Group, 5: 147–150, doi:10.1038/ngeo1373
- 1 2 3 Quittmeyer & Jacob 1979, p. 792
- 1 2 Quittmeyer & Jacob 1979, p. 807
- 1 2 Quittmeyer & Jacob 1979, p. 806
- ↑ Quittmeyer & Jacob 1979, p. 805
Sources
- NGDC, Significant Earthquake Database, National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA, doi:10.7289/V5TD9V7K
- Quittmeyer, R. C.; Jacob, K. H. (1979), "Historical and modern seismicity of Pakistan, Afghanistan, northwestern India, and southeastern Iran", Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Seismological Society of America, 69 (3): 773–823
External links
- Northern Pakistan 1974 December 28 12:11:43 UTC Magnitude 6.2 USGS accessed Jan 2009
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.