New Bedford Regional Airport
| New Bedford Regional Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | City of New Bedford | ||||||||||||||
| Location | New Bedford, Massachusetts | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 80 ft / 24 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°40′34″N 070°57′25″W / 41.67611°N 70.95694°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | flyewb.com | ||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||
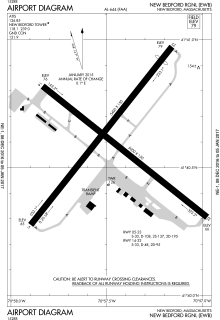 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||||||
 EWB Location of airport in Massachusetts / United States  EWB EWB (the US) | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2006) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
New Bedford Regional Airport (IATA: EWB, ICAO: KEWB, FAA LID: EWB) is a public airport two miles (3 km) northwest of the central business district of New Bedford, a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. It is owned by the City of New Bedford.[1]
The airport lies within Class D airspace and has an operating FAA control tower (open during daytime hours). The Acushnet Cedar Swamp borders the airport to the north.
History
New Bedford Regional Airport was constructed between 1940 and 1942 as a commercial airport, but was soon drafted into use for the United States Army Air Corps until the end of World War II as New Bedford Army Airfield. In April 1944, the Navy took over control of the Airport and used it as a training post and naval auxiliary air facility (NAAF New Bedford) to the Naval Air Station Quonset Point in Rhode Island.[2] After the war ended, the airport was converted back into civilian use and has been improved over the years with additional runway lighting and approach guidance systems.
Historical airline service
Northeast Airlines, a major east coast air carrier, provided scheduled airline service throughout the 1950s and 1960s until 1972 when it was acquired by and merged into Delta Air Lines which in turn then ceased serving New Bedford several years later. In 1960, Northeast was operating Douglas DC-3 aircraft into the airport with nonstop service to New York LaGuardia Airport, Boston and Martha's Vineyard.[3] By 1969, Northeast had introduced larger Fairchild Hiller FH-227 turboprops on nonstop flights to New York LaGuardia, New York JFK Airport and Boston.[4] Following its acquisition of Northeast, Delta continued to serve New Bedford with Fairchild Hiller FH-227 turboprops inherited from Northeast on nonstop flights to New York La Guardia and Boston during the early and mid 1970s.[5]
Following the cessation of service by Delta during the mid 1970s, Air New England provided regional service throughout New England and New York until it ceased all operations and went out of business. In 1975, Air New England was the only airline serving New Bedford with a total of up to fourteen nonstop flights a day into the airport from New York LaGuardia, Boston, Hyannis and Martha's Vineyard with these services being operated with Beechcraft 99 and de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter commuter turboprops as well as with larger Fairchild Hiller FH-227 turboprops and also with Douglas DC-3 aircraft.[6] By 1979, Air New England had reduced its service into New Bedford and was operating four flights a day with DHC-6 Twin Otter turboprops on nonstop services twice a day to New York LaGuardia and Hyannis.[7] Nor-East Commuter Airlines was also serving New Bedford in 1979 with several nonstop flights a day to Martha's Vineyard operated with Piper Navajo twin prop aircraft.[8]
Following Air New England, Provincetown-Boston Airlines (PBA) was the primary airline serving New Bedford until 1989, when it ceased all flights into the airport . In 1985, PBA was operating three nonstop flights a day to New York LaGuardia with Embraer EMB-110 Bandeirante commuter turboprops.[9] At the peak of the PBA's business, 102,880 passengers passed through its facilities in New Bedford.
Facilities
New Bedford Regional Airport covers an area of 847 acres (343 ha) which contains two asphalt runways: 5/23 measuring 5,400 x 150 ft (1,646 x 46 m) and 14/32 measuring 5,000 x 150 ft (1,524 x 46 m).[1]
For 12-month period ending June 1, 2006, the airport had 184,750 aircraft operations, an average of 506 per day: 89% general aviation, 7% military and 3% air taxi. There are 136 aircraft based at this airport: 90% single engine, 7% multi-engine, 3% jet aircraft and 1% ultralight.[1]
Airport tenants
Cape Air, a commuter airline, is one of the air carriers operating scheduled passenger air service at New Bedford Regional Airport. Cape Air's popular destinations include Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket. In 2003, Cape Air served 41,062 passengers at New Bedford Regional Airport.
The airport has a thriving general aviation community and is served by several FBOs:
- Colonial Air
- Nor Easter Aviation Services
- Sandpiper Air
The airport is home to the central training facility where flight operations are conducted for Bridgewater State University's Aviation Science program.
Expansion
Over the past ten years, the FAA, the Massachusetts Aeronautics Commission, and the New Bedford Airport Commission proposed an expansion project to develop New Bedford Regional Airport into a regional air cargo facility. The recommended expansion plans included a proposal to extend runway 5-23 to 8,000 ft (2,438 m) from its current length of 5,400 ft (1,646 m). Air cargo carriers require at least 6,000 to 7,000 ft (1,800 to 2,100 m) of runway.
However, despite the economic benefits that a new cargo facility could bring to the area,[10] there is a substantial local opposition. Large cargo jets will create more noise and pollution than the smaller planes that presently utilize the airport, and the runway extension itself could affect 17 to 58 acres (69,000 to 235,000 m²) of wetlands. Safety could also be a concern, with large aircraft following a flight path directly over populated residential areas.
Due to this opposition, in addition to environmental and safety concerns of the FAA that were not fully addressed by the expansion planning, the plan to extend the runway was rejected by the Airport Commission on May 4, 2005.[11] The commission voted instead to implement various safety upgrades which included an added 503 feet of length.
Airlines and destinations
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Cape Air | Martha's Vineyard, Nantucket |
| Elite Airways | Vero Beach[12] |
| Nantucket Airlines | Nantucket |
References
- 1 2 3 4 FAA Airport Master Record for EWB (Form 5010 PDF), retrieved 2007-03-15
- ↑ City of New Bedford, Massachusetts. "Airport History". Archived from the original on 2014-02-23. Retrieved 2014-02-21.
- ↑ http://www.timetableimages.com, June 24, 1960 Northeast Airlines system timetable
- ↑ http://www.departedflights.com, June 1, 1969 Northeast Airlines system timetable
- ↑ http://www.departedflights.com, March 1, 1973 & Oct. 27, 1974 Delta Air Lines system timetables
- ↑ http://www.departedflights.com, April 15, 1975 Official Airline Guide (OAG), New Bedford flight schedules
- ↑ http://www.departedflights.com, Nov. 15, 1979 Official Airline Guide (OAG), New Bedford flight schedules
- ↑ http://www.departedflights.com, Nov. 15, 1979 Official Airline Guide (OAG), New Bedford flight schedules
- ↑ http://www.departedflights.com, Feb. 15, 1985 Official Airline Guide (OAG), New York LaGuardia Airport flight schedules
- ↑ "New Bedford Regional Airport Improvements Project: Draft Environmental Impact Statement" (PDF). February 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-05-25.
- ↑ "Airport runway expansion dropped". The Standard-Times. May 5, 2005. Archived from the original on May 15, 2005.
- ↑ http://www.southcoasttoday.com/news/20171121/new-bedford-regional-airport-adds-commercial-flights-to-florida
External links
- New Bedford Regional Airport on the City of New Bedford site.
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective October 11, 2018
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KEWB
- ASN accident history for EWB
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KEWB
- FAA current EWB delay information
