List of earthquakes in Greece
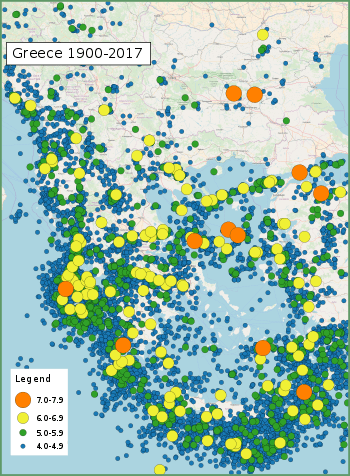
This list of earthquakes in Greece includes notable earthquakes that have affected Greece during recorded history. This list is currently incomplete, representing only a fraction of the possible events.
Tectonic setting
Greece is located at the complex boundary zone in the eastern Mediterranean between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. The northern part of Greece lies on the Eurasian Plate while the southern part lies on the Aegean Sea Plate. The Aegean Sea Plate is moving southwestward with respect to the Eurasian Plate at about 30 mm/yr while the African Plate is subducting northwards beneath the Aegean Sea Plate at a rate of about 40 mm/yr. The northern plate boundary is a relatively diffuse divergent boundary while the southern convergent boundary forms the Hellenic arc.[1]
These two plate boundaries give rise to two contrasting tectonic styles, extension on east-west trending fault zones with strike-slip tectonics on SW-NE trending fault zones throughout west and central Greece, Peloponnese and the northern Aegean and contractional in the southern Aegean, continuing around to the Ionian islands. The south Aegean is the location of the volcanic arc and is characterised by extension. To the east of Crete along the Hellenic Arc, strike-slip tectonics with some extension become important.[1]
The strongest earthquakes historically are those associated with the Hellenic Arc, although none larger than about 7.2 have been observed instrumentally. The events of AD 365 and 1303 are likely to have been much larger than this. In mainland Greece, normal faulting gives earthquakes up to 7 in magnitude, while in the northern Aegean, strike-slip events with a magnitude of 7.2 have been recorded. Large intermediate depth (>50 km) earthquakes of magnitude >7 from within the subducting African Plate have been recorded but such events cause little damage, although they are widely felt.[1]
Earthquakes
| Date | Place | Lat | Lon | Deaths | Mag. | I | Comments | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017-07-21 | Kos | 36.57 | 27.27 | 2 | 6.6 Mw | VII | 150 people injured in Greece, 370 injured in Turkey | |
| 2017-06-12 | Lesbos | 38.93 | 26.37 | 1 | 6.3 Mw | IX | 10+ people injured, significant damage across parts of the island | |
| 2015-11-17 | Lefkada | 38.67 | 20.6 | 2 | 6.5 Mw | VII | Four injured | [2] |
| 2014-05-24 | Limnos | 38.11 | 23.60 | 1 | 6.9 Mw | VIII | 1 injury reported in Greece, dozens of houses collapsed. | |
| 2009-07-01 | Crete | 34.14 | 25.29 | 6.4 Mw | Minor | |||
| 2008-07-15 | Dodecanese | 35.93 | 27.81 | 1 | 6.4 Mw | VII | ||
| 2008-06-08 | Peloponnese | 37.96 | 21.53 | 2 | 6.4 Mw | VIII | 240 injured | |
| 2006-01-08 | Kythira | 36.26 | 23.46 | 6.7 Mw | VII | Three injured | ||
| 1999-09-07 | Athens | 38.06 | 23.51 | 143 | 6.0 Mw | IX | 1,600 injured / $3–4.2 billion in damage | |
| 1995-06-15 | Aigio | 38.40 | 22.28 | 26 | 6.5 Mw | VII | 60 injuries / $660 million in damage | NGDC |
| 1995-05-13 | Kozani–Grevena | 40.15 | 21.70 | 6.6 Mw | VIII | 25 injured / $450 million in damage | NGDC | |
| 1986-09-13 | Kalamata | 37.01 | 22.18 | 20+ | 6.0 Mw | X | 300 injured / $5 million in damage | [3] |
| 1981-02-24 | Gulf of Corinth | 38.22 | 22.93 | 22 | 6.7 Ms | VIII | 400 injured / $812 million in damage | [4] |
| 1978-06-20 | Thessaloniki | 40.6 | 23.2 | 45–50 | 6.2 Mw | VIII | 100–220 injured | |
| 1968-02-19 | Aegean Sea | 39.37 | 25.96 | 20 | 7.2 Mw | X | Limited damage | NGDC |
| 1956-07-09 | Dodecanese | 36.67 | 25.957 | 53 | 7.7 Mw | IX | Triggered a tsunami that affected the entire Aegean Sea | |
| 1953-08-12 | Cephalonia, Zakynthos | 38.18 | 20.94 | 445–800 | 6.8 Mw | X | ||
| 1933-04-23 | Kos | 36.8 | 27.3 | 74 | 6.6 | IX–X | [5] | |
| 1932-09-26 | Ierissos | 39.8 | 23.8 | 491 | 7.0 Ms | X | Tsunami | |
| 1928-04-22 | Corinth | 38 | 23 | 20 | 6.0 Ms | IX | 3,000 homes destroyed / tsunami | NGDC |
| 1894-04-27 | Atalanti | 38.65 | 23.08 | 255 | 6.7 Mw | XI | Two earthquakes, 7 days apart | |
| 1886-08-27 | Filiatra | 37.1 | 21.5 | 600 | 7.5 | X | Tsunami | NGDC |
| 1881-04-03 | Chios, Çeşme, Alaçatı | 38.25 | 26.25 | 7,866 | 6.5–7.3 | XI | ||
| 1867-03-07 | Lesbos | 39.2 | 26.4 | 500 | 7.0 | NGDC | ||
| 1867-02-04 | Cephalonia | 38.4 | 20.2 | 200 | 7.9 | X | NGDC | |
| 1856-10-12 | Rhodes, Crete | 35.5 | 26 | 538 | XI | 8,000 homes destroyed / tsunami | NGDC | |
| 1840-10-30 | Zakynthos | 38 | 21 | 12 | X | NGDC | ||
| 1810-02-16 | Crete, Heraklion | 35.5 | 25.6 | 2,000 | 7.5 Mw | X | ||
| 1481-05-03 | Rhodes | 36.0 | 28.0 | 30,000 | 7.1 Ms | X | ||
| 1303-08-08 | Crete, Alexandria | 35.0 | 27.0 | Many thousands | ~8 | IX | Triggered a major tsunami; severely damaged the Lighthouse of Alexandria | |
| Dec 856 | Corinth | 37.9 | 22.9 | 45,000 | [6] | |||
| 515 | Rhodes | Ambraseys states that the death toll in this nighttime event was high and that the damage was severe | [7] | |||||
| 365-07-21 | Crete, Alexandria | 35.0 | 23.0 | Many thousands | 8.5+ | Raised part of Crete 9 metres, causing severe damage and triggering a tsunami that devastated Alexandria | ||
| 226 BC | Rhodes | 36.43 | 28.21 | Toppled the Colossus of Rhodes | ||||
| 426 BC | Euboic Gulf | 38.87 | 22.62 | The historian Thucydides concluded that the Malian Gulf tsunami of the same year was caused by the earthquake, the first to recognize such a link | [8] | |||
| 464 BC | Sparta | 37.08 | 22.43 | ~20,000 | 7.2 Ms |
References
- 1 2 3 USGS (29 March 2010). "Tectonic Summary of Greece". Archived from the original on 29 July 2010. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ↑ USGS. "M6.5 - 10km WSW of Nidri, Greece". United States Geological Survey.
- ↑ USGS. "M6.0 - southern Greece". United States Geological Survey.
- ↑ NGDC. "Comments for the Significant Earthquake". Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ Utsu 2002, p. 705
- ↑ IISEENET (Information Network of Earthquake disaster Prevention Technologies) - Search Page
- ↑ Ambraseys, N. (2009). Earthquakes in the Mediterranean and Middle East: A Multidisciplinary Study of Seismicity up to 1900 (First ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 180. ISBN 978-0521872928.
- ↑ Antonopoulos, J. (1992). "The Tsunami of 426 BC in the Maliakos Gulf, Eastern Greece". Natural Hazards. 5: 83–93. doi:10.1007/BF00127141.
Sources
- NGDC, Significant Earthquake Database, National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA, doi:10.7289/V5TD9V7K
- Utsu, T. R. (2002), "A List of Deadly Earthquakes in the World: 1500–2000", International Handbook of Earthquake & Engineering Seismology, Part A, Volume 81A (First ed.), Academic Press, ISBN 978-0124406520