List of cloud types
The list of cloud types classifies the tropospheric genera as high (cirrus, cirrocumulus, cirrostratus), middle (altocumulus, altostratus), multi-level (nimbostratus, cumulus, cumulonimbus), and low (stratocumulus, stratus) according to the altitude level or levels at which each cloud is normally found. Small cumulus are commonly grouped with the low clouds because they do not show significant vertical extent. Of the multi-level genus-types, those with the greatest convective activity are often grouped separately as towering vertical. The genus types all have Latin names.
The genera are also grouped into five physical forms. These are, in approximate ascending order of instability or convective activity: stratiform sheets; cirriform wisps and patches; stratocumuliform patches, rolls, and ripples; cumuliform heaps, and cumulonimbiform towers that often have complex structures. Most genera are divided into species with Latin names, some of which are common to more than one genus. Most genera and species can be subdivided into varieties, also with Latin names, some of which are common to more than one genus or species. The essentials of the modern nomenclature system for tropospheric clouds were proposed by Luke Howard, a British manufacturing chemist and an amateur meteorologist with broad interests in science, in an 1802 presentation to the Askesian Society. Very low stratiform cloud that touches the Earth's surface is given the common name, fog, which isn't included with the Latin nommenclature of clouds that form aloft in the troposphere.
Above the troposphere, stratospheric and mesospheric clouds have their own classifications with common names for the major types and alpha-numeric nomenclature for the subtypes. They are characterized by altitude as very high (polar stratospheric] and extreme level (noctilucent) and are both generally cirriform in structure.
Cloud identification and classification: Order of listed types
In section two of this page (Classification of major types), height ranges are sorted in approximate descending order of altitude expressed in general terms. On the cross-classification table, forms and genus types (including some genus sub-types) are shown from left to right in approximate ascending order of instability.
In sections three to five, terrestrial clouds are listed in descending order of the altitude range of each atmospheric layer in which clouds can form:
- mesospheric layer;
- stratospheric layer;
- tropospheric layer.
- Within the troposphere, the cloud levels are listed in descending order of altitude range.
- Non-vertical genus types (including some genus sub-types) are sorted into approximate descending order of altitude of the cloud bases.
- Vertical or multi-level genera and genus sub-types can be based in the low or middle levels and are therefore placed between the non-vertical low and mid-level genus types and sub-types. These thick clouds are listed in approximate descending order of altitude of the cloud tops.
- The species associated with each genus type are listed in approximate ascending order of instability where applicable.
- The constituent varieties and associated supplementary features and mother clouds for each genus or species are arranged in approximate order of frequency of occurrence.
- A count of basic tropospheric variants that result from the division and subdivision of genus types into species and varieties is shown as a number in parentheses from V-1 (variant 1) through V-92 after each variety, after nimbostratus that has no sub-types, and after certain species that are not always dividable into varieties.
- Within the troposphere, the cloud levels are listed in descending order of altitude range.
In section six, the cloud types in the general lists and the mother clouds in the applicable classification table are sorted in alphabetical order except where noted. The species table shows these types sorted from left to right in approximate ascending order of the convective instability of each species. The table for supplementary features has them arranged in approximate descending order of frequency of occurrence.
In section seven, extraterrestrial clouds can be found in the atmospheres of other planets in our solar system and beyond. The planets with clouds are listed (not numbered) in order of their distance from the sun, and the clouds on each planet are in approximate descending order of altitude.
Cloud identification and classification throughout the homosphere
| Level/Form | (1) Stratiform non-convective | (2) Cirriform mostly non-convective | (3) Stratocumuliform limited-convective | (4) Cumuliform free-convective | (5) Cumulonimbiform strong-convective | |
| Extreme-level | Noctilucent (polar mesospheric) | |||||
| Very high-level | Polar stratospheric | |||||
| High-level | Cirrostratus | Cirrus | Cirrocumulus | |||
| Mid-level | Altostratus | Altocumulus | ||||
| Towering vertical | Cumulus congestus | Cumulonimbus | ||||
| Vertical/multi-level | Nimbostratus | Cumulus mediocris | ||||
| Low-level | Stratus | Stratocumulus | Cumulus humilis | |||
| Surface-level | Fog |
Homospheric types include the ten tropospheric genera and two additional major types above the troposphere. The cumulus genus includes three species as defined by vertical size.
Polar mesospheric cloud identification and classification
Clouds that form in the mesosphere have a generally cirriform structure, but are not given Latin names based on that characteristic. Polar mesospheric clouds are the highest in the atmosphere and are given the Latin name noctilucent which refers to their illumination during deep twilight. They are sub-classified alpha-numerically according to specific details of their cirriform physical structure.
Extremely high cirriform

Noctilucent clouds are thin, mostly cirriform-looking clouds, based from about 80 to 85 kilometres (262,000–279,000 ft) and occasionally seen in deep twilight after sunset and before sunrise.[1][2]
- Type 1
- Very tenuous; resembles cirrus.
- Type 2
- Bands. Long streaks, often in parallel groups or interwoven at small angles.
- Subtypes
- 2A
- Streaks with diffuse, blurred edges.
- 2B
- Streaks with sharply defined edges.
- Type 3
- Billows. Clearly spaced, roughly parallel short streaks.
- Subtypes
- 3A
- Short, straight, narrow streaks.
- 3B
- Wave-like structures with undulations.
- Type 4
- Whirls. Partial (or, more rarely, complete) rings with dark centers.
- Subtypes
- 4A
- Whirls possessing a small angular radius of curvature, sometimes resembling light ripples on a water surface.
- 4B
- Simple curve of medium angular radius with one or more bands.
- 4C
- Whirls with large-scale ring structures.
Polar stratospheric cloud identification and classification
Polar stratospheric clouds form at very high altitudes in polar regions of the stratosphere. Those that show mother-of-pearl colors are given the name nacreous.[3] Both these and non-nacreous types are classified alpha-numerically according to their physical state and chemical makeup.
Very high cirriform
Nacreous (mother of pearl) and non-nacreous

A thin usually cirriform-looking cloud based from about 18 to 30 kilometres (59,000–98,000 ft) and seen most often between sunset and sunrise.[3]
- Type 1 (non-nacreous)
- Contains supercooled nitric acid and water droplets.
- Subtypes
- 1A
- Crystals of nitric acid and water.
- 1B
- Additionally contains supercooled sulfuric acid in ternary solution.
- Type 2 (nacreous)
- Consists of ice crystals only.
Columnar clouds – rare, column-shaped.
Cloud identification and classification in the troposphere
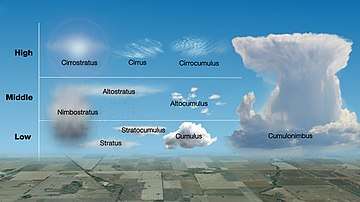
Tropospheric clouds are divided into physical forms defined by structure, and levels defined by altitude range. These divisions are cross-classified to produce ten basic genus-types. They have Latin names as authorized by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) that indicate physical structure, altitude or étage, and process of formation
High-level cirriform, stratocumuliform, and stratiform
High clouds form in the highest and coldest region of the troposphere from about 5 to 12 km (16,500 to 40,000 ft) in temperate latitudes.[4][5] At this altitude water almost always freezes so high clouds are generally composed of ice crystals or supercooled water droplets.
Genus cirrus


Abbreviation: Ci
Cirriform clouds tend to be wispy and are mostly transparent or translucent. Isolated cirrus do not bring rain; however, large amounts of cirrus can indicate an approaching storm system eventually followed by fair weather.
There are several variations of clouds of the cirrus genus based on species and varieties:
Species
- Cirrus fibratus (V-1)
High clouds having the traditional "mare's tail" appearance. These clouds are long, fibrous, and curved, with no tufts or curls at the ends. - Cirrus uncinus (V-2)
Filaments with up-turned hooks or curls. - Cirrus spissatus (V-3)
Dense and opaque or mostly opaque patches. - Cirrus castellanus (V-4)
A series of dense lumps, or "towers", connected by a thinner base. - Cirrus floccus (V-5)
Elements which take on a rounded appearance on the top, with the lower part appearing ragged.[6]
- Opacity-based varieties
- None; always translucent except species spissatus which is inherently opaque.[7]
- Opacity-based varieties
- Fibratus pattern-based varieties
- Cirrus fibratus intortus (V-6)
Irregularly curved or tangled filamegnts. - Cirrus fibratus vertebratus (V-7)
Elements arranged in the manner of a vertebrate or fish skeleton.
- Cirrus fibratus intortus (V-6)
- Fibratus pattern-based varieties
- Pattern-based variety radiatus
Large horizontal bands that appear to converge at the horizon; normally associated with fibratus and uncinus species.- Cirrus fibratus radiatus (V-8)
- Cirrus uncinus radiatus (V-9)
- Pattern-based variety radiatus
- Pattern-based variety duplicatus
Sheets at different layers of the upper troposphere, which may be connected at one or more points; normally associated with fibratus and uncinus species.- Cirrus fibratus duplicatus (V-10)
- Cirrus uncinus duplicatus (V-11)
- Pattern-based variety duplicatus
- Varieties are not commonly associated with Ci species spissatus, castellanus, or floccus.[6][7]
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Not associated with cirrus.
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Mamma
Bubble-like downward protuberances; mostly seen with species castellanus.[8]
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Genitus mother clouds
- Cirrus cirrocumulogenitus
- Cirrus altocumulogenitus
- Cirrus cumulonimbogenitus
- Cirrus homogenitus. Cirrus formed by spreading of aircraft contrails.
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother cloud
- Cirrus cirrostratomutatus
- Mutatus mother cloud
Genus cirrocumulus

Abbreviation: Cc.[4]
High-level stratocumuliform clouds of the genus cirrocumulus form when moist air at high tropospheric altitude reaches saturation, creating ice crystals or supercooled water droplets. Limited convective instability at the cloud level gives the cloud a rolled or rippled appearance. Despite the lack of a strato- prefix, layered cirrocumulus is physically a high stratocumuliform genus.[9]
High stratocumuliform species
- Cirrocumulus stratiformis[10] (V-12)
Sheets or relatively flat patches of cirrocumulus. - Cirrocumulus lenticularis[10] (V-13)
Lenticular, or lens-shaped high cloud. - Cirrocumulus castellanus[10] (V-14)
Cirrocumulus layer with "towers", or turrets joined at the bases. - Cirrocumulus floccus[10] (V-15)
Very small white heaps with ragged bases and rounded tops.[6]
- Opacity-based varieties
- None (always translucent)
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety undulatus
Cirrocumulus with an undulating base; normally associated with stratiformis and lenticularis species. (V-16)- Cirrocumulus stratiformis undulatus (V-17)
- Cirrocumulus lenticularis undulatus [7] (V-18)
- Opacity-based varieties
- Pattern-based variety lacunosus
Cirrocumulus with large clear holes; normally associated with stratiformis and castellanus species (also with cumuliform floccus species). - Stratocumuliform lacunosus
- Cirrocumulus stratiformis lacunosus (V-19)
- Cirrocumulus castellanus lacunosus (V-20)
- Cirrocumulus floccus lacunosus [7] (V-21)
- Pattern-based variety lacunosus
- Precipitation-based supplementary feature
- Virga
Light precipitation that evaporates well above ground level; mostly seen with species stratiformis, castellanus, and floccus.[8]
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary feature
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Mamma
Bubble-like downward protuberances; mostly seen with species castellanus.
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Genitus mother clouds
- Cirrocumulus homogenitus. Cirrocumulus formed by the spreading of aircraft contrails.
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Cirrocumulus cirromutatus
- Cirrocumulus cirrostratomutatus
- Cirrocumulus altocumulomutatus
- Mutatus mother clouds
Genus cirrostratus

Abbreviation: Cs[4]
Clouds of the genus cirrostratus consist of mostly continuous, wide sheets of cloud that covers a large area of the sky. It is formed when convectively stable moist air cools to saturation at high altitude, forming ice crystals.[11] Frontal cirrostratus is a precursor to rain or snow if it thickens into mid-level altostratus and eventually nimbostratus as the weather front moves closer to the observer.
Species
- Cirrostratus fibratus[10] (V-22)
Cirrostratus sheet with a fibrous appearance, but not as detached as cirrus. - Cirrostratus nebulosus[10] (V-23)
Featureless, uniform sheet.[6]
- Opacity-based varieties
- None (always translucent)[7]
- Opacity-based varieties
- Varieties are not commonly associated with Cs species nebulosus.[7]
- Supplementary features/accessory clouds
- Not associated with cirrostratus.[8]
- Supplementary features/accessory clouds
- Genitus mother clouds
- Cirrostratus cirrocumulogenitus
- Cirrostratus cumulonimbogenitus
- Cirrostratus homogenitus. Cirrostratus formed by the spreading of aircraft contrails.
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Cirrostratus cirromutatus
- Cirrostratus cirrocumulomutatus
- Cirrostratus altostratomutatus.
- Mutatus mother clouds
Mid-level stratocumuliform and stratiform
Middle cloud forms from 2 to 7 km (6,500-23,000 ft) in temperate latitudes, and may be composed of water droplets or ice crystals depending on the temperature profile at that altitude range.[5]
Genus altocumulus





Abbreviation: Ac[4]
Mid-level stratocumuliform clouds of the genus altocumulus are not always associated with a weather front but can still bring precipitation, usually in the form of virga which does not reach the ground. Layered forms of altocumulus are generally an indicator of limited convective instability, and are therefore mainly stratocumuliform in structure.
Mid-level stratocumuliform species
- Altocumulus stratiformis (always dividable into opacity-based varieties)
Sheets or relatively flat patches of altocumulus. - Altocumulus lenticularis (V-26)
Lens-shaped middle cloud. Includes informal variant altocumulus Kelvin–Helmholtz cloud, lenticular spiral indicative of severe turbulence. - Altocumulus volutus (V27) elongated, tube shaped, horizontal stratocumuliform cloud.
- Altocumulus castellanus (V-28)
Turreted layer cloud. - Altocumulus floccus (V29)
Tufted cumuliform clouds with ragged bases.[6]
- Stratocumuliform opacity-based varieties
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety radiatus
Rows of altocumulus that appear to converge at the horizon; normally associated with stratiformis species.- Altocumulus stratiformis translucidus radiatus (V-33)
- Altocumulus stratiformis perlucidus radiatus (V-34)
- Altocumulus stratiformis opacus radiatus (V-35)
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety radiatus
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety duplicatus
Altocumulus in closely spaced layers, one above the other; normally associated with stratiformis and lenticularis species.- Altocumulus stratiformis translucidus duplicatus (V-36)
- Altocumulus stratiformis perlucidus duplicatus (V-37)
- Altocumulus stratiformis opacus duplicatus (V-38)
- Altocumulus lenticularis duplicatus (V-39)
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety duplicatus
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety undulatus
Altocumulus with wavy undulating base; normally associated with stratiformis and lenticularis species.[7]- Altocumulus stratiformis translucidus undulatus (V-40)
- Altocumulus stratiformis perlucidus undulatus (V-41)
- Altocumulus stratiformis opacus undulatus (V-42)
- Altocumulus lenticularis undulatus (V-43)
- Stratocumuliform pattern-based variety undulatus
- Pattern-based variety lacunosus
Altocumulus with circular holes caused by localized downdrafts; normally associated with stratiformis and castellanus species (also with cumuliform floccus species).[7]
- Pattern-based variety lacunosus
- Stratocumuliform lacunosus
- Altocumulus stratiformis translucidus lacunosus (V-44)
- Altocumulus stratiformis perlucidus lacunosus (V-45)
- Altocumulus stratiformis opacus lacunosus (V-46)
- Altocumulus castellanus lacunosus (V-47)
- Altocumulus floccus lacunosus [6] (V-48)
- Stratocumuliform lacunosus
- Precipitation-based supplementary feature
- Virga
Altocumulus producing precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground; usually associated with species stratiformis, castellanus, and floccus.
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary feature
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Mamma
Altocumulus (usually species castellanus) with downward facing bubble-like protuberances caused by localized downdrafts within the cloud.[8]
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Genitus mother clouds
- Altocumulus cumulogenitus
- Altocumulus cumulonimbogenitus
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Altocumulus cirrocumulomutatus
- Altocumulus altostratomutatus
- Altocumulus nimbostratomutatus
- Altocumulus stratocumulomutatus
- Mutatus mother clouds
Genus altostratus

Abbreviation: As[4]
Stratiform clouds of the genus altostratus form when a large convectively stable airmass is lifted to condensation in the middle level of the troposphere, usually along a frontal system. Altostratus can bring light rain or snow. If the precipitation becomes continuous, it may thicken into nimbostratus which can bring precipitation of moderate to heavy intensity.
Species
- No differentiated species (always nebulous).[6]
- Opacity-based varieties
- Altostratus translucidus (V-49)
Altostratus through which the sun can be seen. - Altostratus opacus (V-50)
Altostratus that completely blocks out the sun.[7]
- Altostratus translucidus (V-49)
- Opacity-based varieties
- Pattern-based variety radiatus
Bands that appear to converge at the horizon.- Altostratus translucidus radiatus (V-51)
- Altostratus opacus radiatus (V-52)
- Pattern-based variety radiatus
- Pattern-based variety duplicatus
Altostratus in closely spaced layers, one above the other.- Altostratus translucidus duplicatus (V-53)
- Altostratus opacus duplicatus (V-54)
- Pattern-based variety duplicatus
- Pattern-based variety undulatus
Altostratus with wavy undulating base.- Altostratus translucidus undulatus (V-55)
- Altostratus opacus undulatus [6] (V-56)
- Pattern-based variety undulatus
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Virga
Accompanied by precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground. Seen mostly with opacus varieties. - Praecipitatio
Produces precipitation that reaches the ground; associated with opacus varieties.[8]
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Mamma
Altostratus with downward facing bubble-like protuberances caused by localized downdrafts within the cloud.
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Accessory cloud
Seen mostly with opacus varieties- Pannus
Accompanied by ragged lower layer of fractus species clouds forming in precipitation.[8]
- Pannus
- Accessory cloud
- Genitus mother clouds
- Altostratus altocumulogenitus
- Altostratus cumulonimbogenitus
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Altostratus cirrostratomutatus
- Altostratus nimbostratomutatus
- Mutatus mother clouds
Vertical or multi-level cumulonimbiform, cumuliform, and stratiform (low to mid-level cloud base)
Clouds with upward-growing vertical development usually form below 2 kilometres (6,600 ft),[5] but can be based as high as 2.5 kilometres (8,200 ft) in temperate climates, and often much higher in arid regions. Downward-growing cloud forms mostly above 2 kilometres (6,600 ft) and achieves vertical extent as the base subsides into the low altitude range during precipitation.
Genus cumulonimbus: Towering vertical


Abbreviation: Cb[4]
Clouds of the genus cumulonimbus have very dark gray to nearly black flat bases and very high tops that can penetrate the tropopause. They develop from cumulus when the airmass is convectively highly unstable. They generally produce thunderstorms, rain or showers, and sometimes hail, strong outflow winds, and/or tornadoes at ground level.
Species
- Cumulonimbus calvus (V-57)
Cumulonimbus with high domed top. - Cumulonimbus capillatus (V-58)
Towering vertical cloud with high cirriform top.[6]
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
Associated with calvus and capillatus species.- Virga
Precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground. - Praecipitatio
Precipitation that reaches the ground.[8]
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Cloud-based supplementary features
- Incus (species capillatus only)
Cumulonimbus with flat anvil-like cirriform top caused by wind shear where the rising air currents hit the inversion layer at the tropopause.[8][12] - Mamma
Also sometimes called Mammatus, consisting of bubble-like protrusions on the underside caused by localized downdrafts. - Arcus (including roll and shelf clouds)
Low, horizontal cloud formation associated with the leading edge of thunderstorm outflow. - Tuba
Column hanging from the cloud base which can develop into a funnel cloud or tornado.[8]
- Incus (species capillatus only)
- Cloud-based supplementary features
- Accessory clouds
Seen with species and capillatus except where noted.- Pannus
Accompanied by a lower layer of fractus species cloud forming in precipitation. - Pileus (species calvus only)
Small cap-like cloud over parent cumulonimbus. - Velum
A thin horizontal sheet that forms around the middle of a cumulonimbus.[8]
- Pannus
- Accessory clouds
- Genitus mother clouds
- Cumulonimbus altocumulogenitus
- Cumulonimbus altostratogenitus
- Cumulonimbus nimbostratogenitus
- Cumulonimbus stratocumulogenitus
- Cumulonimbus flammagenitus that are formed by large scale fires or volcanic eruptions.
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother cloud
- Cumulonimbus cumulomutatus
- Mutatus mother cloud
Genus cumulus: Towering vertical

Abbreviations: Cu con (cumulus congestus) or Tcu (towering cumulus)[13]
Species
- Cumulus congestus[6] (V-59)
- These large cumulus clouds have flat dark grey bases and very tall tower-like formations with tops mostly in the high level of the troposphere. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) designates this species as towering cumulus (Tcu).
- Opacity-based varieties
- None (always opaque).
- Opacity-based varieties
- Pattern-based variety
- None (not generally discerned with highly unstable cumulus congestus).
- Pattern-based variety
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Virga
Accompanied by precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground. - Praecipitatio
Produces precipitation that reaches the ground.[8]
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Cloud-based supplementary features
- Mamma
Downward facing bubble-like protuberances caused by localized downdrafts within the cloud. - Arcus (including roll and shelf clouds)
Low horizontal cloud formation associated with the leading edge of a thunderstorm outflow. - Tuba
Column hanging from the cloud base which can develop into a small funnel cloud.[8]
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary features
- Accessory clouds
- Pannus
Accompanied by a lower layer of fractus species cloud forming in precipitation. - Pileus
Small cap-like cloud over parent cumulus cloud. - Velum
A thin horizontal sheet that forms around the middle of a cumulus cloud.[8]
- Pannus
- Accessory clouds
- Mother clouds
- Cumulus congestus flammagenitus.
- Other genitus and mutatus types are the same as for small and moderate cumulus.
- Mother clouds
Genus nimbostratus: Moderate or deep vertical
Abbreviation: Ns[4] (V-60)
Clouds of the genus nimbostratus tend to bring constant precipitation and low visibility. This cloud type normally forms above 2 kilometres (6,600 ft)[5] from altostratus cloud but tends to thicken into the lower levels during the occurrence of precipitation. The top of a nimbostratus deck is usually in the middle level of the troposphere.
Species
- No differentiated species (always nebulous).[6]
- Accessory cloud
- Pannus
Nimbostratus with lower layer of fractus species cloud forming in precipitation.[8]
- Pannus
- Accessory cloud
- Genitus mother clouds
- Nimbostratus cumulogenitus
- Nimbostratus cumulonimbogenitus
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Nimbostratus altostratomutatus
- Nimbostratus altocumulomutatus
- Nimbostratus stratocumulomutatus
- Mutatus mother clouds
Genus cumulus: Moderate vertical


Abbreviation: Cu[4]
Moderate vertical cumulus is the product of free convective airmass instability. Continued upward growth suggests showers later in the day.
Species
- Cumulus mediocris (V-61)
- Moderate vertical clouds with flat medium grey bases and higher tops than cumulus humilis.[6]
- Opacity-based varieties
- None (always opaque)
- Opacity-based varieties
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Virga
Accompanied by precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground. - Praecipitatio
Produces precipitation that reaches the ground.[8]
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Mamma
Downward facing bubble-like protuberances caused by localized downdrafts within the cloud.[8]
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Accessory clouds
- Pileus
Small cap-like cloud over parent cumulus cloud.[8] - Velum
A thin horizontal sheet that forms around the middle of a cumulus cloud.
- Pileus
- Accessory clouds
- Mother clouds
- Genitus and mutatus types are the same as for cumulus of little vertical extent.
- Mother clouds
Low-level stratocumuliform, cumuliform, and stratiform
Low cloud forms from near surface to ca. 2 kilometres (6,600 ft) and are generally composed of water droplets.[5]
Genus stratocumulus
Abbreviation: Sc[4]
Clouds of the genus stratocumulus are lumpy, often forming in slightly unstable air, and they can produce very light rain or drizzle.
Species
- Stratocumulus stratiformis (always dividable into opacity-based varieties)
Sheets or relatively flat patches of stratocumulus - Stratocumulus lenticularis (V-63)
Lens-shaped low cloud. - Stratocumulus volutus (V-64)
Elongated, low-level, tube shaped, horizontal stratocumuliform cloud. - Stratocumulus floccus (V-65)
Scattered or isolated stratocumulus tufts with domed tops and ragged bases. - Stratocumulus castellanus (V-66)
Layer of turreted stratocumulus cloud with tower-like formations protruding upwards.[6]
- Stratocumuliform opacity-based varieties
- Stratocumulus stratiformis translucidus (V-67)
Thin translucent stratocumulus through which the sun or moon can be seen. - Stratocumulus stratiformis perlucidus (V-68)
Opaque low clouds with translucent breaks. - Stratocumulus stratiformis opacus (V-69)
Opaque stratocumulus clouds.[7]
- Stratocumulus stratiformis translucidus (V-67)
- Stratocumuliform opacity-based varieties
- Pattern-based variety radiatus
Stratocumulus arranged in parallel bands that appear to converge on the horizon; normally associated with stratiformis species.- Stratocumulus stratiformis translucidus radiatus (V-70)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis perlucidus radiatus (V-71)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis opacus radiatus (V-72)
- Pattern-based variety radiatus
- Pattern-based variety duplicatus
Closely spaced layers of stratocumulus, one above the other; normally associated with stratiformis and lenticularis species.- Stratocumulus stratiformis translucidus duplicatus (V-73)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis perlucidus duplicatus (V-74)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis opacus duplicatus (V-75)
- Stratocumulus lenticularis duplicatus (V-76)
- Pattern-based variety duplicatus
- Pattern-based variety undulatus
Stratocumulus with wavy undulating base; normally associated with stratiformis and lenticularis species.[7]- Stratocumulus stratiformis translucidus undulatus (V-77)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis perlucidus undulatus (V-78)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis opacus undulatus (V-79)
- Stratocumulus lenticularis undulatus (V-80)
- Pattern-based variety undulatus
- Pattern-based variety lacunosus
Sc with circular holes caused by localized downdrafts; normally associated with stratiformis and castellanus species.- Stratocumulus stratiformis translucidus lacunosus (V-81)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis perlucidus lacunosus (V-82)
- Stratocumulus stratiformis opacus lacunosus (V-83)
- Stratocumulus castellanus lacunosus[6] (V-84)
- Pattern-based variety lacunosus
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
Usually associated with species stratiformis and castellanus:- Virga
Low cloud producing precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground. - Praecipitatio
Stratocumulus clouds producing precipitation that reaches the ground.[8]
- Virga
- Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Cloud-based supplementary feature
- Mamma
Stratocumulus with bubble-like protrusions on the underside; usually associated with species castellanus.[8]
- Mamma
- Cloud-based supplementary feature

- Genitus mother clouds
- Stratocumulus cumulogenitus
- Stratocumulus nimbostratogenitus
- Stratocumulus cumulonimbogenitus
- Stratocumulus altostratogenitus
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Stratocumulus nimbostratomutatus
- Stratocumulus altocumulomutatus
- Stratocumulus stratomutatus
- Mutatus mother clouds
Genus cumulus (little vertical extent)

Abbreviation: Cu
These are fair weather cumuliform clouds of limited convection that do not grow vertically. The vertical height from base to top is generally less than the width of the cloud base. They appear similar to stratocumulus but the elements are generally more detached and less wide at the base.
Species
- Cumulus fractus (V-85)
Ragged shreds of cumulus clouds. - Cumulus humilis (V-86)
"Fair weather clouds" with flat light grey bases and small white domed tops.[6]
- Opacity-based varieties
- None (always opaque except species fractus which is always translucent).[7]
- Opacity-based varieties
- Humilis pattern-based variety
- Cumulus humilis radiatus (V-87)
Small cumulus clouds arranged in parallel lines that appear to converge at the horizon.[15]
- Cumulus humilis radiatus (V-87)
- Humilis pattern-based variety
- Supplementary features/accessory clouds
- Not commonly seen with cumulus fractus or humilis.[8]
- Supplementary features/accessory clouds
- Genitus mother clouds
- Cumulus stratocumulogenitus
- Cumulus homogenitus clouds formed by air-mass convection associated with contained industrial activity.
- Genitus mother clouds
- Mutatus mother clouds
- Cumulus stratocumulomutatus
- Cumulus stratomutatus
- Mutatus mother clouds
Genus stratus


Abbreviation: St[4]
Clouds of the genus stratus form in low horizontal layers having a ragged or uniform base. Ragged stratus often forms in precipitation while more uniform stratus forms in maritime or other moist stable air mass conditions. The latter often produces drizzle. Stratus that touches the Earth's surface is given the common name, fog, rather than a Latin name that applies only to clouds that form and remain aloft in the troposphere.
Species
- Stratus nebulosus
Uniform fog-like low cloud. - Stratus fractus (V-88)
Ragged shreds of stratus clouds usually under base of precipitation clouds.[6]
- Nebulosus opacity-based varieties
- Stratus nebulosus translucidus (V-89)
Thin translucent stratus. - Stratus nebulosus opacus (V-90)
Opaque stratus that obscures the sun or moon.[7]
- Stratus nebulosus translucidus (V-89)
- Nebulosus opacity-based varieties
- Pattern-based variety undulatus
Wavy undulating base.- Stratus nebulosus translucidus undulatus (V-91)
- Stratus nebulosus opacus undulatus (V-92)
- Pattern-based variety undulatus
- Precipitation-based supplementary feature
- Praecipitatio
Stratus (usually species nebulosus) producing precipitation.[8]
- Praecipitatio
- Precipitation-based supplementary feature
- Accessory clouds
- Not usually seen with stratus.[8]
- Accessory clouds
- Genitus mother clouds and other mother sources
- Stratus nimbostratogenitus
- Stratus cumulogenitus
- Stratus cumulonimbogenitus
- Stratus cataractagenitus are generated by the spray from waterfalls.
- Stratus silvagenitus is a stratus cloud that forms as water vapor is added to the air above a forest.
- Genitus mother clouds and other mother sources
- Mutatus mother cloud
- Stratus stratocumulomutatus
- Mutatus mother cloud
Tropospheric cloud types with Latin etymologies where applicable
Cloud types are sorted in alphabetical order except where noted.
WMO genera
- Altocumulus (altus and cumulus) - Latin for "high heap": Applied to mid-level stratocumuliform.
- Altostratus (altus and stratus) - "High sheet": Applied to mid-level stratiform.
- Cirrocumulus (cirrus and cumulus) - "Hair-like heap": Applied to high-level stratocumuliform.
- Cirrostratus (cirrus and stratus) - "Hair-like sheet": Applied to high-level stratiform.
- Cirrus - "Hair-like": Applied to high-level cirriform.
- Cumulonimbus - (cumulus and nimbus) "Precipitation-bearing heap": Applied to vertical/multi-level cumulonimbiform.
- Cumulus - "Heap": Applied to low-level and vertical/multi-level cumuliform.
- Nimbostratus (nimbus and stratus) - "Precipitation-bearing sheet": Applied to multi-level stratiform with vertical extent that produces precipitation of significant intensity.
- Stratocumulus (stratus and cumulus) - "Sheet-like heap": Applied to low-level stratocumuliform.
- Stratus - "Sheet": Applied to low-level mostly shallow stratiform.
WMO species
- Castellanus (Cas) – Latin for "castle-like": Applies to stratocumuliform (Sc cas, Ac cas, Cc cas) and dense cirriform (Ci cas) with a series of turret shapes – indicates air mass instability.
- Congestus (Con) – Latin for "congested": Applies to cumuliform (Cu con/Tcu) with great vertical development and heaped into cauliflower shapes – indicates considerable airmass instability and strong upcurrents.
- Fibratus (Fib) – "Fibrous": Cirriform (Ci fib) or high stratiform (Cs fib) in the form of filaments, can be straight or slightly curved.
- Floccus (Flo) – "Tufted": Applies to stratocumuliform (Sc flo, Ac flo, Cc flo) and high cirriform (Ci flo); indicates some mid or high-level instability.
- Fractus (Fra) - "Broken": Low stratiform (St fra) or cumuliform (Cu fra) with an irregular shredded appearance – forms in precipitation and/or gusty winds.
- Humilis (Hum) – "Small": Applies to cumuliform (Cu hum) with little vertical extent; indicates relatively slight airmass instability.
- Lenticularis (Len) "Lens–like": Stratocumuliform (Sc len, Ac len, Cc len) having a lens-like appearance – formed by standing waves of wind passing over mountains or hills.
- Mediocris (Med) – "Medium-size": Cumuliform (Cu med) with moderate vertical extent; indicates moderate instability and upcurrents.
- Nebulosus (Neb) – "Nebulous": Indistinct low and high stratiform (St neb, Cs neb) without features; indicates light wind if any and stable air mass.
- Spissatus (Spi) – "Dense": Thick cirriform (Ci spi) with a grey appearance; indicates some upward movement of air in the upper troposphere.
- Stratiformis (Str) – "Sheet-like": Horizontal cloud sheet of flattened stratocumuliform (Sc str, Ac str, Cc str); indicates very slight airmass instability.
- Uncinus (Unc) – "Hook-like": Cirriform (Ci unc) with a hook shape at the top; indicates a nearby backside of a weather system.
- Volutus (Vol) - "Rolled": Elongated, low or mid-level, tube shaped, stratocumuliform (Sc vol, Ac vol).
The division of genus types into species is as shown in the following table. The species are sorted from left to right in approximate ascending order of instability or vertical extent. The genus types are arranged from top to bottom in the same ascending order of instability within each étage. (1)=Stratiform types, (2)=Cirriform types, (3)=Stratocumuliform types, (4)=Cumuliform types, (5)=Cumulonimbiform types.
| Species (L-R) | Abbrev. | (1) | Neb (1) | Fib (1,2) | Unc (2) | Spi (2) | Str (3) | Len (3) | Vol (3) | Flo (2,3) | Cas (2,3) | Fra (1,4) | Hum (4) | Med (4) | Con (4) | Cal (5) | Cap (5) | |
| Level | Genus name | Species name L-R | (no species) | Nebulosus | Fibratus | Uncinus | Spissatus | Stratiformis | Lenticularis | Volutus | Floccus | Castellanus | Fractus | Humilis | Mediocris | Congestus | Calvus | Capillatus |
| High | Cirrostratus (1) | Cs | + (1) | + (1) | ||||||||||||||
| Cirrus (2) | Ci | + (2) | + (2) | + (2) | + (2) | + (2) | ||||||||||||
| Cirrocumulus (3) | Cc | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | |||||||||||||
| Mid | Altostratus (1) | As | + (1) | |||||||||||||||
| Altocumulus (3) | Ac | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | ||||||||||||
| Vert | Nimbostratus-MV (1) | Ns | + (1) | |||||||||||||||
| Cumulus-MV (4) | Cu | + (4) | ||||||||||||||||
| Cumulus-TV (4) | Tcu | + (4) | ||||||||||||||||
| Cumulonimbus-TV (5) | Cb | + (5) | + (5) | |||||||||||||||
| Low | Stratus (1) | St | + (1) | + (1) | ||||||||||||||
| Stratocumulus (3) | Sc | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | + (3) | ||||||||||||
| Cumulus (4) | Cu | + (4) | + (4) |
Vert=Vertical or multi-level, MV=Moderate or deep vertical, TV=Towering vertical.
WMO varieties
Opacity-based
- Opacus - Latin for "Opaque": A thick sheet of stratiform or stratocumuliform cloud.
- Perlucidus - "Semi-transparent": Sheet of stratocumuliform cloud with small spaces between elements.
- Translucidus - "Translucent": Thin translucent patch or sheet of stratiform or stratocumuliform.
Pattern-based
- Duplicatus - Latin for "Double": Closely spaced often partly merged layers of cloud in one of several possible forms.
- Intortus - "Twisted": Curved and tangled cirriform.
- Lacunosus - "Full of holes": Thin stratocumuliform cloud distinguished by holes and ragged edges.
- Radiatus - "Radial": Clouds in one of several possible forms arranged in parallel lines that appear to converge at a central point near the horizon.
- Undulatus - "Wavy": stratiform or stratocumuliform cloud displaying an undulating pattern.
- Vertebratus - "In the form of a back-bone": Cirriform arranged to look like the back-bone of a vertebrate.
The following table shows the cloud varieties arranged across the top of the chart from left to right in approximate descending order of frequency of appearance. The genus types associated with each variety are sorted from top to bottom in the left column in approximate descending order of average overall altitude range. Where applicable, the genera and varieties are cross-classified to show the species normally associated with each combination of genus and variety. The exceptions include altostratus that has varieties but no species, towering cumulus and cumulonimbus that have species but no varieties, and nimbostratus has no species or varieties.
| Abbrev. | Tra | Per | Opa | Dup | Und | Rad | Lac | Int | Ver | ||
| Level | Name | Abbrev. | Translucidus | Perlucidus | Opacus | Duplicatus | Undulatus | Radiatus | Lacunosus | Intortus | Vertebratus |
| High | Cirrus | Ci | + Fib + Unc | + Fib + Unc | + Fib | + Fib | |||||
| Cirrocumulus | Cc | + Str + Len | + Str + Cas + Flo | ||||||||
| Cirrostratus | Cs | + Fib | + Fib | ||||||||
| Mid | Altocumulus | Ac | + Str | + Str | + Str | + Str + Len | + Str + Len | + Str | + Str + Cas + Flo | ||
| Altostratus | As | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| Vert | Cumulonimbus (TV) | Cb | |||||||||
| Cumulus (TV) | Tcu | ||||||||||
| Nimbostratus (MV) | Ns | ||||||||||
| Cumulus (MV) | Cu | + Med | |||||||||
| Low | Stratocumulus | Sc | + Str | + Str | + Str | + Str + Len | + Str + Len | +Str | +Str + Cas + Flo | ||
| Cumulus | Cu | + Hum | |||||||||
| Stratus | St | + Neb | + Neb | + Neb | |||||||
WMO supplementary features

Precipitation-based supplementary features
- Praecipitatio - Latin for "falling": Cloud whose precipitation reaches the ground.
- Virga - "Twig" or "branch": Cloud whose precipitation evaporates before reaching the ground.
Cloud-based supplementary features
- Arcus - Latin for "arch" or "bow": Feature mostly attached to cumulus, thick with ragged edges.
- Asperitas - "Roughness": A highly disturbed and chaotic wave feature occasionally seen with a stratocumulus or altocumulus cloud.
- Cavum - "Hole": Supercooled altocumulus or cirrocumulus distinguished by a hole with ragged edges and virga or wisps of cirrus.
- Cauda: - "Tail": A tail cloud that extends horizontally away from the murus cloud and is the result of air feeding into the storm.
- Fluctus: Crested wave-like stratocumulus, altocumulus, or cirrus cloud formed by wind-shear.
- Incus - "Anvil": Top part of a mature cumulonimbus cloud; anvil-shaped feature.

- Mammatus; WMO term mamma: - "Breast": A feature in the form of round pouches on under-surface of a cloud.
- Murus: - "Wall": Cumulonimbus wall cloud with a lowering rotating base that can portend tornadoes.
- Tuba: - "Funnel" or "tube": Feature in the form of a column hanging from the bottom of cumulus or cumulonimbus.
Accessory clouds
- Pannus - Latin for "shredded cloth": A ragged or shredded accessory cloud that forms in precipitation below the main cloud.
- Pileus - "Capped": A hood-shaped accessory cloud.
- Velum - "A ship's sail": An accessory cloud in the form of a sail.
The supplementary features are associated with particular genera as follows. They are sorted from left to right in approximate decreasing order of frequency of occurrence for each of three categories. The genus types (including some cumulus sub-types) are arranged from top to bottom in approximate descending order of average overall altitude range.
| Class | Precipitation-based | Cloud-based | Accessory cloud | ||||||||
| Level | Name | Abbrev. | Virga | Praecipitatio | Incus | Mamma | Arcus | Tuba | Pannus | Pileus | Velum |
| High | Cirrus | Ci | + | ||||||||
| Cirrocumulus | Cc | + | + | ||||||||
| Cirrostratus | Cs | ||||||||||
| Mid | Altocumulus | Ac | + | + | |||||||
| Altostratus | As | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| Vert | Cumulonimbus (TV) | Cb | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Cumulus (TV) | Tcu | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| Nimbostratus (MV) | Ns | + | + | + | |||||||
| Cumulus (MV) | Cu | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| Low | Stratocumulus | Sc | + | + | + | ||||||
| Cumulus | Cu | + | |||||||||
| Stratus | St | ||||||||||
Genitus mother clouds
- Altocumulogenitus - formed by the partial transformation of altocumulus mother cloud.
- Altostratogenitus - formed by the partial transformation of altostratus.
- Cirrogenitus - partial transformation of cirrus.
- Cirrocumulogenitus - partial transformation of cirrocumulus.
- Cirrostratogenitus - partial transformation of cirrostratus.
- Cumulogenitus – spreading out or partial transformation of cumulus.
- Cumulonimbogenitus – spreading out or partial transformation of cumulonimbus.
- Nimbostratogenitus - partial transformation of nimbostratus.
- Stratogenitus - partial transformation of stratus.
- Stratocumulogenitus - partial transformation of stratocumulus.
Other genitus clouds
- Cataractagenitus (cataracta-/pertaining to a river cataract) - formed from the mist at a waterfall.
- Flammagenitus (flamma-/pertaining to fire) - formed by convection associated with large wildfires.
- Homogenitus (homo-/pertaining to humans) - formed as a result of human activities, particularly aircraft at high altitudes and heat-generating industrial activities at surface level. If a homogenitus cloud of one genus changes to another genus type, it is then termed a homomutatus cloud.
- Silvagenitus (silva-/pertaining to trees or forests) - formed by low-level condensation of water vapor released by vegetation, especially forest canopies.
Mutatus mother clouds
- Nomenclature works the same way as for genitus mother clouds except for the mutatus suffix to indicate the complete rather than the partial transformation of the original cloud type. e.g. Altocumulomutatus - formed by the complete transformation of altocumulus mother cloud.
The possible combinations of genera and mother clouds can be seen in this table. The genitus and mutatus clouds are each sorted from left to right in alphabetical order. The genus types (including some cumulus sub-types) are arranged from top to bottom in the left column in approximate descending order of average overall altitude range.
| Class | Genitus mother | Mutatus mother | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbrev. | Ac | As | Ci | Cc | Cs | Cu | Cb | Ns | St | Sc | Ac | As | Ci | Cc | Cs | Cu | Cb | Ns | St | Sc | ||
| Level | Name | Abbrev. | altocumulo | altostrato | cirro | cirrocumulo | cirrostrato | cumulo | cumulonimbo | nimbostrato | strato | stratocumulo | altocumulo | altostrato | cirro | cirrocumulo | cirrostrato | cumulo | cumulonimbo | nimbostrato | strato | stratocumulo |
| High | Cirrus | Ci | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Cirrocumulus | Cc | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cirrostratus | Cs | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Mid | Altocumulus | Ac | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| Altostratus | As | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Vert | Cumulonimbus (TV) | Cb | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| Cumulus (TV) | Tcu | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Nimbostratus (MV) | Ns | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Cumulus (MV) | Cu | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Low | Stratocumulus | Sc | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| Cumulus | Cu | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Stratus | St | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
Informal terms recently accepted for WMO classification with Latin nomentclature

- Aviaticus cloud - persistent condensation trails (contrails) formed by ice crystals originating from water vapor emitted by aircraft engines. May resemble cirrus, cirrocumulus, or cirrostratus depending on atmospheric stability and wind shear. Accepted as a WMO genitus cloud homogenitus (man-made).
- Fallstreak hole – supercooled altocumulus or cirrocumulus distinguished by a hole with ragged edges and virga or wisps of cirrus. Accepted as a WMO supplementary feature to be named cavum (hole).
- Kelvin–Helmholtz cloud - Crested wave-like clouds formed by wind-shear instability that may occur at any altitude in the troposphere. Accepted as a WMO supplementary feature with the Latin name fluctus.
- Pyrocumulus and Pyrocumulonimbus - cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds formed by quickly generated ground heat; including forest fires, volcanic eruptions and low level nuclear detonation. Accepted as a WMO genitus cloud with the Latin name flammagenitus, or homogenitus in the case of small cumulus formed by contained human activity.

- Roll cloud – elongated, low-level, tube shaped, horizontal formation not associated with a parent cloud. Accepted as a WMO stratocumulus or altocumulus species with the Latin name volutus.[16]
WMO and informal terms related to free-convective cloud types and storms
- Accessory cloud (WMO supplementary feature) – secondary cloud that is associated with but separate from a main cloud.
- Anvil (WMO supplementary feature incus) – the anvil top of a cumulonimbus cloud.
- Anvil dome (WMO supplementary feature incus) – the overshooting top on a Cb that is often present on a supercell.
- Anvil rollover – (slang) circular protrusion attached to underside of anvil.
- Arcus cloud (WMO supplementary feature) – arch or a bow shape, attached to cumulus, thick with ragged edges.
- Backsheared anvil – (slang) anvil that spreads upwind, indicative of extreme weather.
- Clear slot or dry slot (informal term) – an evaporation of clouds as a rear flank downdraft descends and dries out cloud and occludes around a mesocyclone.
- Cloud tags (WMO species fractus) – ragged detached portions of cloud.
- Collar cloud (WMO velum accessory cloud) – ring shape surrounding upper part of wall cloud.
- Condensation funnel (WMO supplementary feature tuba) – the cloud of a funnel cloud aloft or a tornado.
- Altocumulus castellanus (WMO genus and species) – castle crenellation-shaped altocumulus clouds.
- Cumulus (WMO genus) – heaped clouds.
- Cumulus castellanus – (informal variation of WMO genus and species cumulus congestus) cumulus with tops shaped like castle crenellations.
- Cumulus congestus (WMO genus and species) – considerable vertical development and heaped into cauliflower shapes.
- Cumulus fractus (WMO genus and species) – ragged detached portions of cumulus cloud.
- Cumulus humilis (WMO genus and species) – small, low, flattened cumulus, early development.
- Cumulus mediocris (WMO genus and species) – medium-sized cumulus with bulges at the top.
- Cumulus pileus (WMO genus and accessory cloud) – capped, hood-shaped cumulus cloud.
- Cumulus praecipitatio (WMO genus and supplementary feature) – cumulus whose precipitation reaches the ground.
- Cumulus radiatus (WMO genus and variety) – cumulus arranged in parallel lines that appear to converge near the horizon.
- Cumulus tuba (WMO genus and supplementary feature) – column hanging from the bottom of cumulus.
- Cumulonimbus (WMO genus) – heaped towering rain-bearing clouds that stretch to the upper levels of the troposphere.
- Cumulonimbus calvus (WMO genus and species) – cumulonimbus with round tops like cumulus congestus.
- Cumulonimbus capillatus (WMO genus and species) – Cb with cirriform top.
- Cumulonimbus incus (WMO genus and supplementary feature) – Cb capillatus with anvil top.
- Cumulonimbus mamma (WMO genus and supplementary feature) – Cb with pouch-like protrusions that hang from under anvil or cloud base.
- Cumulonimbus pannus (WMO genus and accessory cloud) – shredded sections attached to main Cb cloud.
- Cumulonimbus pileus (WMO genus and accessory cloud) – capped, hood-shaped cloud above a cumulonimbus cloud.
- Cumulonimbus praecipitatio (WMO genus and supplementary feature) – Cb whose precipitation reaches the ground.
- Cumulonimbus tuba (WMO genus and supplementary feature) – column hanging from the bottom of cumulonimbus.
- Debris cloud (informal term) – rotating "cloud" of debris found at base of tornado.
- Funnel cloud (WMO supplementary feature tuba) – rotating funnel of cloud hanging from under Cb, not making contact with ground.
- Hail fog (informal term) – a shallow surface layer of fog that sometimes forms in vicinity of deep hail accumulation, can be very dense.
- Hot tower (informal term) - a tropical cumulonimbus cloud that penetrates the tropopause.
- Inflow band (informal term) – a laminar band marking inflow to a Cb, can occur at lower or mid levels of the cloud.
- Inverted cumulus (informal variation of WMO supplementary feature mamma) – cumulus which has transferred momentum from an exceptionally intense Cb tower and is convectively growing on the underside of an anvil.
- Knuckles (informal variation of WMO supplementary feature mamma) – lumpy protrusion that hangs from edge or underside of anvil.
- Pyrocumulus and Pyrocumulonimbus– intense ground-heat cloud proposed for WMO classification (see above).
- Rope – (slang) narrow, sometimes twisted funnel type cloud seen after a tornado dissipates.
- Rope cloud (informal term) – A narrow, long, elongated lines of cumulus cloud formation that develop at the leading edge of an advancing cold front or weather fronts that is often visible in satellite imagery.[17]
- Scud cloud (informal term for WMO species fractus) – ragged detached portions of cloud that usually form in precipitation.
- Shelf cloud (informal term for WMO supplementary feature arcus) – wedge-shaped cloud often attached to the underside of Cb.
- Stratus fractus (WMO genus and species) – ragged detached portions of stratus cloud that usually form in precipitation (see also scud cloud).
- Striations (informal term for WMO accessory cloud velum) – a groove or band of clouds encircling an updraft tower, indicative of rotation.
- Tail cloud (informal term) – an area of condensation consisting of laminar band and cloud tags extending from a wall cloud towards a precipitation core.
- Towering cumulus (TCu) -aviation term for WMO genus and species cumulus congestus, a large cumulus cloud with great vertical development, usually with a cauliflower-like appearance, but lacking the characteristic anvil of a Cb.
- Wall cloud (informal term) – distinctive fairly large lowering of the rain-free base of a Cb, often rotating.
Other planets
Venus
Thick overcast clouds of sulfur dioxide in three main layers at altitudes of 45 to 65 km that obscure the planet's surface and can produce virga.[18]
Stratiform
Overcast opaque clouds sheets.
Stratocumuliform
Wave clouds with clear gaps through which lower stratiform layers may be seen.[19]
Cumuliform and cumulonimbiform
Embedded convective cells that can produce lightning.
Mars
Clouds resembling several terrestrial types can be seen over Mars and are believed to be composed of water-ice.[20][21]
Extremely high cirriform
Noctilucent clouds are known to form near the poles at altitudes similar to or higher than the same type of clouds over Earth.[22]
High cirriform
Thin scattered wispy cloud resembling cirrus through which the planet's surface can be seen.
High stratocumuliform
Thin scattered wave-cloud resembling cirrocumulus.
Low stratocumuliform
Wave-cloud resembling stratocumulus, especially as a polar cap cloud over the winter pole which is mostly composed of suspended frozen carbon dioxide.[20][21]
Surface-based
Morning fog of water and/or carbon dioxide commonly forms in low areas of the planet.
Jupiter and Saturn
Cloud decks in parallel latitudinal bands at and below the tropopause alternatingly composed of ammonia crystals and ammonium hydrosulfate.
Cirriform
Bands of cloud resembling cirrus located mainly in the highest of three main layers that cover Jupiter.[23]
Stratiform and Stratocumuliform
Wave and haze clouds that are seen mostly in the middle layer.
Cumuliform and cumulonimbiform
Convective clouds in the lowest layer that are capable of producing thunderstorms and may be composed at least partly of water droplets.[24] an intermediate deck of ammonium hydrosulfide, and an inner deck of cumulus water clouds.[25][26]
Uranus and Neptune
Clouds layers made mostly of methane gas.[27]
Cirriform
High wispy formations resembling cirrus.
Stratiform
Layers of haze-cloud that lack any distinct features.
Cumuliform and cumulonimbiform
Lower-based convective clouds that can produce thunderstorms.[27]
Notes and references
- ↑ World Meteorological Organization, ed. (1975). Noctilucent, International Cloud Atlas (PDF). I. p. 66. ISBN 92-63-10407-7. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ Michael Gadsden & Pekka Parviainen (September 2006). Observing Noctilucent Clouds (PDF). International Association of Geomagnetism & Aeronomy. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 October 2008. Retrieved 31 January 2011.
- 1 2 Les Cowley (2011). "Nacreous and polar stratospheric clouds". Atmospheric optics, atoptics.co.uk. Retrieved 7 November 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Clouds Online (2012). "Cloud Atlas". Retrieved 1 February 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 JetStream (5 January 2010). "Cloud Classifications". National Weather Service. Retrieved 31 January 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Boyd, Sylke (2008). "Clouds – Species and Varieties". University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on December 30, 2010. Retrieved 4 February 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Aerographer/Meteorology (2012). "Cloud Variety". meteorologytraining.tpub.com. Archived from the original on 21 December 2012. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 World Meteorological Organization, ed. (1975). Features, International Cloud Atlas (PDF). I. pp. 22–24. ISBN 92-63-10407-7. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ Burroughs, William James; Crowder, Bob (January 2007). Weather, p.216. Fog City Press, San Francisco. ISBN 978-1-74089-579-8.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 World Meteorological Organization, ed. (1975). Species, International Cloud Atlas (PDF). I. pp. 17–20. ISBN 92-63-10407-7. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ Burroughs, William James; Crowder, Bob (January 2007). Weather, p.215. Fog City Press, San Francisco. ISBN 978-1-74089-579-8.
- ↑ "Cumulonimbus Incus". Universities Space Research Association. 5 August 2009. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ↑ Paul de Valk; Rudolf van Westhrenen & Cintia Carbajal Henken (2010). "Automated CB and TCU detection using radar and satellite data: from research to application" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-11-16. Retrieved 2011-09-15.
- ↑ World Meteorological Organization (1995). "Cloud Atlas" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-08-26.
- ↑ Cumulus-skynews (2013). "Clouds: Their curious natures". Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ Task Team On Revision of the International Cloud Atlas (2013). "Final Report" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 2014-10-06.
- ↑ http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/archives/555
- ↑ Franck Montmessin (2013). "Clouds in the terrestrial planets" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-05-16. Retrieved 2013-11-05.
- ↑ David Shiga (2006). "Mysterious waves seen in Venus's clouds". New Scientist. Retrieved 2013-11-05.
- 1 2 "Clouds Move Across Mars Horizon". Phoenix Photographs. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. 19 September 2008. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- 1 2 "NASA SP-441: Viking Orbiter Views of Mars". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved 26 January 2013.
- ↑ SPACE.com staff (2006-08-28). "Mars Clouds Higher Than Any On Earth". SPACE.com. Retrieved 2008-10-19.
- ↑ Phillips, Tony (20 May 2010). "Big Mystery: Jupiter Loses a Stripe". Nasa Headline News – 2010. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ↑ Dougherty & Esposito 2009, p. 118
- ↑ A.P. Ingersoll; T.E. Dowling; P.J. Gierasch; G.S. Orton; P.L. Read; A. Sanchez-Lavega; A.P. Showman; A.A. Simon-Miller; A.R. Vasavada. "Dynamics of Jupiter's Atmosphere" (PDF). Lunar & Planetary Institute. Retrieved 2007-02-01.
- ↑ Monterrey Institute for Research in Astronomy (2006-08-11). "Saturn". Retrieved 2011-01-31.
- 1 2 Nola Taylor Redd (2012). "Neptune's Atmosphere: Composition, Climate, & Weather". Space.com. Retrieved 2013-11-05.
See also
External links
- http://nephology.eu International Cloud Atlas online
- Introduction to Clouds (National Weather Service)
- Ten Basic Cloud Types (National Weather Service)
- Cloud Appreciation Society
- Texas A&M Cloud Glossary
- Cloud-identification site
- UK Met Office cloud classification page
- Cloud Atlas (Atlas Chmur) (in Polish)
- NOAA