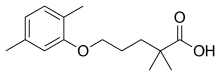
Gemfibrozil
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lopid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a686002 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Close to 100% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP3A4) |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion |
Renal 94% Feces 6% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.042.968 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H22O3 |
| Molar mass | 250.333 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 61 to 63 °C (142 to 145 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Gemfibrozil is the generic name for an oral drug used to lower lipid levels. It belongs to a group of drugs known as fibrates. It is most commonly sold as the brand name, Lopid. Other brand names include Jezil and Gen-Fibro.
Development history
Gemfibrozil was selected from a series of related compounds synthesized in the laboratories of the American company Parke-Davis in the late 1970s. It came from research for compounds that lower plasma lipid levels in humans and in animals.[1]
Actions
The exact mechanism of action of gemfibrozil is unknown; however, several theories exist regarding the very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) effect; it can inhibit lipolysis and decrease subsequent hepatic fatty acid uptake as well as inhibit hepatic secretion of VLDL; together these actions decrease serum VLDL levels and increase HDL-cholesterol; the mechanism behind HDL elevation is currently unknown.
Gemfibrozil increases the activity of extrahepatic lipoprotein lipase (LL), thereby increasing lipoprotein triglyceride lipolysis. It does so by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) 'transcription factor ligand', a receptor that is involved in metabolism of carbohydrates and fats, as well as adipose tissue differentiation. This increase in the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase thereby increases the clearance of triglycerides. Chylomicrons are degraded, VLDLs are converted to LDLs, and LDLs are converted to HDL. This is accompanied by a slight increase in secretion of lipids into the bile and ultimately the intestine. Gemfibrozil also inhibits the synthesis and increases the clearance of apolipoprotein B, a carrier molecule for VLDL.[2]
Therapeutic effects
- Reduce triglyceride levels [3]
- Reduce very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) levels
- Modest reduction of low density lipoprotein (LDL) levels
- Moderate increase in high density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
Side effects and toxicities
- GI distress
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Increased incidence of gallstone
- Hypokalemia (low blood potassium)
- Increased risk of cancer
Indications
- Hyperlipidemia (Type III): Gemfibrozil is the drug of choice for therapy.
- Hypertriglyceridemia (Type IV): Gemfibrozil, though not as effective as niacin, is better tolerated.
Contraindications and precautions
- Gemfibrozil should not be given to these patients:
- Hepatic dysfunction
- Gemfibrozil should be used with caution in these higher risk categories:
- Biliary tract disease
- Renal dysfunction
- Pregnant women
- Obese patients
Drug interactions
- Anticoagulants: Gemfibrozil potentiates the action of warfarin and indanedione anticoagulants.
- Statin drugs: Concomitant administration of fibrates (including gemfibrozil) with statin drugs increases the risk of muscle cramping, myopathy, and rhabdomyolysis.
- Gemfibrozil inhibits the activation of the liver's Cytochrome P450 system and CYP2C8, reducing hepatic metabolism of many drugs, and prolonging their half lives and duration of action.
- Drugs metabolized by the Cytochrome P450 system include:
- Many antidepressants
- Many antipsychotics
- Many antiepileptics
- Theophylline and other methylxanthine drugs
- Several anesthetic agents
- Oral contraceptive pills
- Statins
- Warfarin
- Selexipag
- Drugs metabolized by the Cytochrome P450 system include:
Environmental data
Gemfibrozil has been detected in biosolids (the solids remaining after sewage treatment) at concentrations up to 2650 ng/g wet weight.[4] This indicates that it survives the wastewater treatment process. It is also detected as environmental persistent micropollutant in aquifers and in groundwaters in karstic areas.[5]
References
- ↑ Rodney, G; et al. (1976). "The Hypolipidemic Effect of Gemfibrozil (CI-719) in Laboratory Animals". Proc. R. Soc. Med. 69 (Supplement 2): 6–9. PMC 1864017. PMID 828263.
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/gemfibrozil#section=Mechanism-of-Action
- ↑ "Gemfibrozil." WebMD.com Accessed 14 June 2014. http://www.webmd.com/drugs/drug-11423-gemfibrozil+oral.aspx
- ↑ http://water.epa.gov/scitech/wastetech/biosolids/tnsss-overview.cfm
- ↑ Doummar, Joanna; Aoun, Michel (2018-08-01). "Assessment of the origin and transport of four selected emerging micropollutants sucralose, Acesulfame-K, gemfibrozil, and iohexol in a karst spring during a multi-event spring response". Journal of Contaminant Hydrology. 215: 11–20. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2018.06.003. ISSN 0169-7722.
External links
- DrugBank Gemfibrozil
- NIH Gemfibrozil Drug Info
- Lopid International Study
- Author (2004). "Safety of Statins". Circulation. 109: III-50–III-57. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000131519.15067.1f. PMID 15198967.
- http://www.ihs.gov/nptc/documents/NPTC%20Lipid%20Review.pdf