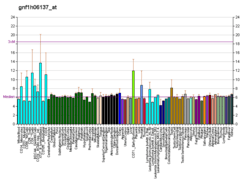
Cyclin B2
G2/mitotic-specific cyclin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNB2 gene.
Function
Cyclin B2 is a member of the cyclin family, specifically the B-type cyclins. The B-type cyclins, B1 and B2, associate with p34cdc2 and are essential components of the cell cycle regulatory machinery. B1 and B2 differ in their subcellular localization. Cyclin B1 co-localizes with microtubules, whereas cyclin B2 is primarily associated with the Golgi region. Cyclin B2 also binds to transforming growth factor beta RII and thus cyclin B2/cdc2 may play a key role in transforming growth factor beta-mediated cell cycle control.[5]
Interactions
Cyclin B2 has been shown to interact with TGF beta receptor 2.[6]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000157456 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032218 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CCNB2 cyclin B2".
- ↑ Liu JH, Wei S, Burnette PK, Gamero AM, Hutton M, Djeu JY (Jan 1999). "Functional association of TGF-beta receptor II with cyclin B". Oncogene. 18 (1): 269–75. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202263. PMID 9926943.
Further reading
- He J, Choe S, Walker R, Di Marzio P, Morgan DO, Landau NR (1995). "Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral protein R (Vpr) arrests cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting p34cdc2 activity". J. Virol. 69 (11): 6705–11. PMC 189580. PMID 7474080.
- Re F, Braaten D, Franke EK, Luban J (1995). "Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr arrests the cell cycle in G2 by inhibiting the activation of p34cdc2-cyclin B". J. Virol. 69 (11): 6859–64. PMC 189600. PMID 7474100.
- Di Marzio P, Choe S, Ebright M, Knoblauch R, Landau NR (1995). "Mutational analysis of cell cycle arrest, nuclear localization and virion packaging of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr". J. Virol. 69 (12): 7909–16. PMC 189735. PMID 7494303.
- Jowett JB, Planelles V, Poon B, Shah NP, Chen ML, Chen IS (1995). "The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpr gene arrests infected T cells in the G2 + M phase of the cell cycle". J. Virol. 69 (10): 6304–13. PMC 189529. PMID 7666531.
- Jackman M, Firth M, Pines J (1995). "Human cyclins B1 and B2 are localized to strikingly different structures: B1 to microtubules, B2 primarily to the Golgi apparatus". EMBO J. 14 (8): 1646–54. PMC 398257. PMID 7737117.
- Pines J, Hunter T (1994). "The differential localization of human cyclins A and B is due to a cytoplasmic retention signal in cyclin B". EMBO J. 13 (16): 3772–81. PMC 395290. PMID 8070405.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Poon B, Jowett JB, Stewart SA, Armstrong RW, Rishton GM, Chen IS (1997). "Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpr gene induces phenotypic effects similar to those of the DNA alkylating agent, nitrogen mustard". J. Virol. 71 (5): 3961–71. PMC 191548. PMID 9094673.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Mahalingam S, Ayyavoo V, Patel M, Kieber-Emmons T, Kao GD, Muschel RJ, Weiner DB (1998). "HIV-1 Vpr interacts with a human 34-kDa mov34 homologue, a cellular factor linked to the G2/M phase transition of the mammalian cell cycle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (7): 3419–24. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.7.3419. PMC 19851. PMID 9520381.
- Brandeis M, Rosewell I, Carrington M, Crompton T, Jacobs MA, Kirk J, Gannon J, Hunt T (1998). "Cyclin B2-null mice develop normally and are fertile whereas cyclin B1-null mice die in utero". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (8): 4344–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.8.4344. PMC 22491. PMID 9539739.
- Felzien LK, Woffendin C, Hottiger MO, Subbramanian RA, Cohen EA, Nabel GJ (1998). "HIV transcriptional activation by the accessory protein, VPR, is mediated by the p300 co-activator". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95 (9): 5281–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.9.5281. PMC 20252. PMID 9560267.
- Liu JH, Wei S, Burnette PK, Gamero AM, Hutton M, Djeu JY (1999). "Functional association of TGF-beta receptor II with cyclin B". Oncogene. 18 (1): 269–75. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202263. PMID 9926943.
- Elder RT, Yu M, Chen M, Edelson S, Zhao Y (2000). "Cell cycle G2 arrest induced by HIV-1 Vpr in fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) is independent of cell death and early genes in the DNA damage checkpoint". Virus Res. 68 (2): 161–73. doi:10.1016/S0168-1702(00)00167-2. PMID 10958988.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, Böcher M, Blöcker H, Bauersachs S, Blum H, Lauber J, Düsterhöft A, Beyer A, Köhrer K, Strack N, Mewes HW, Ottenwälder B, Obermaier B, Tampe J, Heubner D, Wambutt R, Korn B, Klein M, Poustka A (2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, Pepperkok R, Wiemann S (2000). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- Elder RT, Yu M, Chen M, Zhu X, Yanagida M, Zhao Y (2001). "HIV-1 Vpr induces cell cycle G2 arrest in fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) through a pathway involving regulatory and catalytic subunits of PP2A and acting on both Wee1 and Cdc25". Virology. 287 (2): 359–70. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1007. PMID 11531413.
- Mouland AJ, Coady M, Yao XJ, Cohen EA (2002). "Hypophosphorylation of poly(A) polymerase and increased polyadenylation activity are associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr expression". Virology. 292 (2): 321–30. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1261. PMID 11878934.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.