Battle of Ain Jalut
| Battle of Ain Jalut | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mongol invasions of the Levant | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
| Kitbuga † | ||||||||
| Units involved | |||||||||
| Light cavalry and horse archers, heavy cavalry, infantry | Mongol lancers and horse archers, Cilician Armenian troops, Georgian contingent, local Ayyubid contingents | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| 15,000-20,000[2][3][4] | 10,000-12,000[5][6][7][8] | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Heavy | Destruction of the Mongol force | ||||||||
 | |
| Coordinates | 32°33′01″N 35°21′22″E / 32.550354°N 35.356032°E |
|---|---|
The Battle of Ain Jalut (Ayn Jalut, in Arabic: عين جالوت, the "Spring of Goliath", or Harod Spring, in Hebrew: מעין חרוד) took place in September 1260 between Muslim Mamluks and the Mongols in the southeastern Galilee, in the Jezreel Valley, in the vicinity of Nazareth,[9] not far from the site of Zir'in.
Preceding events
When Möngke Khan became Great Khan in 1251, he immediately set out to implement his grandfather Genghis Khan's plan for world empire. To lead the task of subduing the nations of the West, he selected his brother, another of Genghis Khan's grandsons, Hulagu Khan.[10]
Assembling the army took five years, and it was not until 1256 that Hulagu was prepared to begin the invasions. Operating from the Mongol base in Persia, Hulagu proceeded south. Möngke Khan had ordered good treatment for those who yielded without resistance, and destruction for those who did not. In this way Hulagu and his army had conquered some of the most powerful and longstanding dynasties of the time. Other countries in the Mongols' path submitted to Mongol authority, and contributed forces to the Mongol army. By the time that the Mongols reached Baghdad, their army included Cilician Armenians, and even some Frankish forces from the submissive Principality of Antioch. The Hashshashin in Persia fell, the 500-year-old Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad was destroyed (see Battle of Baghdad), and so too fell the Ayyubid dynasty in Damascus. Hulagu's plan was to then proceed southwards through the Kingdom of Jerusalem towards the Mamluk Sultanate, to confront the major Islamic power.[10]
During the Mongol attack on the Mamluks in the Middle East, most of the Mamluks were Kipchaks, and the Golden Horde's supply of Kipchaks replenished the Mamluk armies and helped them fight off the Mongols.[11]
Mongol envoys to Egypt
In 1260, Hulagu sent envoys to Qutuz in Cairo, demanding his surrender:
| “ | From the King of Kings of the East and West, the Great Khan. To Qutuz the Mamluk, who fled to escape our swords. You should think of what happened to other countries and submit to us. You have heard how we have conquered a vast empire and have purified the earth of the disorders that tainted it. We have conquered vast areas, massacring all the people. You cannot escape from the terror of our armies. Where can you flee? What road will you use to escape us? Our horses are swift, our arrows sharp, our swords like thunderbolts, our hearts as hard as the mountains, our soldiers as numerous as the sand. Fortresses will not detain us, nor armies stop us. Your prayers to God will not avail against us. We are not moved by tears nor touched by lamentations. Only those who beg our protection will be safe. Hasten your reply before the fire of war is kindled. Resist and you will suffer the most terrible catastrophes. We will shatter your mosques and reveal the weakness of your God and then will kill your children and your old men together. At present you are the only enemy against whom we have to march. | ” |
| — Hulagu, [12] | ||
Qutuz responded, however, by killing the envoys and displaying their heads on Bab Zuweila, one of the gates of Cairo.[10]
The campaign
Shortly before the battle, Hulegu withdrew from the Levant with the bulk of his army, leaving his forces west of the Euphrates with only one tumen (nominally 10,000 men but usually smaller),[2][7] and a handful of vassal troops under the Nestorian Christian Naiman Kitbuqa Noyan.[13] Contemporary Mamluk chronicler Al-Yunini's "Dhayl Mirat Al-Zaman" states that the Mongol army under Kitbuga, including vassals, numbered 100,000 men in total, but this was likely an exaggeration.[14] Until the late 20th century historians believed that Hulagu's sudden retreat was because the power dynamic had changed due to the death of the Great Khan Möngke on an expedition to China, requiring Hulagu and other senior Mongols to return home to decide upon his successor. However, contemporary documentation discovered in the 1980s reveals this to be untrue, as Hulagu himself claimed that he withdrew most of his forces because he could not sustain such a large army logistically, saying that the fodder in the region had been mostly used up and that it was a Mongol custom to withdraw to cooler lands for the summer.[15]
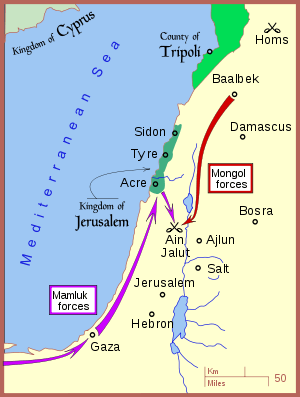
Upon receiving news of Hulagu's departure, Mamluk Sultan Qutuz quickly assembled a large army at Cairo and invaded Palestine.[16] In late August, Kitbuqa's forces proceeded south from their base at Baalbek, passing to the east of Lake Tiberias into Lower Galilee.
The Mamluk Sultan Qutuz at that time allied with a fellow Mamluk, Baibars, who chose to ally himself with Qutuz in the face of a greater enemy, after the Mongols captured Damascus and most of Bilad al-Sham.[17]
The Mongols, for their part, attempted to form a Franco-Mongol alliance with (or at least demand the submission of) the remnant of the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem, now centered on Acre; but Pope Alexander IV had forbidden this. Tensions between Franks and Mongols had also increased when Julian of Sidon caused an incident which resulted in the death of one of Kitbuqa's grandsons. Angered, Kitbuqa sacked Sidon. The Barons of Acre and the remainder of the Crusader outposts, contacted by the Mongols, had also been approached by the Mamluks, seeking military assistance against the Mongols.[17]
Though the Mamluks were the traditional enemies of the Franks, the Barons of Acre recognized the Mongols as the more immediate menace, and so the Crusaders opted for a position of cautious neutrality between the two forces.[18] In an unusual move, they agreed that the Egyptian Mamluks could march north through the Crusader territories unmolested, and even camp to resupply near Acre. When news arrived that the Mongols had crossed the Jordan River, Sultan Qutuz and his forces proceeded southeast toward the spring at Ain Jalut in the Jezreel Valley.[19]
The battle

The first to advance were the Mongols, whose force also included troops from the Kingdom of Georgia and about 500 troops from the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, both of which had submitted to Mongol authority. The Mamluks had the advantage of knowledge of the terrain, and Qutuz capitalized on this by hiding the bulk of his force in the highlands, hoping to bait the Mongols with a smaller force under Baibars.
The two armies fought for many hours, with Baibars most of the time implementing hit-and-run tactics, in order to provoke the Mongol troops and at the same time preserve the bulk of his troops intact. When the Mongols carried out another heavy assault, Baibars – who it is said had laid out the overall strategy of the battle since he had spent much time in that region, earlier in his life, as a fugitive – and his men feigned a final retreat, drawing the Mongols into the highlands to be ambushed by the rest of the Mamluk forces concealed among the trees. The Mongol leader Kitbuqa, already provoked by the constant fleeing of Baibars and his troops, committed a grave mistake; instead of suspecting a trick, Kitbuqa decided to march forwards with all his troops on the trail of the fleeing Mamluks. When the Mongols reached the highlands, Mamluk forces emerged from hiding and began to fire arrows and attack with their cavalry. The Mongols then found themselves surrounded on all sides. Additionally, Timothy May hypothesizes that a key moment in the battle was the defection of the Mongol Syrian allies.[20]
The Mongol army fought very fiercely and very aggressively to break out. Some distance away, Qutuz watched with his private legion. When Qutuz saw the left wing of the Mamluk army almost destroyed by the desperate Mongols seeking an escape route, Qutuz threw away his combat helmet, so that his warriors could recognize him. He was seen the next moment rushing fiercely towards the battlefield yelling "wa islamah!" ("Oh my Islam"), urging his army to keep firm, and advanced towards the weakened side, followed by his own unit. The Mongols were pushed back and fled to a vicinity of Bisan, followed by Qutuz's forces, but they managed to reorganize and return to the battlefield, making a successful counterattack. However, the battle shifted in favor of the Mamluks, who now had both the geographic and psychological advantage, and eventually some of the Mongols were forced to retreat. Kitbuqa and almost the whole Mongol army that had remained in the region perished.
Aftermath
On the way back to Cairo after the victory at Ain Jalut, Qutuz was assassinated by several emirs in a conspiracy led by Baibars.[21] Baibars became the new Sultan. Local Ayyubid emirs sworn to the Mamluk sultunate subsequently defeated another Mongol force of 6,000 at Homs, which ended the first Mongol expedition into Syria. Baibars and his successors would go on to capture the last of the Crusader states in The Holy Land by 1291.
Internecine conflict prevented Hulagu Khan from being able to bring his full power against the Mamluks to avenge the pivotal defeat at Ain Jalut. Berke Khan, the Khan of the Golden Horde to the north of Ilkhanate, had converted to Islam, and watched with horror as his cousin destroyed the Abbasid Caliph, the spiritual head of Islam. Muslim historian Rashid-al-Din Hamadani quoted Berke as sending the following message to Mongke Khan, protesting the attack on Baghdad (not knowing Mongke had died in China): "He (Hulagu) has sacked all the cities of the Muslims, and has brought about the death of the Caliph. With the help of God I will call him to account for so much innocent blood."[22] The Mamluks, learning through spies that Berke was both a Muslim and not fond of his cousin, were careful to nourish their ties to him and his Khanate.
After the Mongol succession was finally settled, with Kublai as the last Great Khan, Hulagu returned to his lands by 1262, and massed his armies to attack the Mamluks and avenge Ain Jalut. However, Berke Khan initiated a series of raids in force which lured Hulagu north, away from the Levant to meet him. Hulagu suffered severe defeat in an attempted invasion north of the Caucasus in 1263. This was the first open war between Mongols, and signaled the end of the unified empire.
Hulagu was able to send only a small army of two tumens in his sole attempt to attack the Mamluks after Ain Jalut, and it was repulsed. Hulagu Khan died in 1265 and was succeeded by his son Abaqa.
Legacy
Due to the large number of sources in vastly different languages Mongol historians have generally focused on one limited aspect of the empire. From this standpoint, the Battle of Ain Jalut has been represented by numerous academic and popular historians as an epochal battle that was the first time the Mongol advance had been permanently halted, and even their first major defeat.[17][23] However, Ain Jalut, placed in the broader scope of the Mongol conquests in more comprehensive recent research, was actually not a first or as pivotal as these earlier histories portrayed it to be.
The Mongols had been defeated several times before Ain Jalut, not even including Temujin's defeats to Jamuqa and the Kerait's during the Mongol wars of unification. The Mongol general Boro'qul was ambushed and killed by the Siberian Tumad tribe sometime during the 1215-1217 period, which prompted Genghis to send Dorbei Doqshin who outmaneuvered and captured the Tumad tribe.[24] In 1221, Shigi Qutugu was defeated by Jalal al-Din during the Mongol conquest of the Khwarezmian Empire at the battle of Parwan. As a result, Genghis Khan himself made forced marches to bring the Sultan Jalal al-Din to battle and annihilated him at the battle of Indus. During the initial reign of Ogedei Khan, his general Dolqolqu was heavily defeated by the Jin generals Wan Yen-Yi and Pu'a. In response, Ogedei dispatched the legendary Subutai and after encountering fierce resistance, the Mongols brought their entire army to bear under a vast encirclement of the Jin Empire by separate armies under Ogedei, Tolui, and Subutai.[25] The Jin armies were decisively defeated and Subutai conquered Kaifeng in 1233, effectively dooming the Jin Dynasty.
Additionally, Ain Jalut did not mark the limit of Mongol expansion or show an end to their conquests. In 1299, the Ilkhanid army under Ghazan Khan decisively defeated the Mamluks at Battle of Wadi al-Khazandar, capturing Damascus, and pursuing as far as Gaza. However, a combination of poor pasturage and the ongoing war against the Chagatai Khanate forced Ghazan to recall his army to northeast Iran. After that campaign ended, he sent another smaller force back into Syria, but this was defeated at the much more important Battle of Marj al-Saffar in 1303. This was the battle that marked the limits of Mongol expansion. Due to the war against the Chagatai's and his failing health, Ghazan was unable to launch a counteroffensive before he died in 1305.
Put in proper perspective, Ain Jalut actually was the first time a Mongol detachment was defeated and did not immediately return with a stronger army to avenge their loss. Though it was only a minor defeat in the grand scheme, it showed a problem that would continually plague future Mongol attempts at expansion. Mongol forces looking to attack or exact revenge were often diverted due to the death of a key Khan, or greater priority was given to fighting off opposing Mongol khanates.
Battle of Ain Jalut in fiction
Robert Shea's historical novel The Saracen deals extensively with the Battle of Ain Jalut and the subsequent assassination of Sultan Qutuz.
Notes
- ↑ Encyclopedia Grammatica
- 1 2 John, Simon (2014). Crusading and warfare in the Middle Ages : realities and representations. Burlington, VT: Ashgate Publishing Limited. ISBN 9781472407412.
- ↑ D. Nicolle, The Mongol Warlords: Genghis Khan, Kublai Khan, Hülägü, Tamerlane. Plates by R. Hook, Firebird books: Pole 1990, p. 116.
- ↑ Waterson, p. 75
- ↑ Amitai-Preiss, p. 27
- ↑ Smith Jr, J. M. (1984). Ayn Jālūt: Mamlūk Success or Mongol Failure?. Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, p.310.
- 1 2 Blair, S. (1995). A compendium of chronicles: Rashid al-Din's illustrated history of the world. Nour Foundation.
- ↑ John Masson Smith, Jr. (1984) Mongol Armies And Indian Campaigns, University of California, Berkeley.
- ↑ "Baybars, Al-Zahir", http://encyclopedia.com/history/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/baybars-al-zahir . Accessed 2018 May 7.
- 1 2 3 Man, John (2006). Kublai Khan: From Xanadu to Superpower. London: Bantam. pp. 74–87. ISBN 978-0-553-81718-8.
- ↑ Halperin, Charles J. 2000. “The Kipchak Connection: The Ilkhans, the Mamluks and Ayn Jalut”. Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London 63 (2). Cambridge University Press: 229–45. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1559539.
- ↑ Tschanz, David W. "Saudi Aramco World : History's Hinge: 'Ain Jalut".
- ↑ René Grousset (1970). The Empire of the Steppes: A History of Central Asia. Rutgers University Press. pp. 361, 363. ISBN 0-8135-1304-9.
- ↑ Yunini, "Dhayl," Vol. 4, p. 93.
- ↑ Paul Meyvaert, “An Unknown Letter of Hulagu, Il-khan of Persia, to King Louis IX of France,” Viator 11 (1980): 258; 249.
- ↑ p. 424, 'The Collins Encyclopedia of Military History' (4th edition, 1993), Dupuy & Dupuy,
- 1 2 3 Tschanz, David W. "Saudi Aramco World : History's Hinge: 'Ain Jalut".
- ↑ Morgan, p. 137.
- ↑ Bartlett, p. 253
- ↑ Timothy May, the Mongol Art of War (2016).
- ↑ Although medieval historians give conflicting accounts, modern historians assign responsibility for Qutuz's assassination to Baibars, as Baibars had been promised Syria as a reward for his efforts in Ain Jalut but when it was time to claim his prize, Qutuz commanded him to be patient. See Perry (p. 150), Amitai-Preiss (p. 47, "a conspiracy of amirs, which included Baybars and was probably under his leadership"), Holt et al. (Baibars "came to power with [the] regicide [of Qutuz] on his conscience"), and Tschanz. For further discussion, see article on "Qutuz".
- ↑ The Mongol Warlords quotes Rashid al Din's record of Berke Khan's pronouncement; this quote is also found in Amitai-Preiss's The Mamluk-Ilkhanid War.
- ↑ Jack Weatherford, Genghis Khan and the Making of the Modern World.
- ↑ Timothy May, The Mongol Empire: A Historical Encyclopedia, 203-4.
- ↑ Christopher P. Atwood, Pu'a's Boast and Doqolqu's Death: Historiography of a Hidden Scandal in the Mongol Conquest of the Jin.
References
- Al-Maqrizi, Al Selouk Leme'refatt Dewall al-Melouk, Dar al-kotob, 1997.
- Bohn, Henry G. (1848) The Road to Knowledge of the Return of Kings, Chronicles of the Crusades, AMS Press, New York, 1969 edition, a translation of Chronicles of the Crusades : being contemporary narratives of the crusade of Richard Coeur de Lion by Richard of Devizes and Geoffrey de Vinsauf and of the crusade of St. Louis, by Lord John de Joinville.
- Amitai-Preiss, Reuven (1995). Mongols and Mamluks: The Mamluk-Ilkhanid War, 1260–1281. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. ISBN 978-0-521-46226-6.
- Bartlett, W. B. (1999). God Wills It! – An Illustrated History of the Crusades. Sutton Publishing Limited. ISBN 0-7509-1880-2.
- Eric H. Cline (2002). The Battles of Armageddon. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-06739-7.
- Robert Cowley; Geoffrey Parker (2001). The Reader's Companion to Military History. Houghton Mifflin. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-618-12742-9. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- J. D. Fage; Roland Anthony Oliver (1975). The Cambridge History of Africa. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-20981-1.
- Grousset, René (1991), Histoire des Croisades, III, Editions Perrin, ISBN 2-262-02569-X.
- Hildinger, Erik. (1997). Warriors of the Steppe. Sarpedon Publishing. ISBN 0-306-81065-4
- Holt, P. M.; Lambton, Ann; Lewis, Bernard (1977) The Cambridge History of Islam, Vol. 1A: The Central Islamic Lands from Pre-Islamic Times to the First World War, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-29135-4.
- Morgan, David (1990) The Mongols. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-17563-6
- Nicolle, David, (1998). The Mongol Warlords Brockhampton Press.
- Perry, Glenn E. (2004) The History of Egypt, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN 978-0-313-32264-8.
- Reagan, Geoffry, (1992). The Guinness Book of Decisive Battles . Canopy Books, NY.
- Saunders, J. J. (1971) The History of the Mongol Conquests, Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd. ISBN 0-8122-1766-7
- Sicker, Martin (2000) The Islamic World in Ascendancy: From the Arab Conquests to the Siege of Vienna, Praeger Publishers.
- Soucek, Svatopluk (2000) A History of Inner Asia, Cambridge University Press.
- Tschanz, David W. (July–August 2007). "History's Hinge: 'Ain Jalut". Saudi Aramco World. Archived from the original on 12 September 2007. Retrieved 2007-09-24. 4
- Blair, S. (1995). A compendium of chronicles: Rashid al-Din's illustrated history of the world. Nour Foundation.
- John Masson Smith, Jr. (1984) MONGOL ARMIES AND INDIAN CAMPAIGNS, University of California, Berkeley
- Smith Jr, J. M. (1984). Ayn Jālūt: Mamlūk Success or Mongol Failure?. Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, 307-345.
- Waterson, James (2007) The Knights of Islam: The Wars of the Mamluks. Greenhill Books, London. ISBN 978-1-85367-734-2