Barranbinya
The Barranbinya, also written Baranbinja,[1] were an indigenous Australian people of New South Wales.
Country
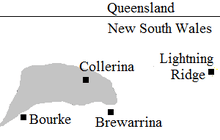
Map showing the traditional lands of the Baranbinya people
Barranbinya territory extended over an estimated 1,200 square miles (3,100 km2) along the northern bank of the Darling River from Bourke to Brewarrina.[1][lower-alpha 1]
Alternative names
- Barren-binya.
- Parran-binye.
- Burranbinya, Burrunbinya.
- Barrumbinya, Burrumbinya, Barrunbarga( typo)
- Burranbinga, Burrabinya.[1]
Notes
Citations
- 1 2 3 Tindale 1974, p. 191.
- ↑ Pechey 1872, p. 146.
- ↑ Honery 1878, p. 246.
Sources
- Honery, Thomas (1878). Ridley, William, ed. "Australian Languages and Traditions: Wailwun Language and Traditions". The Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland. 7: 232–274. JSTOR 2841001.
- Mathews, R. H. (1903). "Murrawarri and other Australian languages" (PDF). Queensland Geographical Journal. 18: 52–68.
- Mathews, R. H. (1907). "Initiation ceremonies of Murawarri and other aboriginal tribes of Queensland" (PDF). Queensland Geographical Journal. 22: 64–73.
- Oates, Lynette F. (1 January 1985). Barranbinya: Fragments of a N.S.W. Aboriginal language. Pacific Linguistics. Series A. Occasional Papers. Australian National University. pp. 185–204.
- Pechey, W. A (1872). "Vocabulary of the Cornu Tribes of Australia". The Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland. 1: 143–147. JSTOR 2840949.
- Tindale, Norman Barnett (1974). "Baranbinja (NSW)". Aboriginal Tribes of Australia: Their Terrain, Environmental Controls, Distribution, Limits, and Proper Names. Australian National University.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.