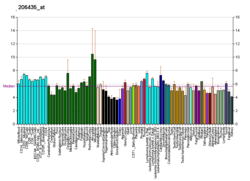
B4GALNT1
Beta-1,4 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B4GALNT1 gene.[5][6]
GM2 and GD2 gangliosides are sialic acid-containing glycosphingolipids. GalNAc-T is the enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of G(M2) and G(D2) glycosphingolipids. GalNAc-T catalyzes the transfer of GalNAc into G(M3) and G(D3) by a beta-1,4 linkage, resulting in the synthesis of G(M2) and G(D2), respectively.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000135454 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000006731 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Nagata Y, Yamashiro S, Yodoi J, Lloyd KO, Shiku H, Furukawa K (Jul 1992). "Expression cloning of beta 1,4 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase cDNAs that determine the expression of GM2 and GD2 gangliosides". J Biol Chem. 267 (17): 12082–9. PMID 1601877.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: B4GALNT1 beta-1,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 1".
External links
- Human B4GALNT1 genome location and B4GALNT1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Nagata Y, Yamashiro S, Yodoi J, et al. (1994). "Expression cloning of beta 1,4 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase cDNAs that determine the expression of GM2 and GD2 gangliosides". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (9): 7045. PMID 8120069.
- Meurer JA, Naylor JM, Baker CA, et al. (1996). "cDNA cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of a human UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase". J. Biochem. 118 (3): 568–74. PMID 8690719.
- Furukawa K, Soejima H, Niikawa N, Shiku H (1996). "Genomic organization and chromosomal assignment of the human beta1, 4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase gene. Identification of multiple transcription units". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (34): 20836–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.34.20836. PMID 8702839.
- Jaskiewicz E, Zhu G, Bassi R, et al. (1996). "Beta1,4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GM2 synthase) is released from Golgi membranes as a neuraminidase-sensitive, disulfide-bonded dimer by a cathepsin D-like protease". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (42): 26395–403. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.42.26395. PMID 8824296.
- Giraudo CG, Rosales Fritz VM, Maccioni HJ (1999). "GA2/GM2/GD2 synthase localizes to the trans-golgi network of CHO-K1 cells". Biochem. J. 342. Pt 3: 633–40. PMC 1220504. PMID 10477274.
- Toba S, Tenno M, Konishi M, et al. (2000). "Brain-specific expression of a novel human UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GalNAc-T9)". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1493 (1–2): 264–8. doi:10.1016/S0167-4781(00)00180-9. PMID 10978536.
- Li J, Yen TY, Allende ML, et al. (2001). "Disulfide bonds of GM2 synthase homodimers. Antiparallel orientation of the catalytic domains". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (52): 41476–86. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007480200. PMID 11018043.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Gornati R, Chini V, Rimoldi S, et al. (2007). "Evaluation of SAT-1, SAT-2 and GalNAcT-1 mRNA in colon cancer by real-time PCR". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 298 (1–2): 59–68. doi:10.1007/s11010-006-9350-0. PMID 17119850.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.