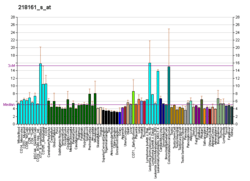
CLN6
Ceroid-lipofuscinosis neuronal protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLN6 gene.[5][6][7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000128973 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000032245 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Sharp JD, Wheeler RB, Lake BD, Savukoski M, Jarvela IE, Peltonen L, Gardiner RM, Williams RE (Jul 1997). "Loci for classical and a variant late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis map to chromosomes 11p15 and 15q21-23". Hum Mol Genet. 6 (4): 591–5. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.4.591. PMID 9097964.
- ↑ Wheeler RB, Sharp JD, Schultz RA, Joslin JM, Williams RE, Mole SE (Jan 2002). "The gene mutated in variant late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (CLN6) and in nclf mutant mice encodes a novel predicted transmembrane protein". Am J Hum Genet. 70 (2): 537–42. doi:10.1086/338708. PMC 384927. PMID 11727201.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CLN6 ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 6, late infantile, variant".
External links
- GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Neuronal Ceroid-Lipofuscinoses
- Human CLN6 genome location and CLN6 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Dawson G, Cho S (2000). "Batten's disease: clues to neuronal protein catabolism in lysosomes". J. Neurosci. Res. 60 (2): 133–40. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(20000415)60:2<133::AID-JNR1>3.0.CO;2-3. PMID 10740217.
- Holopainen JM, Saarikoski J, Kinnunen PK, Järvelä I (2001). "Elevated lysosomal pH in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs)". Eur. J. Biochem. 268 (22): 5851–6. doi:10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02530.x. PMID 11722572.
- Gao H, Boustany RM, Espinola JA, et al. (2002). "Mutations in a novel CLN6-encoded transmembrane protein cause variant neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis in man and mouse". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70 (2): 324–35. doi:10.1086/338190. PMC 384912. PMID 11791207.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Teixeira CA, Espinola J, Huo L, et al. (2003). "Novel mutations in the CLN6 gene causing a variant late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis". Hum. Mutat. 21 (5): 502–8. doi:10.1002/humu.10207. PMID 12673792.
- Sharp JD, Wheeler RB, Parker KA, et al. (2003). "Spectrum of CLN6 mutations in variant late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis". Hum. Mutat. 22 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1002/humu.10227. PMID 12815591.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Heine C, Koch B, Storch S, et al. (2004). "Defective endoplasmic reticulum-resident membrane protein CLN6 affects lysosomal degradation of endocytosed arylsulfatase A.". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (21): 22347–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400643200. PMID 15010453.
- Mole SE, Michaux G, Codlin S, et al. (2004). "CLN6, which is associated with a lysosomal storage disease, is an endoplasmic reticulum protein". Exp. Cell Res. 298 (2): 399–406. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.04.042. PMID 15265688.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Siintola E, Topcu M, Kohlschütter A, et al. (2005). "Two novel CLN6 mutations in variant late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis patients of Turkish origin". Clin. Genet. 68 (2): 167–73. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2005.00471.x. PMID 15996215.
- Otsuki T, Ota T, Nishikawa T, et al. (2007). "Signal sequence and keyword trap in silico for selection of full-length human cDNAs encoding secretion or membrane proteins from oligo-capped cDNA libraries". DNA Res. 12 (2): 117–26. doi:10.1093/dnares/12.2.117. PMID 16303743.
- Teixeira CA, Lin S, Mangas M, et al. (2006). "Gene expression profiling in vLINCL CLN6-deficient fibroblasts: Insights into pathobiology". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1762 (7): 637–46. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2006.06.002. PMID 16857350.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Heine C, Quitsch A, Storch S, et al. (2007). "Topology and endoplasmic reticulum retention signals of the lysosomal storage disease-related membrane protein CLN6". Mol. Membr. Biol. 24 (1): 74–87. doi:10.1080/09687860600967317. PMID 17453415.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.