Antimony pentoxide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(dioxo-λ5-stibanyl)oxy-dioxo-λ5-stibane | |
| Other names
antimony(V) oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.853 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Sb2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 323.517 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow powdery solid |
| Density | 3.78 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 380 °C (716 °F; 653 K) (decomposes) |
| 0.3 g/100 mL | |
| Solubility | insoluble in nitric acid |
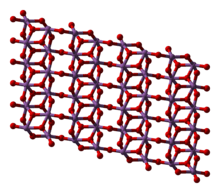
| Structure | |
| cubic | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
117.69 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
-1008.18 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
not listed |
| NFPA 704 | |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (as Sb)[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 0.5 mg/m3 (as Sb)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Antimony pentoxide (Sb2O5) is a chemical compound of antimony and oxygen. It always occurs in hydrated form, Sb2O5·nH2O. It contains antimony in the +5 oxidation state.
Structure
Antimony pentoxide has the same structure as the B form of niobium pentoxide and can be derived from the rutile structure, with antimony coordinated by six oxygens in a distorted octahedral arrangement. The SbO6 octahedra are corner- and edge-sharing.[2]
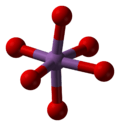 | 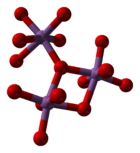 | 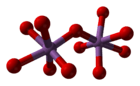 |
Preparation
The hydrated oxide is prepared by hydrolysis of antimony pentachloride; or by acidification of potassium hexahydroxoantimonate(V). It may also be prepared by oxidation of antimony trioxide with nitric acid.[3]
Uses
It finds use as a flame retardant in ABS and other plastics, a flocculant in the production of titanium dioxide and is sometimes used in the production of glass, paint and adhesives.[4][5]
It is also used as an ion-exchange resin for a number of cations in acidic solution including Na+ (especially for their selective retentions); and as a polymerization and oxidation catalyst.
Properties and reactions
The hydrated oxide is insoluble in nitric acid, but dissolves in concentrated potassium hydroxide solution to give potassium hexahydroxoantimonate(V), KSb(OH)6.[6]
When heated at 700 °C the yellow hydrated pentoxide converts to an anhydrous white solid with a formula Sb6O13 containing both Sb(III) and Sb(V). Heating at 900 °C produces a white insoluble powder of Sb2O4 of both α and β forms. The β form consists of Sb(V) in octahedral interstices and pyramidal Sb(III) O4 units. In these compounds, Sb(V) atom is octahedrally coordinated to six –OH groups.
The pentoxide can be reduced to antimony metal by heating with hydrogen or potassium cyanide.[7]
References
- 1 2 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0036". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ M. Jansen (March 1979). "Die Kristallstruktur von Antimon(V)-oxid". Acta Crystallogr. B. 35 (3): 539–542. doi:10.1107/S056774087900409X.
- ↑ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0-07-049439-8
- ↑ Bartlett, Jeffrey (1997-03-19). "Colloidal Antimony Pentoxide in Flame Retarded ABS". Nyacol Products, Inc. Archived from the original on 3 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-07-28.
- ↑ "ANTIMONY PENTOXIDE". chemicalLAND21.com. Archived from the original on 27 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-07-28.
- ↑ Pradyot Patnaik (2002). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill. p. 54. ISBN 0-07-049439-8.
- ↑ "Antimony" in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Edited by G. Brauer, Academic Press, 1963, NY. Vol. 1. p. 606.
