Alaskan Way Viaduct replacement tunnel
 A visualization of the future tunnel | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Location | Seattle, Washington, U.S. |
| Coordinates | 47°36′37″N 122°20′41″W / 47.61028°N 122.34472°WCoordinates: 47°36′37″N 122°20′41″W / 47.61028°N 122.34472°W |
| Status | Under construction |
| Route |
|
| Start | 47°35′48″N 122°20′09″W / 47.596534°N 122.335699°W |
| End | 47°37′14″N 122°20′41″W / 47.620520°N 122.344674°W |
| Operation | |
| Work begun | July 30, 2013[1] |
| Opens | February 2019 |
| Operator | Washington State Department of Transportation |
| Traffic | Automotive |
| Technical | |
| Length | 2 miles (3.2 km)[2] |
| No. of lanes | 4 |
| Route map | |
 | |
The Alaskan Way Viaduct replacement tunnel is a bored road tunnel that is under construction in the city of Seattle in the U.S. state of Washington. The 2-mile (3.2 km) tunnel will carry State Route 99 under Downtown Seattle from the SoDo neighborhood to South Lake Union in the north.
Since the 2001 Nisqually earthquake, the replacement of the Alaskan Way Viaduct has been the source of much political controversy demonstrating the Seattle process. Options for replacing the viaduct, which carries 110,000 vehicles per day, included either replacing it with a cut-and-cover tunnel, replacing it with another elevated highway, or eliminating it while modifying other surface streets and public transportation. The current plan emerged in 2009 when government officials agreed to a deep-bore tunnel.
Construction began in July 2013 using "Bertha," at the time the world's largest-diameter tunnel boring machine. After several delays, tunnel boring was completed in April 2017, and the tunnel is scheduled to be open to traffic in February 2019.
Construction timeline
Boring of the tunnel with the world's largest-diameter tunnel-boring machine, "Bertha," began on July 30, 2013.[3][4] The project was scheduled for completion in December 2015,[5] but work was halted on December 6, 2013 after the machine overheated and shut down [6] approximately 1,083 feet (330 m) into the planned 9,270-foot-long (2,830 m) route. Investigations later revealed the seal system that protects the machine’s main bearing had been damaged.” Three days prior to stopping, the machine mined through an 8-inch-steel well-casing used to help measure groundwater in 2002 around Alaskan Way. Whether this pipe had anything to do with the machine’s failure is at the center of legal dispute between WSDOT and the contractor, Seattle Tunnel Partners.[7] Over the next two years, a recovery pit was dug from the surface in order to access and lift the machine's cutterhead for repair and partial replacement. Bertha resumed tunnel boring on December 22, 2015.[8]
Tunneling was paused again on January 18, 2016, when a sinkhole formed above Bertha near the launch pit.[9] Tunneling resumed on February 23, 2016.[10]
In July 2016, WSDOT estimated that the tunnel would be completed and open to traffic in early 2019.[11] On April 4, 2017, Bertha broke through to the exit pit.[12]
As of September 2018, the viaduct is scheduled to be closed permanently on January 11, 2019, and the tunnel is scheduled to open in early February. Tolls will be waived for the first few months of operations.[13]
Planning history
Alaskan Way Viaduct issues

The Alaskan Way Viaduct, completed on April 4, 1953, is a double-decked elevated section of State Route 99 (SR 99) that runs along the Elliott Bay waterfront in the Industrial District and Downtown of Seattle. It is the smaller of the two major north–south traffic corridors through Seattle (the other being Interstate 5), carrying up to 110,000 vehicles per day.[14] The viaduct runs above the surface street, Alaskan Way, from S. Nevada Street in the south to the entrance of Belltown's Battery Street Tunnel in the north, following previously existing railroad lines.
The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake destroyed the similarly designed Cypress Street Viaduct in Oakland, California with the loss of 42 lives.[15] The 2001 Nisqually earthquake damaged the viaduct and its supporting Alaskan Way Seawall and required the Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT) to invest US$14.5 million in emergency repairs. Experts gave a 1-in-20 chance that the viaduct could be shut down by an earthquake within the following decade.[16] After the Nisqually earthquake, the viaduct has been closed twice a year for WSDOT to conduct inspections of the structure.[17] Those inspections have discovered continuing settlement damage. In 2005, a group of researchers and faculty from the University of Washington urged political officials to close the viaduct within a two-year timeframe.[18]


Options and politics
Several replacement proposals were developed. Many Seattle leaders, including then-Mayor Greg Nickels and state and city transportation officials, favored building a tunnel. Plans for a six-lane, "cut-and-cover" double-decker tunnel were developed.[20] The tunnel was envisioned to solve not only the viaduct's traffic limitations and safety problems, but also to allow better uses for the waterfront real estate, including parks, housing, and retail developments. While future development of the Alaskan Way real estate corridor may provide tax revenue for the city, many state lawmakers objected to the cost of the proposed six-lane tunnel. One criticism compared the plan to Boston's Big Dig project, which was said to illustrate the schedule and budget challenges of a large cut-and-cover tunnel. Proponents responded that the Seattle proposal was significantly smaller in scale than the Big Dig.[21]
Another proposal aimed to replace the current viaduct with another elevated structure with updated seismic standards. This new viaduct would be larger, 12-foot (3.7 m) wide lanes with new shoulders on both sides, compared to the structure it would replace, which had no shoulders and lanes as narrow as 10 feet (3.0 m) in places. The on and off ramps at the northern and southern portion of the viaduct would remain the same with an additional full intersection at South Atlantic Street and South Royal Brougham Way. The First Avenue off ramp would be removed. The plan included a complete replacement of the sea wall. It was estimated to cost $2.8 billion and take 10–12 years to construct.[22] Many prominent leaders and organizations opposed the elevated structure and believed this was a unique opportunity to remove the viaduct and connect downtown Seattle to the waterfront. Former Governors Dan Evans and Gary Locke, former U.S. Senator Slade Gorton,[23] and the American Institute of Architects[24] recommended against rebuilding the viaduct.
WSDOT evaluated five proposals in 2003–2004 and decided that the six-lane cut-and-cover tunnel was the preferred alternative. Rebuilding the viaduct was retained as a backup plan.[25]
However, due to the costs and scope of the project, other options were still being discussed in the local media. A proposal to remove the viaduct and replace it with surface street and transit improvements was backed by former King County Executive Ron Sims,[26] the People's Waterfront Coalition,[27] and the Congress for the New Urbanism.[27] Proponents of this plan offered examples of successes in removing highways in other cities. They envisioned the waterfront becoming a pedestrian-friendly neighborhood with a mix of commercial, retail, and public park spaces. Traffic needs would be addressed through modifications to existing streets, I-5, and public transit; they argued that these modifications would be desirable in any event. Proponents further argued that this plan had the potential to improve the tourist economy, create jobs, and encourage a denser and more residential downtown through the offering of a generous waterfront park.[28] The total cost of removal of the viaduct, repairing the seawall, and improvements to I-5 and existing streets was unofficially estimated to be $1.6 billion. In 2006, Seattle City Council member Peter Steinbrueck noted, "While the mayor's first choice is the tunnel, he supports the City Council's resolution that designates a surface and transit alternative as a backup."[29]
In response to concerns about the cost of the originally proposed tunnel construction, the city council created a scaled-down, four-lane hybrid tunnel option. This would have combined the smaller tunnel with surface transit improvements to address traffic needs. The tunnel's 14-foot (4.3 m) shoulders would be used as an extra travel lane each way during periods of high demand. Transit service would be increased during peak commuter periods. Cars entering and exiting from Elliott and Western Avenues would each have a dedicated lane. Third Avenue would become a permanent transit corridor. The cost estimate for the four-lane tunnel was $3.4 billion. On February 13, 2007, Governor Christine Gregoire rejected the tunnel hybrid option, saying that a WSDOT review showed the tunnel proposal "does not meet state and federal safety standards." Of particular concern was that the use of shoulders as traffic lanes during peak traffic times would leave no additional lanes for emergency access.[30] However, several of the viaduct "stakeholders committee" brought on board to advise the city indicated that the tunnel option should remain on the table.[31]
State and city officials deadlocked in late 2006 over whether to build an elevated structure (the state's preference) or a hybrid tunnel (the city's preference). Governor Gregoire stated "no action" was not an option for the viaduct.[32] The state government called for an advisory ballot on March 13, 2007, for Seattle residents, which was supported by the city council. The advisory ballot allowed Seattleites to vote on whether they supported a surface-tunnel hybrid and whether they supported an elevated structure.[33] Voters rejected both options, with the surface-tunnel hybrid getting only 30% support and the elevated structure only 43%.[34]
In 2011, Seattleites were asked to vote on the deep bore tunnel option and approved it with 60% in favor.[35]
Bored tunnel selection
In January 2008, as debate on its replacement continued, Governor Gregoire announced that the State of Washington would take down the viaduct in 2012.[36] On January 12, 2009, the state of Washington, King County, the city of Seattle, and the Port of Seattle revealed that they had agreed to replace the viaduct with a bored underground tunnel.[37] On March 4, 2009, the state senate passed a bill endorsing the tunnel option.[38] On May 12, 2009, Governor Gregoire signed Senate Bill 5768, authorizing $2.8 billion in state funds for a possible deep-bore tunnel.
Disparate factions, ranging from some environmentalists to some industrialists, criticized the tunnel decision.[37][39] A business owner argued that the restrictions on hazardous cargo through the tunnel would restrict movement of freight through downtown,[39] though hazardous cargo is already prohibited from the Battery Street Tunnel and the viaduct at peak hours.[40] Similarly, another argued that surface traffic would increase, which would cause further problems to downtown freight transport.[37] A chairman of a local Sierra Club chapter argued that the large investment in automobile transport did not take into account global warming concerns.[37]
Design and funding

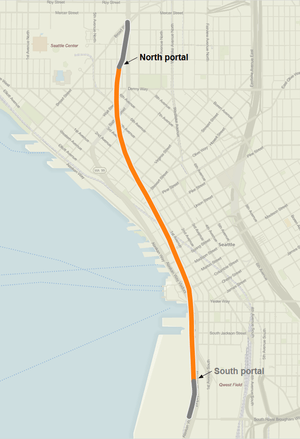
The approved design is a four-lane, 2-mile (3.2 km) long bored underground tunnel.[37] The tunnel will have a south portal in SoDo, near CenturyLink Field, and a north portal in South Lake Union, east of Seattle Center.[39] The route goes beneath Pioneer Square, the central business district of Downtown, and Belltown.
The project is estimated to cost US$3.29 billion, with $2.8 billion coming from the state and federal governments to cover the tunnel boring and a new interchange in SoDo. "Budget". wsdot.wa.gov. WSDOT. May 1, 2018. Retrieved May 1, 2018. The tables below reflect the budget as approved by the Legislature.
The replacement project also includes the following projects and funding sources:
- The city of Seattle will fund surface street improvements, utility relocation, and repairs to the Alaskan Way Seawall, which was also damaged in the 2001 Nisqually earthquake.[39]
- Since the proposed tunnel will contain two lanes in each direction as opposed to the viaduct's three, and no Western Avenue exit to serve the Belltown, Interbay, Magnolia, and Ballard areas, King County will fund transit improvements to offset the loss.[39]
- The Port of Seattle is considering funding part of the project in SoDo.[39]
- $200 million will be collected from tolls[41] at rates set by the Washington State Transportation Commission[42] with input from the Advisory Committee on Tolling and Traffic Management.[43]
WSDOT began part of the larger project in 2008, while the replacement debate was still on-going, by repairing some of the viaduct columns.[44]
The $80 million tunnel boring machine (TBM) Bertha was created for this project by Hitachi Zosen Corporation near Osaka, Japan. The 326 ft (99 m), 6,700-short-ton (6,100 t) TBM was disassembled into 40 pieces and shipped to Seattle where it was reassembled in the launch pit near the south end of the future tunnel.[45] From there, the record-breaking 57.5-foot (17.5 m) diameter borer moves in 6.5 ft (2.0 m) increments toward the north end.[46][47]
WSDOT nicknamed the TBM "Bertha" after Seattle's first female mayor, Bertha Knight Landes. This name was chosen from names submitted by kindergarten through 12th grade students for a naming competition.[48]
Construction
.jpg)
The initial phase of demolition and removal of the viaduct began on October 21, 2011. Only a southern portion of the viaduct was removed at that time; the viaduct along the central waterfront will remain open for traffic until the tunnel is complete.[49][50]
Boring began on July 30, 2013, and at the time was expected to be completed in 14 months.[1] After three weeks of drilling, the project was estimated to be two weeks behind schedule; problems with fiberglass near the front of the drill and a labor dispute with a local longshoreman's union were blamed.[51] Boring was again delayed in December when Bertha struck a steel pipe, installed as a well casing for an exploratory well drilled as part of the planning phases of the project.[52] This delay lasted for more than two years as the workers had to dig a 120-foot (37 m) vertical shaft down to Bertha's cutting head to repair it. Settling was discovered in Pioneer Square that may be related to this additional excavation.[53]
WSDOT plans to fill in the Battery Street Tunnel after the replacement tunnel is open to traffic, because the 1952 cut-and-cover tunnel does not meet modern safety standards, is expensive to maintain, and will be made redundant by the Alaskan Way tunnel.[54] Dirt produced by tunnel construction will be sent to fill a CalPortland quarry in nearby Port Ludlow, Washington.[55]
Tunnel boring had resumed on December 22, 2015.[9] The tunnel boring was halted 23 days later on January 14, 2016, after a 30-foot-wide (9.1 m) sinkhole developed on the ground in front of the machine, causing Governor Jay Inslee to halt drilling until the contractors can perform a root cause analysis to show that the machine can be run safely.[56] Even though contractors filled the hole with 250 cubic yards (190 m3) of material, the ground above the tunnel-boring machine is continuing to sink, according to the Washington State Department of Transportation. The tunneling restriction was lifted on February 23, 2016, and tunneling resumed that day.[10] Bertha passed under the Alaskan Way Viaduct in early May, closing the roadway for 11 days as the machine had 15 feet (4.6 m) of vertical clearance under the structure's pilings.[57] On April 4, 2017, the tunnel boring machine broke through to the recovery pit on the north end of the tunnel, completing the excavation process. The boring machine was dismantled and removed from the site over the next four months.[58]
.jpg)
In October 2017, Seattle Tunnel Partners expected to have the tunnel completed and open to traffic in early 2019. An estimated $223 million in cost overruns were reported as a result of the two-year stoppage.[11][59]
As of March 2018, Seattle Tunnel Partners are targeting an August 2018 completion of work, with the tunnel possibly opening in October 2018. The contractor Seattle Tunnel Partners and machine manufacturer Hitachi Zosen incurred the costs of repairs. The dispute over the cause of the damage and whether they are entitled to reimbursement is now with the courts. "Budget". wsdot.wa.gov. WSDOT. October 9, 2015. Retrieved May 1, 2018. Today, WSDOT filed a lawsuit against STP in King County Superior Court.
See also
- Big Dig, a cut‑and‑cover elevated‑to‑tunnel conversion of the formerly elevated Central Artery in Boston
References
- 1 2 Esser, Doug (July 31, 2013). "Bertha takes first bite of new Seattle tunnel". KOMO. Archived from the original on 2013-08-03. Retrieved 2013-07-31.
- 1 2 "Tunneling toward a new SR 99; The SR 99 tunnel route (map)". Washington State Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on 2012-12-10. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
- ↑ Yerkan, KaDeena (July 30, 2013). "Bertha starts digging: tunneling underway in Seattle" (Press release). Washington State Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on 2015-12-08. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (July 30, 2013). "Bertha's excavation mission beginning under downtown". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2015-12-15. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ↑ Aitchison, Sarah (July 17, 2015). "State officials skeptical Bertha contractor can deliver on new deadline". Puget Sound Business Journal. Archived from the original on 2015-07-24. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (August 19, 2017). "Insurance lawyers' new findings increase arguments in case of Bertha machine breakdown". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2017-08-19. Retrieved August 19, 2017.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (February 7, 2014). "Bad news: Bertha is damaged". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2015-03-24. Retrieved February 7, 2014.
- ↑ Newborn, Laura (December 22, 2015). "Bertha tunnels into next phase of testing" (Press release). Washington State Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on 2015-12-27. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- 1 2 Lindblom, Mike (December 22, 2015). "Bertha back on the move after 2 years of delays". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2016-01-05. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- 1 2 "Feb. 23 project update: Seattle Tunnel Partners resumes mining". 23 February 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-02-23. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- 1 2 Lindblom, Mike (July 21, 2016). "Bertha's woes grind on: more delay, higher cost for Highway 99 tunnel". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2016-07-22. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (April 4, 2017). "Bertha's breakthrough just 'halftime' for tunnel project". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2017-04-04. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (September 17, 2018). "Permanent closure of Alaskan Way Viaduct delayed until January". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2018-09-17. Retrieved September 18, 2018.
- ↑ "Is most of the traffic using the viaduct today going to downtown or through downtown?". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2013-04-27. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
- ↑ "Cypress Viaduct Freeway". Archived from the original on 2009-07-07.
- ↑ Anderson, Ross (April 7, 2002). "Dutiful Servant, Brutal Barrier: The Viaduct at a Crossroads". Pacific Northwest. The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- ↑ "Viaduct Inspections". Washington State Department of Transportation. 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-09-06. Retrieved 2018-10-11.
- ↑ Miles, Scott; Montgomery, David R.; Beyers, Bill (March 2, 2006). "Shut down the viaduct". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2012-10-08. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- ↑ Barnett, Erica C. (February 22, 2007). "No and Hell No". The Stranger. Archived from the original on 2008-09-19. Retrieved 2008-11-25.
- ↑ "Alaskan Way Viaduct In-depth". Seattle Channel. Archived from the original on December 28, 2012. Retrieved December 8, 2012. (See the "Background" tab in particular.)
- ↑ Howland, Jr, Greg (April 19, 2006). "Seattle's Little Dig". Seattle Weekly. Archived from the original on 2015-09-12. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- ↑ "WSDOT Viaduct Alternatives Information". WSDOT. Archived from the original on October 26, 2006.
- ↑ Gilmore, Susan (December 12, 2006). "Opposition to viaduct addressed to Gregoire". Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2018-10-11. Retrieved 2018-10-11.
- ↑ Bennett, Sam (January 14, 2009). "Tunnel to replace Alaskan Way Viaduct in Seattle". Portland, OR: Daily Journal of Commerce – via Newspaper Source Plus.
- ↑ "Appendix B: Alternatives Description and Construction Methods". Alaskan Way Viaduct Replacement Project: Final Environmental Impact Statement (PDF). WSDOT. July 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-07-10. Retrieved 2012-12-11.
- ↑ "Gregoire nixes surface option for viaduct". KOMONews.com. AP. February 19, 2007. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2012-12-07.
- 1 2 "Seattle's Alaskan Way Viaduct". Congress for the New Urbanism. Archived from the original on 2013-01-07. Retrieved December 8, 2012.
- ↑ Holden, Dominic (March 16, 2011). "Stop the Insanity". The Stranger. Archived from the original on 2013-07-28. Retrieved August 1, 2013.
- ↑ Steinbrueck, Peter (October 10, 2006). "Climate's Right For Fresh Viaduct Plan". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2012-08-26. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- ↑ Garber, Andrew; Gilmore, Susan; Lindblom, Mike (February 14, 2007). "State says no tunnel; mayor still wants vote". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on February 2, 2013.
- ↑ Garber, Andrew; Lindblom, Mike; Heffter, Emily (January 12, 2009). "City, county, state agree on tunnel to replace viaduct". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on October 13, 2012.
- ↑ McGann, Chris; Santos, Melissa; Lange, Larry (January 17, 2007). "Tunnel option off table for viaduct replacement". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 2012-10-15. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- ↑ Young, Bob (March 7, 2007). "Viaduct vote set; state may ignore it". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on July 6, 2008.
- ↑ "King County Election Results (Mar. 13 special election)". King County. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on 2012-08-23. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- ↑ "Seattle Viaduct Tunnel Replacement Question (August 2011)". Ballotpedia. Archived from the original on 2017-06-02. Retrieved September 26, 2016.
- ↑ McGann, Chris (January 3, 2008). "Gregoire: 'Watch me' tear down the viaduct". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 2012-10-15. Retrieved 2012-12-08.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Garber, Andrew (January 13, 2009). "Tunnel in place of viaduct: A deal, but how to pay?". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on January 15, 2009.
- ↑ Garber, Andrew (March 4, 2009). "Senate passes bill to replace viaduct with tunnel". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2010-11-12. Retrieved 2009-03-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Lindblom, Mike; Sara Jean Green (January 13, 2009). "Gregoire announces tunnel plans; car-tab taxes might help pay for it". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on January 15, 2009.
- ↑ "Alaskan Way Viaduct: Will there be restrictions on freight using the tunnel?". wa.gov. Archived from the original on 2015-09-12. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- ↑ "Alaskan Way Viaduct: Budget". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2013-08-07. Retrieved December 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Will tolling cause diversion?". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2014-07-12. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ↑ "Advisory Committee on Tolling and Traffic Management (2011–present)". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2014-02-14. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ↑ Seattle Tunnel Partners (December 1, 2015). "Seattle Tunnel Partners monthly schedule: November 2015" (PDF). Washington State Department of Transportation. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-12-28. Retrieved December 27, 2015.
- ↑ Robinson, Patrick (September 7, 2012). Seattle Deep Bore Tunnel Tour Sept. 6, 2012. West Seattle Herald. Archived from the original on 2016-04-25. Retrieved 2016-12-01.
- ↑ Newcomb, Tim (August 30, 2012). "Digging an Enormous Tunnel Under Downtown Seattle". Popular Mechanics. Archived from the original on 2012-11-05. Retrieved 2012-12-09.
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk (December 4, 2012). "Engineering Projects Will Transform Seattle, All Along the Waterfront". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2016-11-09. Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- ↑ "SR 99 tunneling machine tweets her name: Bertha". WSDOT. Archived from the original on November 10, 2014. Retrieved December 10, 2012.
- ↑ Gutierrez, Scott (October 22, 2011). "Alaskan Way Viaduct closure, demolition begin". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 2011-11-17. Retrieved 2012-07-16.
- ↑ "When will the viaduct be demolished?". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2015-04-17. Retrieved December 10, 2014.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (August 27, 2013). "Huge tunneling machine off to painfully slow start". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on December 28, 2013.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (January 3, 2014). "What's blocking Bertha: a long steel pipe". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2014-01-04. Retrieved 2014-01-04.
- ↑ Johnson, Kirk (December 9, 2014). "In Seattle, a Sinking Feeling About a Troubled Tunnel". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2016-03-14. Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- ↑ "What will happen to the Battery Street Tunnel?". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2013-12-19. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ↑ "Where will the dirt from tunneling go?". WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2013-12-19. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ↑ Lindblom, Mike (January 14, 2016). "Inslee orders tunnel dig halted as soil sinks above Bertha". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2016-02-06. Retrieved January 15, 2016.
- ↑ Demay, Daniel (May 11, 2016). "Viaduct closure ends, Bertha to make pit stop". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Archived from the original on 2016-07-14. Retrieved July 20, 2016.
- ↑ "Alaskan Way Viaduct - Goodbye Bertha: Final piece of the tunneling machine removed from tunnel". wsdot.wa.gov. WSDOT. Archived from the original on 2017-12-15. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ↑ Seattle Tunnel Partners (June 1, 2016). "Seattle Tunnel Partners monthly schedule – October 2017". Washington State Department of Transportation. Retrieved July 21, 2016.
Further reading
- Gilmore, Susan (September 8, 2006). "Two views of the viaduct". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on December 4, 2008.
- Gilmore, Susan (August 9, 2006). "State offers 3 decidedly different designs for viaduct". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on December 4, 2008.
- Gilmore, Susan (August 2, 2006). "Idea of fixing viaduct seen as having merit but problems as well". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on August 14, 2009.
- Gilmore, Susan (July 25, 2006). "What will happen if viaduct closes? Study takes a look". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on August 14, 2009.
- Lange, Larry (May 3, 2006). "A Longer shelf life for the viaduct". Seattle Post-Intelligencer.
External links
- Official website

- Engineering view into the Earth-pressure-balanced TBM and Seattle-specific tunnel engineering issues, ITA AITES, June 2012.
- Seattle's Alaskan Way Viaduct from the Congress for the New Urbanism
- Alaskan Way/SR 99 Viaduct from Puget Sound Transportation projects