United States Secretary of Defense
The secretary of defense (SecDef) is the leader and chief executive officer of the United States Department of Defense, the executive department of the Armed Forces of the U.S.[5][6][7] The secretary of defense's position of command and authority over the U.S. military is second only to that of the president. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a defense minister in many other countries.[8] The secretary of defense is appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate, and is by custom a member of the Cabinet and by law a member of the National Security Council.[9]
| United States Secretary of Defense | |
|---|---|
 Seal of the Department[1] | |
 Flag of the Secretary[2] | |
.jpg) Mark Esper since July 23, 2019 | |
| United States Department of Defense Office of the Secretary of Defense | |
| Style | Mr. Secretary |
| Status | Leader and chief executive |
| Abbreviation | SecDef |
| Member of | Cabinet National Security Council |
| Reports to | President of the United States |
| Seat | The Pentagon, Arlington County, Virginia |
| Appointer | The President with Senate advice and consent |
| Term length | No fixed term |
| Constituting instrument | 10 U.S.C. § 113 50 U.S.C. § 401 |
| Precursor | Secretary of War Secretary of the Navy |
| Formation | September 17, 1947 |
| First holder | James Forrestal |
| Succession | Sixth[3] |
| Deputy | Deputy Secretary of Defense |
| Salary | Executive Schedule, level I[4] |
| Website | www |
The secretary of defense is a statutory office, and the general provision in 10 U.S.C. § 113 provides that "subject to the direction of the President", its occupant has "authority, direction and control over the Department of Defense". The same statute further designates the secretary as "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to the Department of Defense".[10] To ensure civilian control of the military, no one may be appointed as the secretary of defense within seven years of serving as a commissioned officer of a regular (i.e., non-reserve) component of an armed force.[11]
Subject only to the orders of the president, the secretary of defense is in the chain of command and exercises command and control, for both operational and administrative purposes, over all Department of Defense forces – the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, and Air Force – as well as the U.S. Coast Guard when its command and control is transferred to the Department of Defense.[12][13][14][15][16] Only the secretary of defense (or the president or Congress) can authorize the transfer of operational control of forces between the three military departments (the departments of the Army, Navy, and Air Force) and the 10 Combatant Commands (Africa Command, Central Command, European Command, Indo-Pacific Command, Northern Command, Southern Command, Cyber Command, Special Operations Command, Strategic Command, Transportation Command).[12] Because the Office of Secretary of Defense is vested with legal powers that exceed those of any commissioned officer, and is second only to the president in the military hierarchy, its incumbent has sometimes unofficially been referred to as a de facto "deputy commander-in-chief".[17][18][19] (The chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is the principal military adviser to the secretary of defense and the president, and while the chairman may assist the secretary and president in their command functions, the chairman is not in the chain of command.[20])
The secretary of defense, secretary of state, the attorney general, and the secretary of the treasury are generally regarded as heading the four most important departments.[21]
Since July 23, 2019, the secretary of defense has been Mark Esper, the 27th person to hold the office.[22]
History

An Army, Navy, and Marine Corps were established in 1775, in concurrence with the American Revolution. The War Department, headed by the secretary of war, was created by Act of Congress in 1789 and was responsible for both the Army and Navy until the founding of a separate Department of the Navy in 1798.
Based on the experiences of World War II, proposals were soon made on how to more effectively manage the large combined military establishment. The Army generally favored centralization while the Navy had institutional preferences for decentralization and the status quo. The resulting National Security Act of 1947 was largely a compromise between these divergent viewpoints. The Act split the Department of War into the Department of the Army and Department of the Navy and established the National Military Establishment (NME), presided over by the secretary of defense. The Act also separated the Army Air Forces from the Army to become its own branch of service, the United States Air Force. At first, each of the service secretaries maintained cabinet status. The first secretary of defense, James Forrestal, who in his previous capacity as the secretary of the Navy had opposed creation of the new position, found it difficult to exercise authority over the other branches with the limited powers his office had at the time. To address this and other problems, the National Security Act was amended in 1949 to further consolidate the national defense structure in order to reduce interservice rivalry, directly subordinate the secretaries of the Army, the Navy and the Air Force to the secretary of defense in the chain of command, and rename the National Military Establishment as the Department of Defense, making it one Executive Department. The position of the deputy secretary of defense, the number two position in the department, was also created at this time.
The general trend since 1949 has been to further centralize management in the Department of Defense, elevating the status and authorities of civilian OSD appointees and defense-wide organizations at the expense of the military departments and the services within them. The last major revision of the statutory framework concerning the position was done in the Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1986. In particular, it elevated the status of joint service for commissioned officers, making it in practice a requirement before appointments to general officer and flag officer grades could be made.
Powers and functions
—United States v. Eliason, 41 U.S. 291 (1842)
—In re Brodie, 128 Fed. 668 (CCA 8th 1904)
The secretary of defense, appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate, is by federal law (10 U.S.C. § 113) the head of the Department of Defense, "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to Department of Defense", and has "authority, direction and control over the Department of Defense". Because the Constitution vests all military authority in Congress and the president, the statutory authority of the secretary of defense is derived from their constitutional authorities. Since it is impractical for either Congress or the president to participate in every piece of Department of Defense affairs, the secretary of defense, and the secretary's subordinate officials generally exercise military authority.
As the head of DoD, all officials, employees and service members are "under" the secretary of defense. Some of those high-ranking officials, civil and military (outside of OSD and the Joint Staff) are: the secretary of the Army, secretary of the Navy, and secretary of the Air Force, Army chief of staff, commandant of the Marine Corps, chief of naval operations, and Air Force chief of staff, chief of the National Guard Bureau and the combatant commanders of the Combatant Commands. All of these high-ranking positions, civil and military, require Senate confirmation.
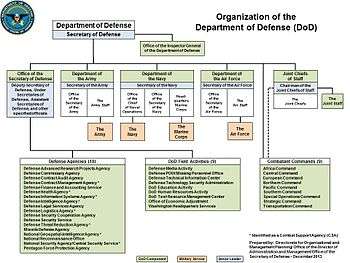
The Department of Defense is composed of the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD), the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) and the Joint Staff (JS), Office of the Inspector General (DODIG), the Combatant Commands, the Military Departments (Department of the Army (DA), Department of the Navy (DON) & Department of the Air Force (DAF)), the Defense Agencies and DoD Field Activities, the National Guard Bureau (NGB), and such other offices, agencies, activities, organizations, and commands established or designated by law, or by the president or by the secretary of defense.
Department of Defense Directive 5100.01 describes the organizational relationships within the Department, and is the foundational issuance for delineating the major functions of the Department. The latest version, signed by former secretary of defense Robert Gates in December 2010, is the first major re-write since 1987.[23][24]
Office of the Secretary of Defense
The secretary's principally civilian staff element is called the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) and is composed of the deputy secretary of defense (DEPSECDEF) and five under secretaries of defense in the fields of acquisition, technology & logistics, comptroller/chief financial officer, intelligence, personnel & readiness, and policy; several assistant secretaries of defense; other directors and the staffs under them.
The name of the principally military staff organization, organized under the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, is the Joint Staff (JS).
Awards and decorations
The Defense Distinguished Service Medal (DDSM), the Defense Superior Service Medal (DSSM), the Defense Meritorious Service Medal (DMSM), the Joint Service Commendation Medal (JSCM) and the Joint Service Achievement Medal (JSAM) are awarded, to military personnel for service in joint duty assignments, in the name of the secretary of defense. In addition, there is the Joint Meritorious Unit Award (JMUA), which is the only ribbon (as in non-medal) and unit award issued to joint DoD activities, also issued in the name of the secretary of defense.
The DDSM is analogous to the distinguished services medals issued by the military departments (i.e. Army Distinguished Service Medal, Navy Distinguished Service Medal & Air Force Distinguished Service Medal), the DSSM corresponds to the Legion of Merit, the DMSM to the Meritorious Service Medal, the JSCM to the service commendation medals, and the JSAM to the achievement medals issued by the services. While the approval authority for DSSM, DMSM, JSCM, JSAM and JMUA is delegated to inferior DoD officials: the DDSM can only be awarded by the secretary of defense.
Recommendations for the Medal of Honor (MOH), formally endorsed in writing by the secretary of the military department concerned and the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, are processed through the under secretary of defense for personnel and readiness, and such recommendations be must approved by the secretary of defense before it can be handed over to the president, who is the final approval authority for the MOH, although it is awarded in the name of Congress.
The secretary of defense, with the concurrence of the secretary of state, is the approval authority for the acceptance and wear of NATO medals issued by the secretary general of NATO and offered to the U.S. permanent representative to NATO in recognition of U.S. servicemembers who meet the eligibility criteria specified by NATO.[25]
Congressional committees
As the head of the department, the secretary of defense is the chief witness for the congressional committees with oversight responsibilities over the Department of Defense. The most important committees, with respect to the entire department, are the two authorizing committees, the Senate Armed Services Committee (SASC) and the House Armed Services Committee (HASC), and the two appropriations committees, the Senate Appropriations Committee and the House Appropriations Committee.
For the DoD intelligence programs the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence and the House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence have the principal oversight role.
National Security Council
The secretary of defense is a statutory member of the National Security Council.[26] As one of the principals, the secretary along with the vice president, secretary of state and the assistant to the president for national security affairs participates in biweekly Principals Committee (PC) meetings, preparing and coordinating issues before they are brought before full NSC sessions chaired by the president.
Role in the military justice system
The secretary is one of only five or six civilians—the others being the president, the three "service secretaries" (the secretary of the Army, secretary of the Navy, and secretary of the Air Force), and the secretary of homeland security (when the United States Coast Guard is under the United States Department of Homeland Security and has not been transferred to the Department of the Navy under the Department of Defense)—authorized to act as convening authority in the military justice system for General Courts-Martial (10 U.S.C. § 822: article 22, UCMJ), Special Courts-Martial (10 U.S.C. § 823: article 23, UCMJ), and Summary Courts-Martial (10 U.S.C. § 824: article 24 UCMJ).
Amenities
Salary
Secretary of Defense is a Level I position of the Executive Schedule,[4] and thus earns a salary of $210,700 per year as of January 2018.
List of secretaries of defense
The longest-serving secretary of defense is Robert McNamara, who served for a total of 7 years, 39 days. Combining his two non-sequential services as the secretary of defense, the second-longest serving is Donald Rumsfeld, who served just ten days fewer than McNamara. The second-longest unbroken tenure was Caspar Weinberger's, at 6 years, 306 days.
The shortest-serving secretary of defense is Elliot Richardson, who served 114 days and then was appointed U.S. attorney general amid the resignations of the Watergate Scandal. (This is not counting deputy secretaries of defense William P. Clements and William Howard Taft IV, who each served a few weeks as temporary/acting secretary of defense).
- Parties
Democratic Republican Political Independent / Unknown
- Status
| No. | Secretary of Defense | Took office | Left office | Time in office | Party | State of residence | President serving under | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | James Forrestal (1892–1949) | September 17, 1947 | March 28, 1949 | 1 year, 192 days | Democratic | New York | Harry S Truman (Dem) | [27] | |
| 2 | Louis A. Johnson (1891–1966) | March 28, 1949 | September 19, 1950 | 1 year, 175 days | Democratic | West Virginia | Harry S Truman (Dem) | [28] | |
| 3 | George Marshall (1880–1959) | September 21, 1950 | September 12, 1951 | 356 days | Independent | Pennsylvania | Harry S Truman (Dem) | [29] | |
| 4 | Robert A. Lovett (1895–1986) | September 17, 1951 | January 20, 1953 | 1 year, 125 days | Republican | New York | Harry S Truman (Dem) | [30] | |
| 5 | Charles Erwin Wilson (1890–1961) | January 28, 1953 | October 8, 1957 | 4 years, 253 days | Republican | Michigan | Dwight D. Eisenhower (Rep) | [31] | |
| 6 | Neil H. McElroy (1904–1972) | October 9, 1957 | December 1, 1959 | 2 years, 53 days | Republican | Ohio | Dwight D. Eisenhower (Rep) | [32] | |
| 7 | Thomas S. Gates Jr. (1906–1983) | December 2, 1959 | January 20, 1961 | 1 year, 49 days | Republican | Pennsylvania | Dwight D. Eisenhower (Rep) | [33] | |
| 8 | Robert McNamara (1916–2009) | January 21, 1961 | February 29, 1968 | 7 years, 39 days | Republican | Michigan | John F. Kennedy (Dem) Lyndon B. Johnson (Dem) | [34] | |
| 9 | Clark Clifford (1906–1998) | March 1, 1968 | January 20, 1969 | 325 days | Democratic | Maryland | Lyndon B. Johnson (Dem) | [35] | |
| 10 | Melvin R. Laird (1922–2016) | January 22, 1969 | January 29, 1973 | 4 years, 7 days | Republican | Wisconsin | Richard Nixon (Rep) | [36] | |
| 11 | Elliot Richardson (1920–1999) | January 30, 1973 | May 24, 1973 | 114 days | Republican | Massachusetts | Richard Nixon (Rep) | [37] | |
| – | Bill Clements (1917–2011) Acting | May 24, 1973 | July 2, 1973 | 39 days | Republican | Texas | Richard Nixon (Rep) | [38] | |
| 12 | James R. Schlesinger (1929–2014) | July 2, 1973 | November 19, 1975 | 2 years, 140 days | Republican | Virginia | Richard Nixon (Rep) Gerald Ford (Rep) | [39] | |
| 13 | Donald Rumsfeld (born 1932) | November 20, 1975 | January 20, 1977 | 1 year, 61 days | Republican | Illinois | Gerald Ford (Rep) | [40] | |
| 14 | Harold Brown (1927–2019) | January 20, 1977 | January 20, 1981 | 4 years, 0 days | Independent | California | Jimmy Carter (Dem) | [41] | |
| 15 | Caspar Weinberger (1917–2006) | January 21, 1981 | November 23, 1987 | 6 years, 306 days | Republican | California | Ronald Reagan (Rep) | [42] | |
| 16 | Frank Carlucci (1930–2018) | November 23, 1987 | January 20, 1989 | 1 year, 58 days | Republican | Virginia | Ronald Reagan (Rep) | [43] | |
| – | William Howard Taft IV (born 1945) Acting | January 20, 1989 | March 21, 1989 | 60 days | Republican | Ohio | George H. W. Bush (Rep) | [44] | |
| 17 | Dick Cheney (born 1941) | March 21, 1989 | January 20, 1993 | 3 years, 305 days | Republican | Wyoming | George H. W. Bush (Rep) | [45] | |
| 18 | Leslie Aspin (1938–1995) | January 20, 1993[46][47] | February 3, 1994 | 1 year, 14 days | Democratic | Wisconsin | Bill Clinton (Dem) | [48] | |
| 19 | William Perry (born 1927) | February 3, 1994 | January 23, 1997[49] / January 24, 1997[46][50] | 2 years, 356 days | Independent | Pennsylvania | Bill Clinton (Dem) | . | |
| 20 | William Cohen (born 1940) | January 24, 1997 | January 20, 2001 | 3 years, 362 days | Republican | Maine | Bill Clinton (Dem) | [51] | |
| 21 | Donald Rumsfeld (born 1932) | January 20, 2001 | December 18, 2006 | 5 years, 332 days (7 years, 29 days total) | Republican | Illinois | George W. Bush (Rep) | [52] | |
| 22 | Robert Gates (born 1943) | December 18, 2006 | June 30, 2011[53] / July 1, 2011[46] | 4 years, 194 days | Republican | Texas | George W. Bush (Rep) Barack Obama (Dem) | . | |
| 23 | Leon Panetta (born 1938) | July 1, 2011 | February 26, 2013 | 1 year, 240 days | Democratic | California | Barack Obama (Dem) | [54] | |
| 24 | Chuck Hagel (born 1946) | February 27, 2013 | February 17, 2015 | 1 year, 355 days | Republican | Nebraska | Barack Obama (Dem) | [55] | |
| 25 | Ash Carter (born 1954) | February 17, 2015 | January 20, 2017 | 1 year, 338 days | Democratic | Massachusetts | Barack Obama (Dem) | [56][46] | |
| 26 | Jim Mattis (born 1950) | January 20, 2017 | December 31, 2018 | 1 year, 345 days | Independent | Washington | Donald Trump (Rep) | [57] | |
| – | Patrick M. Shanahan (born 1962) Acting | January 1, 2019 | June 23, 2019 | 173 days | Independent | Washington | Donald Trump (Rep) | [58] | |
| – | Mark Esper (born 1964) Acting | June 24, 2019 | July 15, 2019 | 21 days | Republican | Virginia | Donald Trump (Rep) | [59] | |
| – | Richard V. Spencer (born 1954) Acting | July 15, 2019 | July 23, 2019 | 8 days | Independent | Wyoming | Donald Trump (Rep) | [60] | |
| 27 | Mark Esper (born 1964) | July 23, 2019 | Incumbent | 277 days | Republican | Virginia | Donald Trump (Rep) | [59] |
Succession
Presidential succession
The secretary of defense is sixth in the presidential line of succession, following the secretary of the treasury and preceding the attorney general.[61]
Secretary of Defense succession
In Executive Order 13533 of March 1, 2010, President Barack Obama modified the line of succession regarding who would act as the secretary of defense in the event of a vacancy or incapacitation, thus reversing the changes made by President George W. Bush in Executive Order 13394 as to the relative positions of the secretaries of the military departments. All of the officials in the line of succession are civilians appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the Senate:
|
Executive Order 13533 (March 1, 2010 – present)
|
Executive Order 13394 (December 22, 2005 – March 1, 2010)
|
Living former secretaries of defense
As of April 2020, there are nine living former secretaries of defense, the oldest being William Perry (1994–1997, born 1927). The most recent secretary of defense to die was Harold Brown (1977–1981), on January 4, 2019.
| Name | Term of office | Date of birth (and age) |
|---|---|---|
| Donald Rumsfeld | 1975–1977, 2001–2006 | July 9, 1932 |
| Dick Cheney | 1989–1993 | January 30, 1941 |
| William Perry | 1994–1997 | October 11, 1927 |
| William Cohen | 1997–2001 | August 28, 1940 |
| Robert Gates | 2006–2011 | September 25, 1943 |
| Leon Panetta | 2011–2013 | June 28, 1938 |
| Chuck Hagel | 2013–2015 | October 4, 1946 |
| Ash Carter | 2015–2017 | September 24, 1954 |
| Jim Mattis | 2017–2018 | September 8, 1950 |
See also
- Base Realignment and Closure Commission
- Boeing E-4
- Challenge coin
- Combat Exclusion Policy
- Commission to Assess the Ballistic Missile Threat to the United States
- Continuity of Operations Plan
- CONPLAN 8022-02
- Defense Policy Board Advisory Committee
- Defense Support of Civil authorities
- Department of Defense Directive 2310
- Designated survivor
- Emergency Action Message
- Global Command and Control System
- Gold Codes
- Hamdan v. Rumsfeld
- Joint Worldwide Intelligence Communications System
- Key West Agreement
- McCarran Internal Security Act
- Military Commissions Act of 2006
- Military operation plan
- National Command Authority
- National Industrial Security Program
- National Security Strategy (United States)
- Office of the Secretary of Defense Identification Badge
- Packard Commission
- Permissive Action Link
- Presidential Successor Support System
- Quadrennial Defense Review
- Rules of engagement
- Secretary of Defense Employer Support Freedom Award
- Single Integrated Operational Plan
- State secrets privilege
- Stop-loss policy
- Two-man rule
- Unconventional warfare (United States Department of Defense doctrine)
- United States Foreign Military Financing
- US Commission on National Security/21st Century
References
Footnotes
- Trask & Goldberg: p. 177.
- "Positional Colors for the Department of Defense". www.tioh.hqda.pentagon.mil. Archived from the original on May 12, 2013. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- "3 U.S. Code § 19 – Vacancy in offices of both President and Vice President; officers eligible to act".
- 5 U.S.C. § 5312
- 10 U.S.C. § 113.
- DoDD 5100.1: Enclosure 2: a
- 5 U.S.C. § 101.
- "NATO – member countries". NATO. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- 50 U.S.C. § 402.
- 10 U.S.C. § 113
- The National Security Act of 1947 originally required an interval of ten years after relief from active duty, which was reduced to seven years by Sec. 903(a) of the 2008 National Defense Authorization Act. In 1950 Congress passed special legislation (Pub. Law 81-788) to allow George C. Marshall to serve as Secretary of Defense while remaining a commissioned officer on the active list of the Army (Army regulations kept all five-star generals on active duty for life), but warned:
It is hereby expressed as the intent of the Congress that the authority granted by this Act is not to be construed as approval by the Congress of continuing appointments of military men to the office of Secretary of Defense in the future. It is hereby expressed as the sense of the Congress that after General Marshall leaves the office of Secretary of Defense, no additional appointments of military men to that office shall be approved.
Defenselink bio, Retrieved February 8, 2010; and Marshall Foundation bio, Retrieved February 8, 2010. - 10 U.S.C. § 162
- Joint Publication 1: II-9, II-10 & II-11.
- 10 U.S.C. § 3011
- 10 U.S.C. § 5011
- 10 U.S.C. § 8011
- Trask & Goldberg: pp.11 & 52
- Cohen: p.231.
- Korb, Lawrence J.; Ogden, Pete (October 31, 2006). "Rumsfeld's Management Failures". Center for American Progress. Retrieved January 6, 2012.
- 10 U.S.C. § 152
- Cabinets and Counselors: The President and the Executive Branch (1997). Congressional Quarterly. p. 87.
- "Dr. Mark T. Esper > U.S. DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE > Biography View". dod.defense.gov. Retrieved August 2, 2019.
- Department of Defense Directive 5100.01 Functions of the Department of Defense and Its Major Components
- DoDD 5100.1: p.1.
- DoDM 1348.33, Vol 3: p.39 (Enclosure 3)
- 50 U.S.C. § 402
- "James V. Forrestal – Harry S. Truman Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Louis A. Johnson – Harry S. Truman Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "George C. Marshall – Harry S. Truman Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Robert A. Lovett – Harry S. Truman Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Charles E. Wilson – Dwight D. Eisenhower Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Neil H. McElroy -Dwight D. Eisenhower Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Thomas S. Gates, Jr. – Dwight D. Eisenhower Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Robert S. McNamara – John F. Kennedy / Lyndon Johnson Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Clark M. Gifford – Lyndon Johnson Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Melvin R. Laird – Richard Nixon Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Elliot L. Richardson – Richard Nixon Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- Cantwell, Gerald T. (1997). Citizen Airmen: A History of the Air Force Reserve 1946–1994. DIANE Publishing. p. 252. ISBN 9781428991620.
In June 1973, Representative O. C. Fisher complained to William P. Clements, Jr., acting Secretary of Defense, that the authority, responsibility, and, consequently, effectiveness of the chiefs of the various reserve components seemed to be eroding.
- "James R. Schlesinger – Richard Nixon / Gerald Ford Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Donald H. Rumsfeld – Gerald Ford Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Harold Brown – James Carter Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Caspar W. Weinberger – Ronald Reagan Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Frank C. Carlucci – Ronald Reagan Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "II. Secretaries of Defense" (PDF). Washington Headquarters Services – Pentagon Digital Library. p. 9.
(Deputy Secretary of Defense William H. Taft served as acting secretary of defense from 20 January 1989 until 21 March 1989).
- "Richard B. Cheney – George H.W. Bush Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- Department of Defense Key Officials September 1947 – February 2019
- "Les Aspin Serves One Year As Defense Secretary".
- "Leslie Aspin – William J. Clinton Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "William J. Perry – William J. Clinton Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "II. Secretaries of Defense" (PDF). Washington Headquarters Services – Pentagon Digital Library. p. 10.
Sworn in as secretary of defense on 3 February 1994 and served until 24 January 1997.
- "William S. Cohen – William J. Clinton Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Donald H. Rumsfeld – George W. Bush Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Robert M. Gates – George W. Bush / Barack Obama Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Leon E. Panetta – Barack Obama Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Chuck Hagel – Barack Obama Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "Ashton B. Carter – Barack Obama Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "James N. Mattis – Donald Trump Administration". Office of the Secretary of Defense – Historical Office.
- "PN583 — Patrick M. Shanahan — Department of Defense". www.congress.gov. Library of Congress. July 18, 2017. Retrieved January 1, 2019.
- "Dr. Mark T. Esper – Acting Secretary of Defense". United States Department of Defense. June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- "Letter from Acting Secretary of Defense Richard V. Spencer to Pentagon". USNI News. July 15, 2019. Retrieved July 16, 2019.
- 3 U.S.C. § 19.
Sources
Federal law
- Title 10 of the United States Code
- Title 50 of the United States Code
Directives, regulations and manuals
- Department of Defense Directive 5100.1: Functions of the Department of Defense and Its Major Components (PDF). Department of Defense Directive. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. December 21, 2010.
- Department of Defense Manual 1348.33, Volume 1: Manual of Military Decorations and Awards: General Information, Medal of Honor, and Defense/Joint Decorations and Awards (PDF). Department of Defense Manual. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. March 7, 2013.
- Department of Defense Manual 1348.33, Volume 2: Manual of Military Decorations and Awards: General Information, Medal of Honor, and Defense/Joint Decorations and Awards (PDF). Department of Defense Manual. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. May 31, 2013.
- Department of Defense Manual 1348.33, Volume 3: Manual of Military Decorations and Awards: General Information, Medal of Honor, and Defense/Joint Decorations and Awards (PDF). Department of Defense Manual. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. November 23, 2010.
- Joint Publication 1 – Doctrine for the Armed Forces of the United States (PDF). Joint Publications. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. March 25, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 27, 2011.
- Joint Publication 1-04 – Legal Support to Military Operations (PDF). Joint Publications. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. August 17, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 13, 2013. Retrieved June 14, 2013.
Further reading
- Cohen, Eliot A. (2003). Supreme Command: soldiers, statesmen and leadership in wartime. New York: Anchor Books. ISBN 978-1-4000-3404-8.
- Cole, Alice C.; Goldberg, Alfred; Tucker, Samuel A.; et al., eds. (1978). The Department of Defense: Documents on Establishment and Organization 1944–1978 (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Historical Office, Office of the Secretary of Defense/U.S. Government Printing Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 14, 2014.
- Huntington, Samuel P. (1957). The Soldier and the State. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-81736-2.
- King, Archibald (1960) [1949]. Command of the Army (PDF). Military Affairs. Charlottesville, Virginia: The Judge Advocate General's School, U.S. Army.
- Mahan, Erin R., and Jeffrey A. Larsen, eds. (2012) "Evolution of the Secretary of Defense in the Era of Massive Retaliation: Charles Wilson, Neil McElroy, and Thomas Gates, 1953–1961," Cold War Foreign Policy Series: Special Study 3 (September 2012), vii–41.
- Stevenson, Charles A. (2006). SECDEF: the nearly impossible job of Secretary of Defense. Dulles, Virginia: Potomac Books. ISBN 1-57488-794-7.
- Trask, Roger R.; Goldberg, Alfred (1997). The Department of Defense 1997-1947: Organization and Leaders (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Historical Office, Office of the Secretary of Defense/U.S. Government Printing Office. ISBN 0-16-049163-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 14, 2014.
- Department of Defense Key Officials September 1947 – February 2019 (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Historical Office, Office of the Secretary of Defense. January 30, 2019.
Primary historical sources
- Cheney, Dick; Cheney, Liz (2011). In My Time: A Personal and Political Memoir. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4391-7619-1.
- Rumsfeld, Donald (2011). Known and Unknown: A Memoir. New York: Sentinel. ISBN 978-1-59523-067-6.
Online sources
- "Department of Defense Directive 5100.01 Functions of the Department of Defense and Its Major Components". Office of the Secretary Defense, Director of Administration and Management, Directorate for Organizational & Management Planning. Archived from the original on May 7, 2013. Retrieved June 13, 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States Secretary of Defense. |
| U.S. order of precedence (ceremonial) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Steve Mnuchin as Secretary of the Treasury |
Order of Precedence of the United States as Secretary of Defense |
Succeeded by William Barr as Attorney General |
| U.S. presidential line of succession | ||
| Preceded by Secretary of the Treasury Steve Mnuchin |
6th in line | Succeeded by Attorney General William Barr |

















.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
