Bielefeld
Bielefeld (German pronunciation: [ˈbiːləfɛlt] (![]()
Bielefeld | |
|---|---|
 Bielefeld as seen from Sparrenberg Castle | |
 Coat of arms | |
Districts of Bielefeld: Bielefeld-Mitte (downtown), Brackwede, Dornberg, Gadderbaum, Heepen, Jöllenbeck, Schildesche, Senne, Sennestadt and Stieghorst 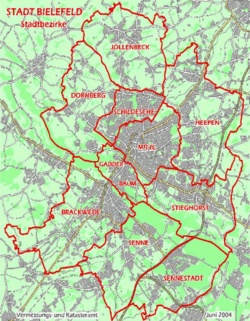 | |
 Bielefeld  Bielefeld | |
| Coordinates: 52°01′16″N 08°32′05″E | |
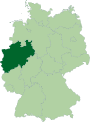
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Detmold |
| District | Urban district |
| Founded | 1214 |
| Subdivisions | 10 districts |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Pit Clausen (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • City | 257.8 km2 (99.5 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 118 m (387 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • City | 333,786 |
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,400/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 591,862 |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 33501-33739 |
| Dialling codes | 0521, 05202-05209 |
| Vehicle registration | BI |
| Website | Welcome to Bielefeld! |
The historical centre of the city is situated north of the Teutoburg Forest line of hills, but modern Bielefeld also incorporates boroughs on the opposite side and on the hills.
Bielefeld is home to a significant number of internationally operating companies, including Dr. Oetker, Gildemeister and Schüco. It has a university and several technical colleges (Fachhochschulen). Bielefeld is also famous for the Bethel Institution, and for the Bielefeld conspiracy, which satirises conspiracy theories by claiming that Bielefeld does not exist. This concept has been used in the town's marketing and alluded to by Chancellor Angela Merkel.
History


Hanseatic League 14th century-
Berg (state) 1346-
Margraviate of Brandenburg 1614-
Minden-Ravensberg 1719–1807
Kingdom of Westphalia
Founded in 1214 by Count Hermann IV of Ravensberg to guard a pass crossing the Teutoburg Forest, Bielefeld was the "city of linen" as a minor member of the Hanseatic League, known for bleachfields into the 19th Century.[3] Bielefeld was part of the Kingdom of Westphalia when it was created in 1807.[4] In 1815 it was incorporated into the Kingdom of Prussia following the defeat of France and the Congress of Vienna.[5]
After the Cologne-Minden railway opened in 1849, the Bozi brothers constructed the first large mechanised spinning mill in 1851. The Ravensberg Spinning Mill was built from 1854 to 1857, and metal works began to open in the 1860s.
Founded in 1867 as a Bielefeld sewing machine repair company, AG Dürkoppwerke employed 1,665 people in 1892; it used Waffenamt code "WaA547" from 1938 to 1939 as the Dürkopp-Werke, and merged with other Bielefeld companies to form Dürkopp Adler AG in 1990.
Between 1904 and 1930, Bielefeld grew, opening a rebuilt railway station, a municipal theatre, and finally, the Rudolf-Oetker-Halle concert hall, renowned for its excellent acoustics.[6] The Dürkopp car was produced 1898–1927. After printing emergency money (German: Notgeld) in 1923 during the inflation in the Weimar Republic, Bielefeld was one of several towns that printed very attractive and highly collectable banknotes with designs on silk, linen and velvet. These pieces were issued by the Bielefeld Stadtsparkasse (town's savings bank) and were sent all around the world in the early 1920s. These pieces are known as Stoffgeld – that is, money made from fabric.[7]
The town's synagogue was burned in 1938. In 1944, B-17 Flying Fortresses of the USAAF bombed the gas works at Bielefeld on September 20[8] and the marshaling yard on September 30;[9] Bielefeld was bombed again on October 7[10] and the RAF bombed the town on the night of December 4/5.[11] On January 17 1945 B-17s bombed the nearby Paderborn marshalling yard, and the railway viaduct in the suburb of Schildesche.[12] On March 14 the RAF bombed the viaduct again, wrecking it. This was the first use of the RAF's Grand Slam bomb. American troops entered the city in April 1945.
Due to the presence of a number of barracks built during the 1930s and its location next to the main East-West Autobahn in northern Germany, after World War II Bielefeld became a headquarters town for the fighting command of the British Army of the Rhine – BAOR (the administrative and strategic headquarters were at Rheindahlen near the Dutch border). Until the 1980s there was a large British presence in the barracks housing the headquarters of the British First Corps and support units, as well as schools, NAAFI shops, officers' and sergeants' messes and several estates of married quarters. The British presence was heavily scaled back after the reunification of Germany and most of the infrastructure has disappeared.
In 1973 the first villages on the south side of the Teutoburg Forest were incorporated.
Climate
Bielefeld has an oceanic climate (Cfb). The average annual high temperature is 14 °C (57 °F), the annual low temperature is 6 °C (43 °F), and the annual precipitation is 483 millimetres (19.02 inches).
| Climate data for Bielefeld | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5 (41) |
6 (43) |
10 (50) |
14 (57) |
19 (66) |
22 (72) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
19 (66) |
14 (57) |
9 (48) |
5 (41) |
14 (58) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0 (32) |
0 (32) |
2 (36) |
4 (39) |
8 (46) |
11 (52) |
13 (55) |
14 (57) |
11 (52) |
7 (45) |
3 (37) |
0 (32) |
6 (43) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 35.3 (1.39) |
35.5 (1.40) |
38.9 (1.53) |
35.4 (1.39) |
57.2 (2.25) |
36.2 (1.43) |
47.4 (1.87) |
41.9 (1.65) |
42.0 (1.65) |
31.6 (1.24) |
36.7 (1.44) |
44.9 (1.77) |
483 (19.01) |
| Source: worldweatheronline.com | |||||||||||||
Industry and education

Bielefeld was a linen-producing town, and in the early 1920s the Town's Savings Bank (Stadtsparkasse) issued money made of linen, silk and velvet. These items were known as 'stoffgeld'.
In addition to the manufacture of home appliances and various heavy industries, Bielefeld companies include Dr. Oetker (food manufacturing), Möller Group (leather products and plastics), Seidensticker (clothing and textiles) and Bethel Institution with 17.000 employees.
Bielefeld University was founded in 1969. Among its first professors was the notable contemporary German sociologist Niklas Luhmann. Other institutions of higher education include the Theological Seminary Bethel (Kirchliche Hochschule Bethel) and the Bielefeld University of Applied Sciences (German: Fachhochschule Bielefeld), which offers 21 courses in 8 different departments (agriculture and engineering are in Minden) and has been internationally recognized for its photography school.[13]
Demographics
| Largest groups of foreign residents (Excluding persons with dual citizenship.)[14] | |
| Nationality | Population (31.12.2017) |
|---|---|
| Turkey | 11,429 |
| Iraq | 5,561 |
| Greece | 3,765 |
| Poland | 3,546 |
| Syria | 2,753 |
| Serbia and Montenegro | 2,704 |
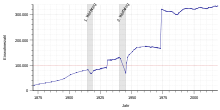
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1510 | 2,500 | — |
| 1718 | 2,967 | +18.7% |
| 1811 | 5,613 | +89.2% |
| 1871 | 21,803 | +288.4% |
| 1900 | 63,046 | +189.2% |
| 1919 | 79,049 | +25.4% |
| 1925 | 86,062 | +8.9% |
| 1933 | 121,031 | +40.6% |
| 1939 | 129,466 | +7.0% |
| 1946 | 132,276 | +2.2% |
| 1961 | 175,517 | +32.7% |
| 1970 | 168,937 | −3.7% |
| 1987 | 305,566 | +80.9% |
| 2011 | 326,870 | +7.0% |
| 2018 | 333,786 | +2.1% |
| source:[15] | ||
Transport
Two major autobahns, the A 2 and A 33, intersect in the south east of Bielefeld. The Ostwestfalendamm expressway connects the two parts of the city, naturally divided by the Teutoburg Forest. Bielefeld Hauptbahnhof, the main railway station of Bielefeld, is on the Hamm–Minden railway and is part of the German ICE high-speed railroad system. The main station for intercity bus services is Brackwede station.[16]
Bielefeld has a small airstrip, Flugplatz Bielefeld,[17] in the Senne district but is mainly served by the three larger airports nearby, Paderborn Lippstadt Airport, Münster Osnabrück International Airport and Hannover Airport.
Bielefeld boasts a well-developed public transport system, served mainly by the companies moBiel[18] (formerly Stadtwerke Bielefeld – Verkehrsbetriebe) and "BVO".[19] The Bielefeld Stadtbahn has four major lines and regional trains connect different parts of the city with nearby counties. Buses also run throughout the entire vicinity.
Main sights
Sparrenburg Castle is Bielefeld's characteristic landmark. It was built between 1240 and 1250 by Count Ludwig von Ravensberg. The 37-metre-high (121 ft) tower and the catacombs of the castle are open to the public.
The Old City Hall (Altes Rathaus) was built in 1904 and still serves the same function. Its façade reflects the so-called Weserrenaissance and features elements of various architectural styles, including Gothic and Renaissance. Though the mayor still holds office in the Old City Hall, most of the city's administration is housed in the adjacent New City Hall (Neues Rathaus).

The City Theatre (Stadttheater) is part of the same architectural ensemble as the Old City Hall, also built in 1904. It has a notable Jugendstil façade, is Bielefeld's largest theatre and home of the Bielefeld Opera. Another theatre (Theater am Alten Markt) resides in the former town hall building on the Old Market Square (Alter Markt), which also contains a row of restored 16th and 17th-century townhouses with noteworthy late Gothic and Weser Renaissance style façades (Bürgerhäuser am Alten Markt).
The oldest city church is Altstädter Nicolaikirche. It is a Gothic hall church with a height of 81.5 m (267 ft). It was founded in 1236 by the Bishop of Paderborn, and enlarged at the beginning of the 14th century. The church was damaged in World War II and later rebuilt. Three times a day, a carillon can be heard. The most valuable treasure of this church is a carved altar from Antwerp, decorated with 250 figures. A small museum housed within illustrates the history of the church up to World War II.
The largest church is the Neustädter Marienkirche, a Gothic hall church dating back to 1293, completed 1512. It stands 78 m (256 ft) tall and has a length of 52 m (171 ft). Historically speaking, this building is considered to be the most precious possession of the town. It was the starting point of the Protestant Reformation in Bielefeld in 1553. A valuable wing-altar with 13 pictures, known as the Marienaltar is also kept inside. The baroque spires were destroyed in World War II and later replaced by two unusually-shaped "Gothic" clocktowers. The altarpiece of the Bielefeld church Neustädter Marienkirche from around 1400 is among the most prominent masterpieces of artwork of the German Middle Ages. Two of the altarpieces, The Flagellation and The Crucifixion are now in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York.
Bielefeld is also the seat of the two largest Protestant social welfare establishments (Diakonie) in Europe, the Bethel Institution[20] and the Evangelisches Johanneswerk.
Other important cultural sights of the region are the art museum (Kunsthalle), the Rudolf Oetker concert hall (Rudolf-Oetker-Halle), and the city's municipal botanical garden (the Botanischer Garten Bielefeld). Bielefeld is home to the widely known Bielefeld Children's Choir (Bielefelder Kinderchor), founded in 1932 and in the postwar era famed for its recordings of traditional German Christmas carols. Particularly notable is the choir's annual Christmas Concert in the Rudolf Oetker concert hall. Foreign tours have taken the choir to many European countries, and also the US and Japan.
On Hünenburg there is an observation tower, next to a 164 meters (538 feet) high radio tower.
Sport
Bielefeld is home to the professional football team DSC Arminia Bielefeld. Currently member of 2. Bundesliga, the club plays at the SchücoArena stadium in the west of the town centre.
Notable people
Born before 1900
- Johann Christoph Hoffbauer (1766–1827), philosopher

- Christian Friedrich Nasse (1778–1851), psychiatrist
- August Krönig (1822–1879), chemist and physicist
- Friedrich von Bodelschwingh, Senior (1831–1910), second boss of the "Evangelischen Heil- und Pflegeanstalt für Epileptische" (Evangelic Sanatorium for Epileptics) (1874 renamed into "Bethel")
- Friedrich von Bodelschwingh (1877–1946), evangelical theologian, third boss of the von Bodelschwinghsche Anstalten, named after F. v. Bodelschwingh, the Older (Later renamed into von Bodelschwinghsche Stiftungen)
- Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau (1888–1931), German film director
- Hermann Stenner (1891–1914), early Expressionist painter
Born 1900–1950
- Erich Consemüller (1902-1957), Bauhaus trained architect and photographer
- Heinz Klingenberg (1905–1959), actor
- Horst Wessel (1907–1930), SA leader

- Hermann Paul Müller (1909–1975), racing driver
- Veronica Carstens (1923–2012), medical doctor, wife of Karl Carstens
- Hajo Meyer (1924–2014), German-Dutch physicist and author
- Werner Lueg (1931–2014), athlete
- Rüdiger Nehberg (born 1935), survival expert and activist for human rights
- Christian Tümpel (1937–2009), art historian
- Klaus Hildebrand (born 1941), historian
- Klaus Kobusch (born 1941), cyclist
- Hannes Wader (born 1942), musician and songwriter
- Bernhard Schlink (born 1944), professor of jurisprudence and author
- Ulrich Wessel (1946–1975), member of the Red Army Faction
- Aleida Assmann (born 1947), anglist, egyptologist and literary and cultural scientist
- Irmgard Möller (born 1947), member of the Red Army faction
- Johannes Friedrich (born 1948), Evangelical Lutheran theologian
- Hans-Werner Sinn (born 1948), economist and president of the Ifo Institute for Economic Research
Born 1951 and later
- Richard Oetker (born 1951), entrepreneur Dr. Oetker
- Michael Diekmann (born 1954), chief executive officer of Allianz SE
- Annette Groth (born 1954), politician (The Left)
- Erich Marks (born 1954), educator
- Christina Rau (born 1956), political scientist and widow of the Federal President Johannes Rau
- Klaus Tscheuschner (born 1956), Lord Mayor of the City of Flensburg
- Rolf Kanies (born 1957), film and theater actor
- Karoline Linnert (born 1958), politician (The Greens)
- Ingolf Lück (born 1958), actor, synchronizer, presenter, comedian and director
- Hartmut Ostrowski (born 1958), chief executive officer of Bertelsmann AG
- Ralf Ehrenbrink (born 1960), versatility rider
- Hartmut Schick (born 1960), musicologist
- Olaf Hampel (born 1965), bob driver
- Anja Feldmann (born 1966), computer scientist
- Oliver Welke (born 1966), author, comedian, sports journalist and moderator
- Ingo Niermann (born 1969), writer, journalist and artist
- Ingo Oschmann (born 1969), comedian, entertainer and magician
- Nina George (born 1973), writer and journalist
- Florian Panzner (born 1976), actor
- Lisa Middelhauve (born 1980), metal singer
- Lena Goeßling (born 1986), women's association football player for Germany women's national football team and VfL Wolfsburg (women)
- Aylin Tezel (born 1983), German actress
International relations
Bielefeld is twinned with:[21]
|
|
References
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2018" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "Aktuelle Einwohnerzahlen".
- Hamburgh Mail, The Times 14 December 1816
- The Times, 9 November 1809; Letters to the Editor
- The Times, 26 August 1815; News
- "Bielefeld – History". Bielefeld.de. Archived from the original on 27 April 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- Many examples can be found on the "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-10-10. Retrieved 2010-04-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) website, where a new catalogue listing all the variants of different coloured borders and edges made on the 100m piece is being compiled.
- "Veterans History Project". Central Connecticut State University. 2005-02-24. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- McKillop, Jack. "Combat Chronology of the USAAF". USAAF. Archived from the original on 2007-06-10. Retrieved 2007-05-25.September 1944
- McKillop, October 1944
- "RAF History – Bomber Command 60th Anniversary". Raf.mod.uk. Archived from the original on 2011-06-06. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- McKillop, January 1945
- "University of Applied Sciences Bielefeld". Archived from the original on 2009-09-14. Retrieved 2009-10-23.
- "Aktuelle Einwohnerzahlen". Retrieved 24 June 2018.
- Link
- "Bielefeld: Stations". Travelinho.com.
- "Flugplatz Bielefeld". Flugplatz-bielefeld.de. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- "Startseite – moBiel.de".
- eCommerce, Deutsche Bahn AG, Unternehmensbereich Personenverkehr, Marketing. "Ostwestfalen-Lippe-Bus".
- Cf. v. Bodelschwinghsche Stiftungen Bethel
- "Städtepartnerschaften" (in German). Büro Oberbürgermeister Bielefeld. Retrieved 2015-01-03.
- "Serwis informacyjny UM Rzeszów – Informacja o współpracy Rzeszowa z miastami partnerskimi". www.rzeszow.pl. Archived from the original on 2012-12-05. Retrieved 2010-02-02.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Bielefeld. |
| Bielefeld, Germany Live webcam |
![]()