Thessaloniki–Alexandroupoli railway
The Thessaloniki–Alexandroupoli railway is an about 440 km long railway in northern Greece connecting the Central Macedonian city of Thessaloniki with Alexandroupoli in Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, via Serres. There is a connection towards Sofia at the Strymonas station. This railway was built in 1896 by The Compagnie du Chemin de Fer Ottoman Jonction Salonique-Constantinople (JSC).
| Thessaloniki–Alexandroupoli railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Route map of the old Chemin de Fer Jonction Salonique–Constantinople | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Fully operational | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Greece (Central Macedonia, East Macedonia and Thrace) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Termini | Thessaloniki 40.6444°N 22.9294°E Alexandroupoli 40.8469°N 25.8844°E | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opened | 1896 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner | OSE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | TrainOSE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 440.1 km (273.5 mi)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of tracks | single track [1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | no [1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
As of 2019, there is regular passenger service twice-daily to Alexandroupoli with connecting services to Dikaia, as well as international services to Sofia, to Belgrade via Skopje. The international service to Istanbul ("Friendship Express") remains suspended.
Course

The western terminus of the Thessaloniki–Svilengrad railway is the New Railway Station, Thessaloniki. It runs north passing Kilkis, until it turns east at the shore of Dojran Lake. It runs along the north shore of Lake Kerkini, and crosses the river Strymonas near Sidirokastro. The line north to Sofia (border crossing Promachonas/Kulata) branches off here. The railway continues east along Serres and Drama. It crosses the river Nestos at Paranesti, and follows it until Toxotes. It passes Xanthi and Komotini, and reaches the Aegean Sea at Alexandroupoli, where it ends at the Alexandroupoli railway station, which is further connected to Pythio via the Alexandroupoli–Svilengrad railway
The line is single line. On the whole, the route has 36 tunnels and 251 bridges.[2] It follows a particularly scenic route. The route first leads through a small pass where, at 320 meters above sea level, it reaches the highest point between Thessaloniki and Alexandroupoli, before descending into the valley of the Nestos River.
The original track was built for vehicles with 13 t axle load. The maximum gradients were below 20‰ with one section of 25 km reaching 25‰, The original rails had weight of 30 kg/m except in large gradients sections where the rails had a weight of 34 kg/m. The steel sleepers used weighed 50 kg.
In 2018, the superstructure of the 116 km section Thessaloniki-Serres consisted of UIC 54 rails laid on B70 concrete sleepers. On the remaining 326 km to Alexandroupoli, rails with UIC 50 or UIC 54 profiles are laid on wooden, steel or bi-block concrete sleepers. The route is between Thessaloniki and Strymonas is now suitable for 22.5 t axle load and can be used at 160 km/h. The remainder of the section is for 20 tons of axle load.
History

The Société du Chemin de Fer Ottoman Jonction Salonique-Constantinople, abbreviated JSC, was founded in October 1892. This company obtained on September 10, 1892, the concession to build and operate a railway 442 km line between Thessaloniki and Alexandroupoli, named Dedeagatch at the time. In Alexandroupoli, the line would join the existing line to Constantinople and Edirne, via Pythio, operated by the Chemins de fer Orientaux.[3]
The JSC was formed according to Ottoman law with its main office in Istanbul and the shareholder committee in Paris.
The line fulfilled the strategic goal of a direct connection from Constantinople to Thessaloniki, by-passing Serbian or Bulgarian territories. Thessaloniki was already since 1888 connected with Istanbul by the Chemins de fer Orientaux, but this connection went through the before mentioned countries, which were once part of the Ottoman Empire but split off at a later stage.
The line was carefully built away from the border and the coast to avoid destruction by warfare. Except near Alexandroupoli the minimum distance from enemy countries and sea was 15 km in oder to keep the route out of artillery and gun boat fire reach. Alexandroupoli received at a later stage a bypass route in the North of the town fulfilling the original requirement. This route had several horseshoe curves to master the steep grades in the geographic wise difficult country and is today closed and razed. Also Thessaloniki received a Northern bypass, which connected the station Kallindria with Karasuli on the line to Mitrovica.
Under the guidance of the Ministry of War the concessionaires were obliged to build 26 stations. Some of them were military stations equipped with all the necessary facilities for the prompt embarkation and disembarkation of troops and war material.[4]
Furthermore, the company was obliged to own and maintain at least 848 wagons; namely: 90 passenger carriages of three classes; 30 baggage wagons; 528 boxcars; 200 gondolas. The boxcars and gondolas must be capable of transporting troops, horses and cattle, guns, etc., so that 27 complete trains can be organised – one more train than the number of stations. For the transport of soldiers, 130 of the 200 gondolas should be capable to be covered as quick as possible if required. Furthermore, the railway had to keep sufficient benches in the store to allow the soldiers to sit during the transport.[5]
In 1895, The Swiss Bank für Orientalische Eisenbahnen purchased 30000 stocks out of 100000 issued, giving it a minority shareholding.[6] Bank für Orientalische Eisenbahnen was also the owner of the Chemins de fer Orientaux and of the Salonica Monastir Railway. The main objective of the Chemins de fer Orientaux was to secure an alternate route between Serbia and Istanbul, through Greece should the main route through Bulgaria be closed by the Bulgarian government.
After the end of Balkan Wars in 1913, the line ended fully in Greek territory. The Greek government purchased the JSC in 1920[7] and the railway became part of the Hellenic State Railways.
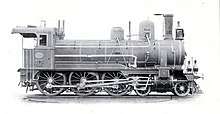
Locomotives
Locomotives from the JSC[8]
| Number | Manufacturer | Qty | Year | Type | Comments | Picture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 to 16 | WrN; SLM | 16 | D | Became SEK class Hβ | ||
| 50 to 54 | WrN | 4 | C | became SEK class Δγ 71 to 75 | ||
| 101 to 111 | StEG | 11 | 2'C | 10 Became SEK class Zγ 321 to 330 |
Services
The Thessaloniki–Alexandroupoli railway is used by the following passenger services:
- Intercity and regular services Thessaloniki–Alexandroupoli[9]. These run twice daily (2019 service). The journey time is 7-8 hours, which is more than twice that by road following completion of the A2 motorway or Egnatia Odos (modern road)

References
- "OSE - 2017 Network Statement Annexes". p. 5.
- OSE Network Statement, 2017, annexes
- Georges Young: Corps de droit Ottoman,Oxford Clarendon Press, 1906. See page 103.
- Georges Young: Corps de droit Ottoman,Oxford Clarendon Press, 1906. See Art. 28 page 106.
- Georges Young: Corps de droit Ottoman,Oxford Clarendon Press, 1906. See page 109: Article 28 of Text B.
- Le Temps, 11 juin 1894 (In French)
- La Correspondance d’Orient, 15 août 1920 (in French)
- "JSC". www.pospichal.net. Retrieved 2018-12-03.
- "2014/15 Intercity schedule" (PDF). TrainOSE. Retrieved 11 March 2015.